Andoni Cortés
Analysis of Classifier Training on Synthetic Data for Cross-Domain Datasets
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:A major challenges of deep learning (DL) is the necessity to collect huge amounts of training data. Often, the lack of a sufficiently large dataset discourages the use of DL in certain applications. Typically, acquiring the required amounts of data costs considerable time, material and effort. To mitigate this problem, the use of synthetic images combined with real data is a popular approach, widely adopted in the scientific community to effectively train various detectors. In this study, we examined the potential of synthetic data-based training in the field of intelligent transportation systems. Our focus is on camera-based traffic sign recognition applications for advanced driver assistance systems and autonomous driving. The proposed augmentation pipeline of synthetic datasets includes novel augmentation processes such as structured shadows and gaussian specular highlights. A well-known DL model was trained with different datasets to compare the performance of synthetic and real image-based trained models. Additionally, a new, detailed method to objectively compare these models is proposed. Synthetic images are generated using a semi-supervised errors-guide method which is also described. Our experiments showed that a synthetic image-based approach outperforms in most cases real image-based training when applied to cross-domain test datasets (+10% precision for GTSRB dataset) and consequently, the generalization of the model is improved decreasing the cost of acquiring images.
* 10 pages
Methodology for generating synthetic labeled datasets for visual container inspection
Jun 26, 2023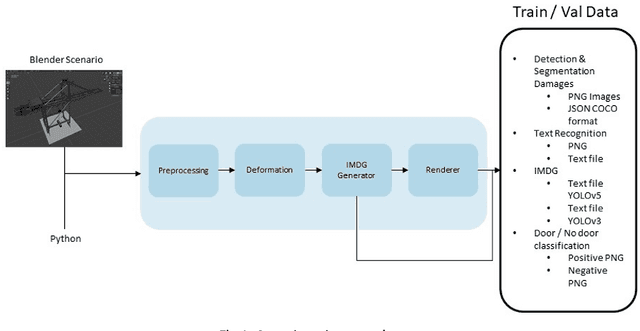
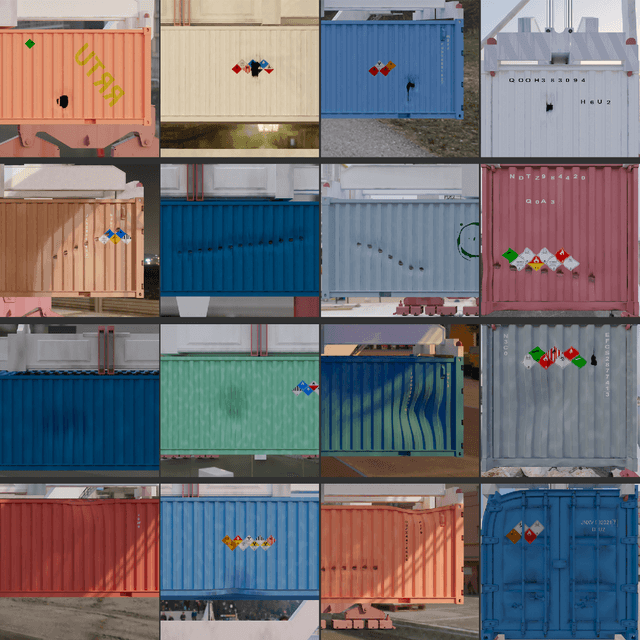



Abstract:Nowadays, containerized freight transport is one of the most important transportation systems that is undergoing an automation process due to the Deep Learning success. However, it suffers from a lack of annotated data in order to incorporate state-of-the-art neural network models to its systems. In this paper we present an innovative methodology to generate a realistic, varied, balanced, and labelled dataset for visual inspection task of containers in a dock environment. In addition, we validate this methodology with multiple visual tasks recurrently found in the state of the art. We prove that the generated synthetic labelled dataset allows to train a deep neural network that can be used in a real world scenario. On the other side, using this methodology we provide the first open synthetic labelled dataset called SeaFront available in: https://datasets.vicomtech.org/di21-seafront/readme.txt.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge