Amir Sadeghipour
Christian Doppler Laboratory for Ophthalmic Image Analysis, Department of Ophthalmology and Optometry, Medical University Vienna, Austria
Fully Automated Segmentation of Hyperreflective Foci in Optical Coherence Tomography Images
May 08, 2018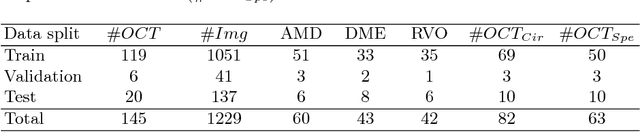
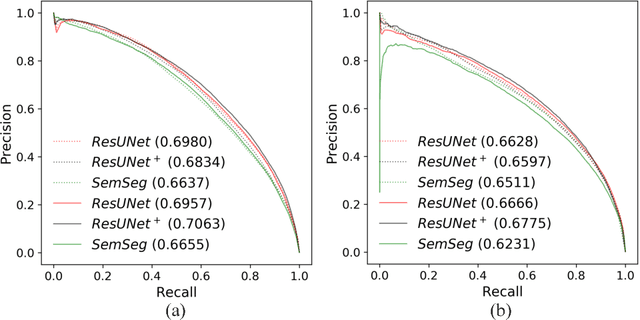
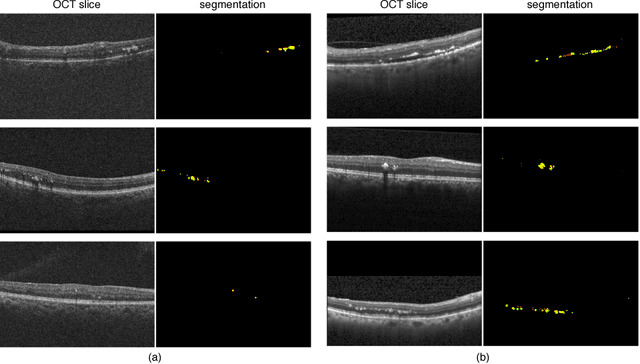
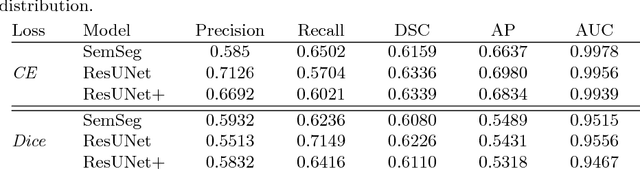
Abstract:The automatic detection of disease related entities in retinal imaging data is relevant for disease- and treatment monitoring. It enables the quantitative assessment of large amounts of data and the corresponding study of disease characteristics. The presence of hyperreflective foci (HRF) is related to disease progression in various retinal diseases. Manual identification of HRF in spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT) scans is error-prone and tedious. We present a fully automated machine learning approach for segmenting HRF in SD-OCT scans. Evaluation on annotated OCT images of the retina demonstrates that a residual U-Net allows to segment HRF with high accuracy. As our dataset comprised data from different retinal diseases including age-related macular degeneration, diabetic macular edema and retinal vein occlusion, the algorithm can safely be applied in all of them though different pathophysiological origins are known.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge