Amita Pal
A Novel Minimum Divergence Approach to Robust Speaker Identification
Dec 16, 2015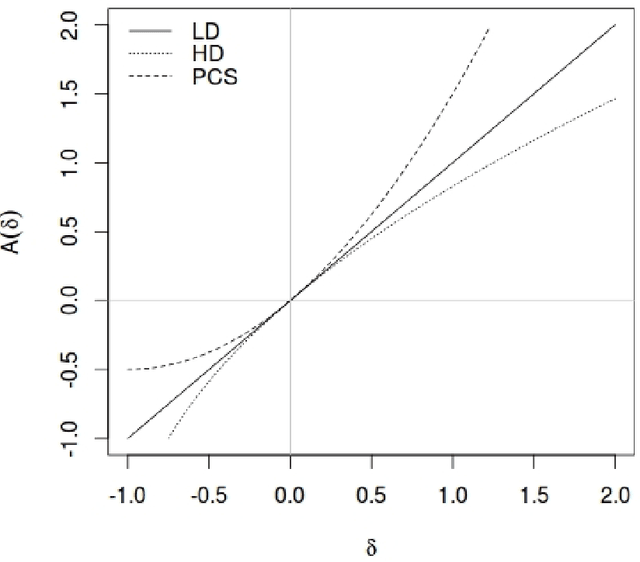
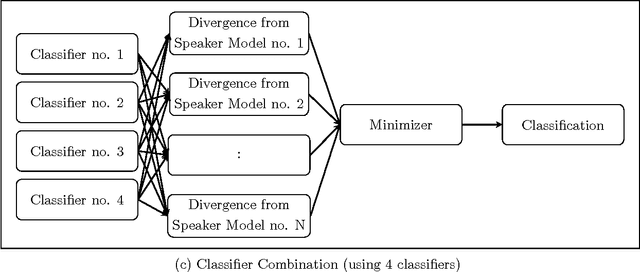
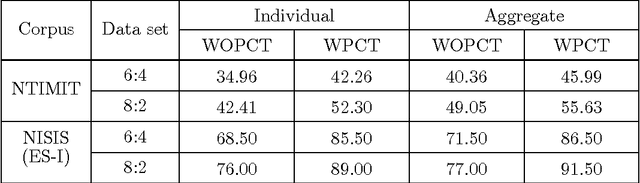
Abstract:In this work, a novel solution to the speaker identification problem is proposed through minimization of statistical divergences between the probability distribution (g). of feature vectors from the test utterance and the probability distributions of the feature vector corresponding to the speaker classes. This approach is made more robust to the presence of outliers, through the use of suitably modified versions of the standard divergence measures. The relevant solutions to the minimum distance methods are referred to as the minimum rescaled modified distance estimators (MRMDEs). Three measures were considered - the likelihood disparity, the Hellinger distance and Pearson's chi-square distance. The proposed approach is motivated by the observation that, in the case of the likelihood disparity, when the empirical distribution function is used to estimate g, it becomes equivalent to maximum likelihood classification with Gaussian Mixture Models (GMMs) for speaker classes, a highly effective approach used, for example, by Reynolds [22] based on Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) as features. Significant improvement in classification accuracy is observed under this approach on the benchmark speech corpus NTIMIT and a new bilingual speech corpus NISIS, with MFCC features, both in isolation and in combination with delta MFCC features. Moreover, the ubiquitous principal component transformation, by itself and in conjunction with the principle of classifier combination, is found to further enhance the performance.
A Hybrid Approach for Improved Content-based Image Retrieval using Segmentation
Feb 11, 2015


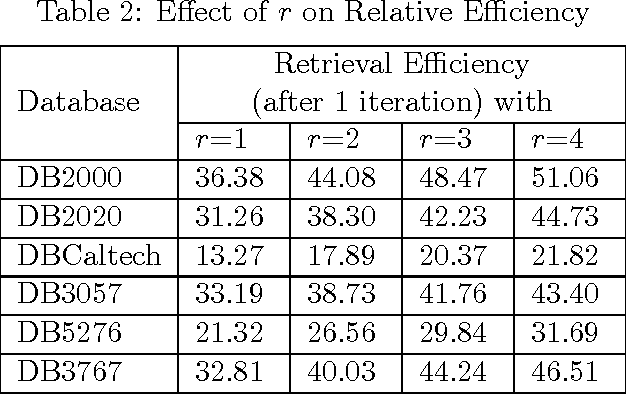
Abstract:The objective of Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) methods is essentially to extract, from large (image) databases, a specified number of images similar in visual and semantic content to a so-called query image. To bridge the semantic gap that exists between the representation of an image by low-level features (namely, colour, shape, texture) and its high-level semantic content as perceived by humans, CBIR systems typically make use of the relevance feedback (RF) mechanism. RF iteratively incorporates user-given inputs regarding the relevance of retrieved images, to improve retrieval efficiency. One approach is to vary the weights of the features dynamically via feature reweighting. In this work, an attempt has been made to improve retrieval accuracy by enhancing a CBIR system based on color features alone, through implicit incorporation of shape information obtained through prior segmentation of the images. Novel schemes for feature reweighting as well as for initialization of the relevant set for improved relevance feedback, have also been proposed for boosting performance of RF- based CBIR. At the same time, new measures for evaluation of retrieval accuracy have been suggested, to overcome the limitations of existing measures in the RF context. Results of extensive experiments have been presented to illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge