Ana Arduengo
A Robot Teleoperation Framework for Human Motion Transfer
Sep 13, 2019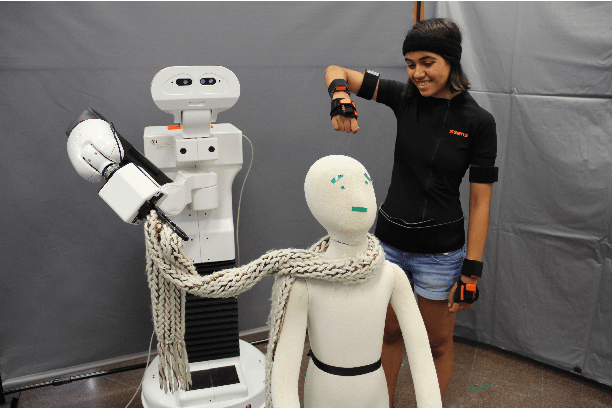
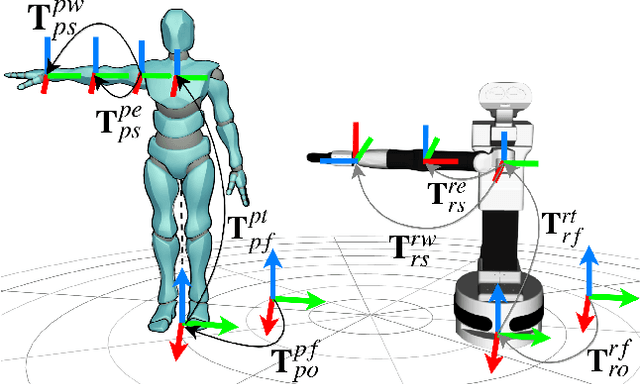
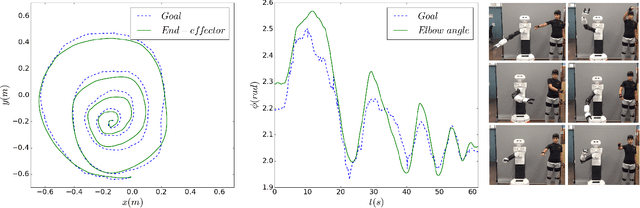
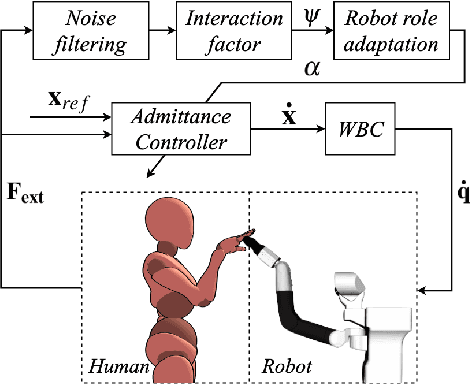
Abstract:Transferring human motion to a mobile robotic manipulator and ensuring safe physical human-robot interaction are crucial steps towards automating complex manipulation tasks in human-shared environments. In this work we present a robot whole-body teleoperation framework for human motion transfer. We propose a general solution to the correspondence problem: a mapping that defines an equivalence between the robot and observed human posture. For achieving real-time teleoperation and effective redundancy resolution, we make use of the whole-body paradigm with an adequate task hierarchy, and present a differential drive control algorithm to the wheeled robot base. To ensure safe physical human-robot interaction, we propose a variable admittance controller that stably adapts the dynamics of the end-effector to switch between stiff and compliant behaviors. We validate our approach through several experiments using the TIAGo robot. Results show effective real-time imitation and dynamic behavior adaptation. This could be an easy way for a non-expert to teach a rough manipulation skill to an assistive robot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge