Andrea Helo
Gaze Distribution Analysis and Saliency Prediction Across Age Groups
May 31, 2017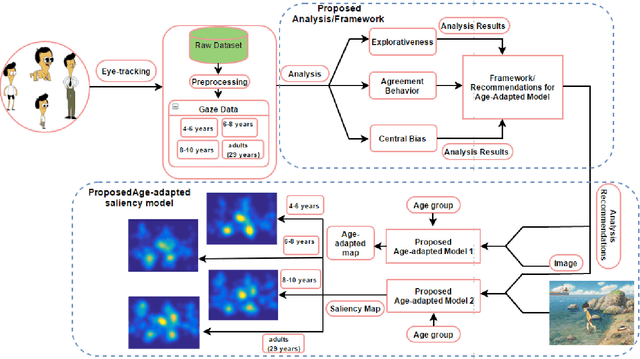
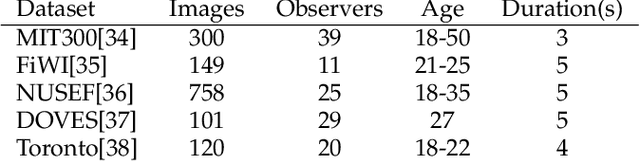
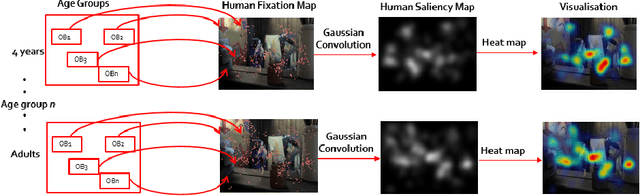
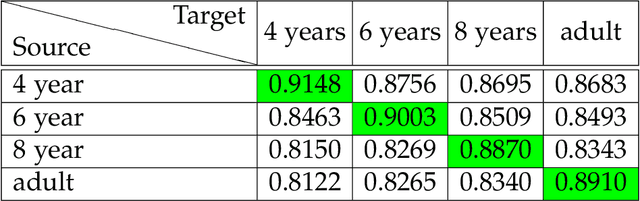
Abstract:Knowledge of the human visual system helps to develop better computational models of visual attention. State-of-the-art models have been developed to mimic the visual attention system of young adults that, however, largely ignore the variations that occur with age. In this paper, we investigated how visual scene processing changes with age and we propose an age-adapted framework that helps to develop a computational model that can predict saliency across different age groups. Our analysis uncovers how the explorativeness of an observer varies with age, how well saliency maps of an age group agree with fixation points of observers from the same or different age groups, and how age influences the center bias. We analyzed the eye movement behavior of 82 observers belonging to four age groups while they explored visual scenes. Explorativeness was quantified in terms of the entropy of a saliency map, and area under the curve (AUC) metrics was used to quantify the agreement analysis and the center bias. These results were used to develop age adapted saliency models. Our results suggest that the proposed age-adapted saliency model outperforms existing saliency models in predicting the regions of interest across age groups.
Computational Model for Predicting Visual Fixations from Childhood to Adulthood
Feb 15, 2017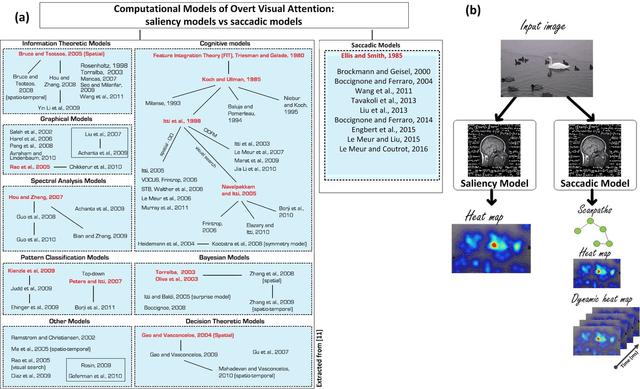

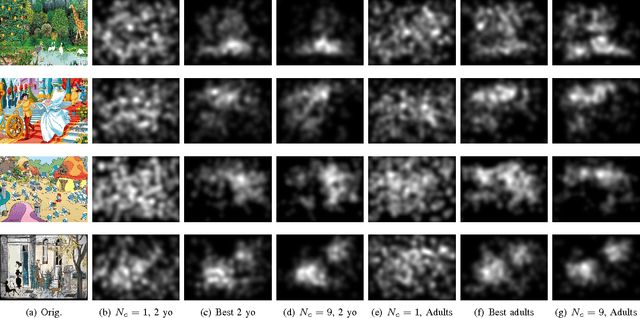
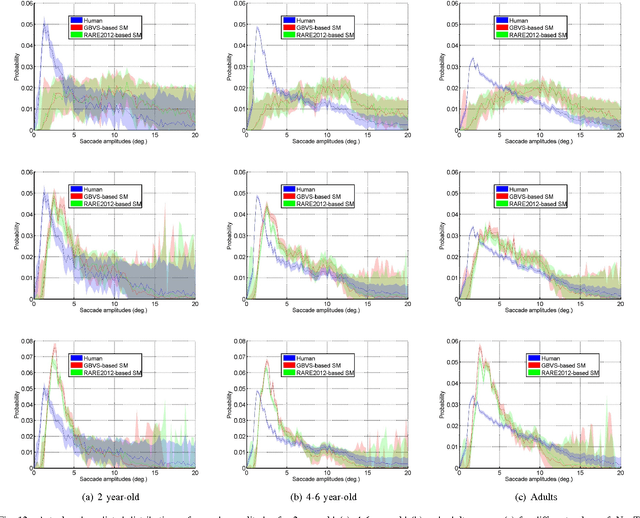
Abstract:How people look at visual information reveals fundamental information about themselves, their interests and their state of mind. While previous visual attention models output static 2-dimensional saliency maps, saccadic models aim to predict not only where observers look at but also how they move their eyes to explore the scene. Here we demonstrate that saccadic models are a flexible framework that can be tailored to emulate observer's viewing tendencies. More specifically, we use the eye data from 101 observers split in 5 age groups (adults, 8-10 y.o., 6-8 y.o., 4-6 y.o. and 2 y.o.) to train our saccadic model for different stages of the development of the human visual system. We show that the joint distribution of saccade amplitude and orientation is a visual signature specific to each age group, and can be used to generate age-dependent scanpaths. Our age-dependent saccadic model not only outputs human-like, age-specific visual scanpath, but also significantly outperforms other state-of-the-art saliency models. In this paper, we demonstrate that the computational modelling of visual attention, through the use of saccadic model, can be efficiently adapted to emulate the gaze behavior of a specific group of observers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge