Ana Fernández Vilas
HLF-FSL. A Decentralized Federated Split Learning Solution for IoT on Hyperledger Fabric
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Collaborative machine learning in sensitive domains demands scalable, privacy preserving solutions for enterprise deployment. Conventional Federated Learning (FL) relies on a central server, introducing single points of failure and privacy risks, while Split Learning (SL) partitions models for privacy but scales poorly due to sequential training. We present a decentralized architecture that combines Federated Split Learning (FSL) with the permissioned blockchain Hyperledger Fabric (HLF). Our chaincode orchestrates FSL's split model execution and peer-to-peer aggregation without any central coordinator, leveraging HLF's transient fields and Private Data Collections (PDCs) to keep raw data and model activations private. On CIFAR-10 and MNIST benchmarks, HLF-FSL matches centralized FSL accuracy while reducing per epoch training time compared to Ethereum-based works. Performance and scalability tests show minimal blockchain overhead and preserved accuracy, demonstrating enterprise grade viability.
Discovering Geo-dependent Stories by Combining Density-based Clustering and Thread-based Aggregation techniques
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:Citizens are actively interacting with their surroundings, especially through social media. Not only do shared posts give important information about what is happening (from the users' perspective), but also the metadata linked to these posts offer relevant data, such as the GPS-location in Location-based Social Networks (LBSNs). In this paper we introduce a global analysis of the geo-tagged posts in social media which supports (i) the detection of unexpected behavior in the city and (ii) the analysis of the posts to infer what is happening. The former is obtained by applying density-based clustering techniques, whereas the latter is consequence of applying natural language processing. We have applied our methodology to a dataset obtained from Instagram activity in New York City for seven months obtaining promising results. The developed algorithms require very low resources, being able to analyze millions of data-points in commodity hardware in less than one hour without applying complex parallelization techniques. Furthermore, the solution can be easily adapted to other geo-tagged data sources without extra effort.
* 11 pages, 12 figures, journal
Twitter Permeability to financial events: an experiment towards a model for sensing irregularities
Dec 14, 2023Abstract:There is a general consensus of the good sensing and novelty characteristics of Twitter as an information media for the complex financial market. This paper investigates the permeability of Twittersphere, the total universe of Twitter users and their habits, towards relevant events in the financial market. Analysis shows that a general purpose social media is permeable to financial-specific events and establishes Twitter as a relevant feeder for taking decisions regarding the financial market and event fraudulent activities in that market. However, the provenance of contributions, their different levels of credibility and quality and even the purpose or intention behind them should to be considered and carefully contemplated if Twitter is used as a single source for decision taking. With the overall aim of this research, to deploy an architecture for real-time monitoring of irregularities in the financial market, this paper conducts a series of experiments on the level of permeability and the permeable features of Twitter in the event of one of these irregularities. To be precise, Twitter data is collected concerning an event comprising of a specific financial action on the 27th January 2017:{~ }the announcement about the merge of two companies Tesco PLC and Booker Group PLC, listed in the main market of the London Stock Exchange (LSE), to create the UK's Leading Food Business. The experiment attempts to answer five key research questions which aim to characterize the features of Twitter permeability to the financial market. The experimental results confirm that a far-impacting financial event, such as the merger considered, caused apparent disturbances in all the features considered, that is, information volume, content and sentiment as well as geographical provenance. Analysis shows that despite, Twitter not being a specific financial forum, it is permeable to financial events.
The irruption of cryptocurrencies into Twitter cashtags: a classifying solution
Dec 14, 2023Abstract:There is a consensus about the good sensing characteristics of Twitter to mine and uncover knowledge in financial markets, being considered a relevant feeder for taking decisions about buying or holding stock shares and even for detecting stock manipulation. Although Twitter hashtags allow to aggregate topic-related content, a specific mechanism for financial information also exists: Cashtag. However, the irruption of cryptocurrencies has resulted in a significant degradation on the cashtag-based aggregation of posts. Unfortunately, Twitter' users may use homonym tickers to refer to cryptocurrencies and to companies in stock markets, which means that filtering by cashtag may result on both posts referring to stock companies and cryptocurrencies. This research proposes automated classifiers to distinguish conflicting cashtags and, so, their container tweets by analyzing the distinctive features of tweets referring to stock companies and cryptocurrencies. As experiment, this paper analyses the interference between cryptocurrencies and company tickers in the London Stock Exchange (LSE), specifically, companies in the main and alternative market indices FTSE-100 and AIM-100. Heuristic-based as well as supervised classifiers are proposed and their advantages and drawbacks, including their ability to self-adapt to Twitter usage changes, are discussed. The experiment confirms a significant distortion in collected data when colliding or homonym cashtags exist, i.e., the same \$ acronym to refer to company tickers and cryptocurrencies. According to our results, the distinctive features of posts including cryptocurrencies or company tickers support accurate classification of colliding tweets (homonym cashtags) and Independent Models, as the most detached classifiers from training data, have the potential to be trans-applicability (in different stock markets) while retaining performance.
A hybrid analysis of LBSN data to early detect anomalies in crowd dynamics
Dec 13, 2023



Abstract:Undoubtedly, Location-based Social Networks (LBSNs) provide an interesting source of geo-located data that we have previously used to obtain patterns of the dynamics of crowds throughout urban areas. According to our previous results, activity in LBSNs reflects the real activity in the city. Therefore, unexpected behaviors in the social media activity are a trustful evidence of unexpected changes of the activity in the city. In this paper we introduce a hybrid solution to early detect these changes based on applying a combination of two approaches, the use of entropy analysis and clustering techniques, on the data gathered from LBSNs. In particular, we have performed our experiments over a data set collected from Instagram for seven months in New York City, obtaining promising results.
QSMVM: QoS-aware and social-aware multimetric routing protocol for video-streaming services over MANETs
Dec 12, 2023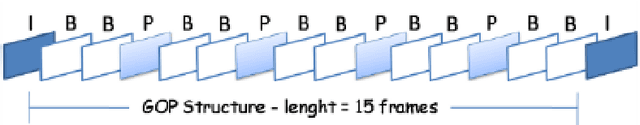
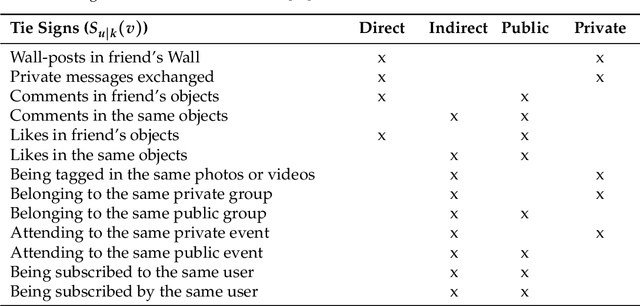
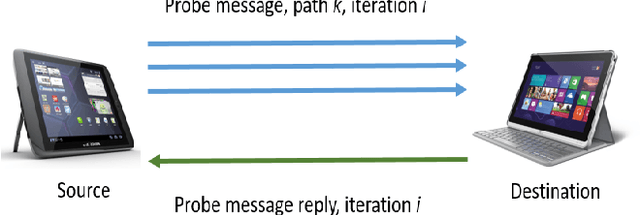
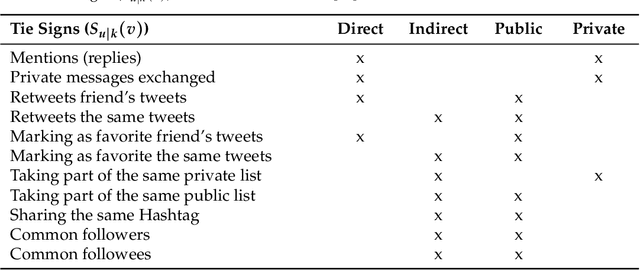
Abstract:A mobile ad hoc network (MANET) is a set of autonomous mobile devices connected by wireless links in a distributed manner and without a fixed infrastructure. Real-time multimedia services, such as video-streaming over MANETs, offers very promising applications, e.g. two members of a group of tourists who want to share a video transmitted through the MANET they form; a video-streaming service deployed over a MANET where users watch a film; among other examples. On the other hand, social web technologies, where people actively interact online with others through social networks, are leading to a socialization of networks. Information of interaction among users is being used to provide socially-enhanced software. To achieve this, we need to know the strength of the relationship between a given user and each user they interact with. This strength of the relationship can be measured through a concept called tie strength (TS), first introduced by Mark Granovetter in 1973. In this article, we modify our previous proposal named multipath multimedia dynamic source routing (MMDSR) protocol to include a social metric TS in the decisions taken by the forwarding algorithm. We find a trade-off between the quality of service (QoS) and the trust level between users who form the forwarding path in the MANET. Our goal is to increase the trust metric while the QoS is not affected significantly.
Anti-Sexism Alert System: Identification of Sexist Comments on Social Media Using AI Techniques
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:Social relationships in the digital sphere are becoming more usual and frequent, and they constitute a very important aspect for all of us. {Violent interactions in this sphere are very frequent, and have serious effects on the victims}. Within this global scenario, there is one kind of digital violence that is becoming really worrying: sexism against women. Sexist comments that are publicly posted in social media (newspaper comments, social networks, etc.), usually obtain a lot of attention and become viral, with consequent damage to the persons involved. In this paper, we introduce an anti-sexism alert system, based on natural language processing (NLP) and artificial intelligence (AI), that analyzes any public post, and decides if it could be considered a sexist comment or not. Additionally, this system also works on analyzing all the public comments linked to any multimedia content (piece of news, video, tweet, etc.) and decides, using a color-based system similar to traffic lights, if there is sexism in the global set of posts. We have created a labeled data set in Spanish, since the majority of studies focus on English, to train our system, which offers a very good performance after the validation experiments.
Towards Adaptive RF Fingerprint-based Authentication of IIoT devices
Nov 27, 2023Abstract:As IoT technologies mature, they are increasingly finding their way into more sensitive domains, such as Medical and Industrial IoT, in which safety and cyber-security are of great importance. While the number of deployed IoT devices continues to increase exponentially, they still present severe cyber-security vulnerabilities. Effective authentication is paramount to support trustworthy IIoT communications, however, current solutions focus on upper-layer identity verification or key-based cryptography which are often inadequate to the heterogeneous IIoT environment. In this work, we present a first step towards achieving powerful and flexible IIoT device authentication, by leveraging AI adaptive Radio Frequency Fingerprinting technique selection and tuning, at the PHY layer for highly accurate device authentication over challenging RF environments.
Prototype of deployment of Federated Learning with IoT devices
Nov 24, 2023Abstract:In the age of technology, data is an increasingly important resource. This importance is growing in the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI), where sub fields such as Machine Learning (ML) need more and more data to achieve better results. Internet of Things (IoT) is the connection of sensors and smart objects to collect and exchange data, in addition to achieving many other tasks. A huge amount of the resource desired, data, is stored in mobile devices, sensors and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices, but remains there due to data protection restrictions. At the same time these devices do not have enough data or computational capacity to train good models. Moreover, transmitting, storing and processing all this data on a centralised server is problematic. Federated Learning (FL) provides an innovative solution that allows devices to learn in a collaborative way. More importantly, it accomplishes this without violating data protection laws. FL is currently growing, and there are several solutions that implement it. This article presents a prototype of a FL solution where the IoT devices used were raspberry pi boards. The results compare the performance of a solution of this type with those obtained in traditional approaches. In addition, the FL solution performance was tested in a hostile environment. A convolutional neural network (CNN) and a image data set were used. The results show the feasibility and usability of these techniques, although in many cases they do not reach the performance of traditional approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge