Andreas Bathelt
The IEEE Signal Processing Society's Leading Role in Developing Standards for Computational Imaging and Sensing: Part II
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:In every imaging or sensing application, the physical hardware creates constraints that must be overcome or they limit system performance. Techniques that leverage additional degrees of freedom can effectively extend performance beyond the inherent physical capabilities of the hardware. An example includes synchronizing distributed sensors so as to synthesize a larger aperture for remote sensing applications. An additional example is integrating the communication and sensing functions in a wireless system through the clever design of waveforms and optimized resource management. As these technologies mature beyond the conceptual and prototype phase they will ultimately transition to the commercial market. Here, standards play a critical role in ensuring success. Standards ensure interoperability between systems manufactured by different vendors and define industry best practices for vendors and customers alike. The Signal Processing Society of the Institute for Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) plays a leading role in developing high-quality standards for computational sensing technologies through the working groups of the Synthetic Aperture Standards Committee (SASC). In this column we highlight the standards activities of the P3383 Performance Metrics for Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) Systems Working Group and the P3343 Spatio-Temporal Synchronization of a Synthetic Aperture of Distributed Sensors Working Group.
Blind Bistatic Radar Parameter Estimation in Doubly-Dispersive Channels
Jul 07, 2024Abstract:We propose a novel method for blind bistatic radar parameter estimation (RPE), which enables integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) by allowing passive (receive) base stations (BSs) to extract radar parameters (ranges and velocities of targets), without requiring knowledge of the information sent by an active (transmit) BS to its users. The contributed method is formulated with basis on the covariance of received signals, and under a generalized doubly-dispersive channel model compatible with most of the waveforms typically considered for ISAC, such as orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) and affine frequency division multiplexing (AFDM). The original non-convex problem, which includes an $\ell_0$-norm regularization term in order to mitigate clutter, is solved not by relaxation to an $\ell_1$-norm, but by introducing an arbitrarily-tight approximation then relaxed via fractional programming (FP). Simulation results show that the performance of the proposed method approaches that of an ideal system with perfect knowledge of the transmit signal covariance with an increasing number of transmit frames.
An Extended Kuramoto Model for Frequency and Phase Synchronization in Delay-Free Networks with Finite Number of Agents
Mar 20, 2024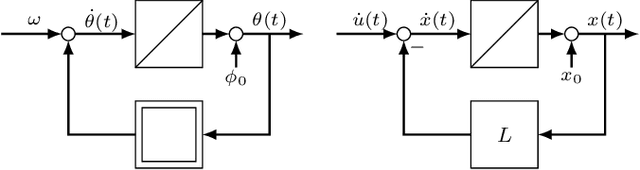
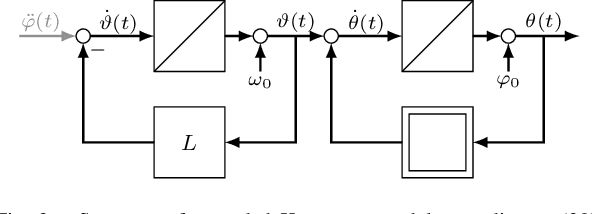
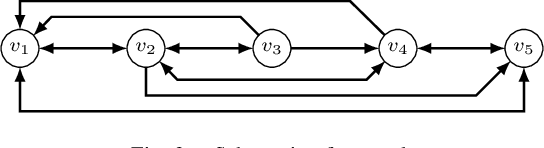
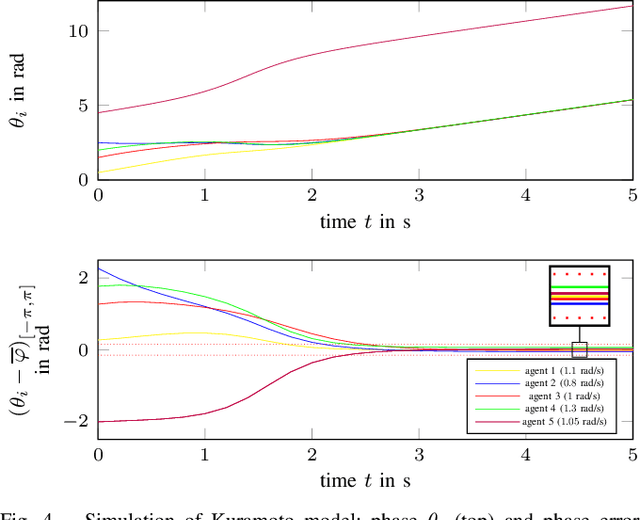
Abstract:Due to its description of a synchronization between oscillators, the Kuramoto model is an ideal choice for a synchronisation algorithm in networked systems. This requires to achieve not only a frequency synchronization but also a phase synchronization - something the standard Kuramoto model can not provide for a finite number of agents. In this case, a remaining phase difference is necessary to offset differences of the natural frequencies. Setting the Kuramoto model into the context of dynamic consensus and making use of the $n$th order discrete average consensus algorithm, this paper extends the standard Kuramoto model in such a way that frequency and phase synchronization are separated. This in turn leads to an algorithm achieve the required frequency and phase synchronization also for a finite number of agents. Simulations show the viability of this extended Kuramoto model.
Sparse Codesigned Communication and Radar Systems
Sep 08, 2023Abstract:In the envisioned beyond-fifth-generation (B5G) and sixth-generation (6G) scenarios which expect massive multiple-input multiple-output (mMIMO) and high frequency communications in the millimeter-wave (mmWave) and Terahertz (THz) bands, efficiency in both energy and spectrum is of increasing significance. To that extent, a novel ISAC framework called "sparse codesigned communication and radar (SCCR)" systems is described, which codesigns both communication and radar signals by a sparsification of the resource domain and the waveform spectrum domain. This improves the spectral and energy efficiency, but at the inherent cost of missing radar spectrum and irregular beampattern, and decreased throughput and diversity. Such challenges can however be corroborated, by leveraging various sparsity-robust signal processing techniques such as sparse radar reconstruction and index modulation (IM). In light of the above, the white paper aims to outlined the proposed article which provide an overview and a novel classification of the relevant state-of-the-art (SotA) methods and the implications of the challenges in the sparse codesign of the system, followed by a variety of novel SCCR frameworks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge