Amir Masoud Rahmani
Enhanced Classification of Heart Sounds Using Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients: A Comparative Study of Single and Ensemble Classifier Strategies
Jun 02, 2024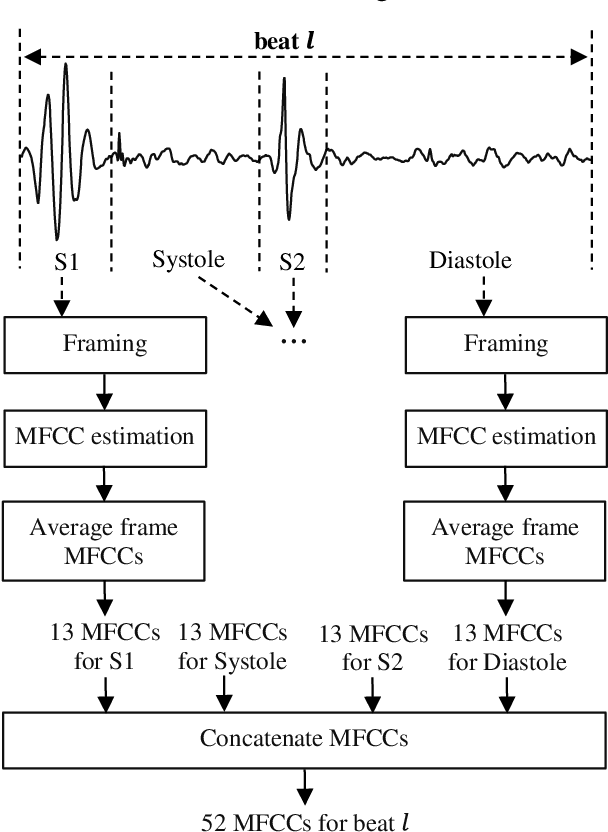
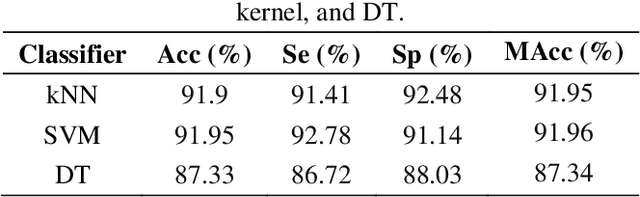
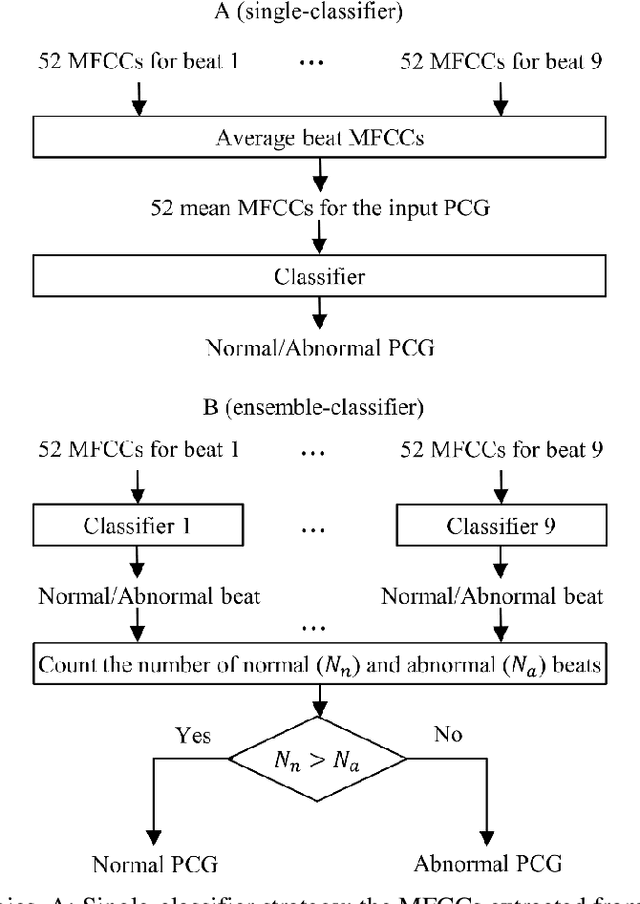
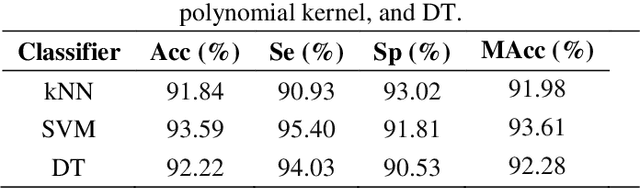
Abstract:This paper explores the efficacy of Mel Frequency Cepstral Coefficients (MFCCs) in detecting abnormal phonocardiograms using two classification strategies: a single-classifier and an ensemble-classifier approach. Phonocardiograms were segmented into S1, systole, S2, and diastole intervals, with thirteen MFCCs estimated from each segment, yielding 52 MFCCs per beat. In the single-classifier strategy, the MFCCs from nine consecutive beats were averaged to classify phonocardiograms. Conversely, the ensemble-classifier strategy employed nine classifiers to individually assess beats as normal or abnormal, with the overall classification based on the majority vote. Both methods were tested on a publicly available phonocardiogram database. Results demonstrated that the ensemble-classifier strategy achieved higher accuracy compared to the single-classifier approach, establishing MFCCs as more effective than other features, including time, time-frequency, and statistical features, evaluated in similar studies.
A comprehensive study on Frequent Pattern Mining and Clustering categories for topic detection in Persian text stream
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:Topic detection is a complex process and depends on language because it somehow needs to analyze text. There have been few studies on topic detection in Persian, and the existing algorithms are not remarkable. Therefore, we aimed to study topic detection in Persian. The objectives of this study are: 1) to conduct an extensive study on the best algorithms for topic detection, 2) to identify necessary adaptations to make these algorithms suitable for the Persian language, and 3) to evaluate their performance on Persian social network texts. To achieve these objectives, we have formulated two research questions: First, considering the lack of research in Persian, what modifications should be made to existing frameworks, especially those developed in English, to make them compatible with Persian? Second, how do these algorithms perform, and which one is superior? There are various topic detection methods that can be categorized into different categories. Frequent pattern and clustering are selected for this research, and a hybrid of both is proposed as a new category. Then, ten methods from these three categories are selected. All of them are re-implemented from scratch, changed, and adapted with Persian. These ten methods encompass different types of topic detection methods and have shown good performance in English. The text of Persian social network posts is used as the dataset. Additionally, a new multiclass evaluation criterion, called FS, is used in this paper for the first time in the field of topic detection. Approximately 1.4 billion tokens are processed during experiments. The results indicate that if we are searching for keyword-topics that are easily understandable by humans, the hybrid category is better. However, if the aim is to cluster posts for further analysis, the frequent pattern category is more suitable.
Dynamic Pricing of Applications in Cloud Marketplaces using Game Theory
Sep 20, 2023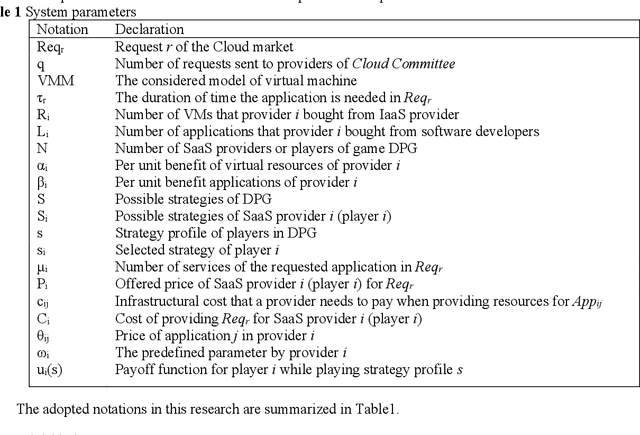
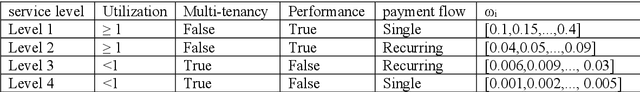
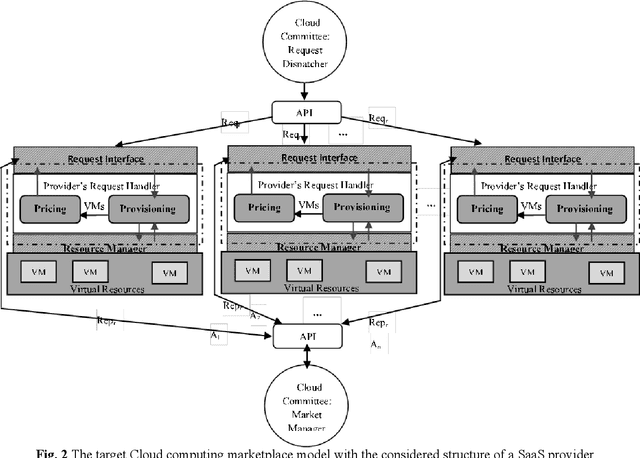
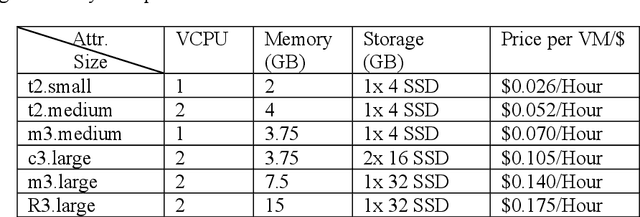
Abstract:The competitive nature of Cloud marketplaces as new concerns in delivery of services makes the pricing policies a crucial task for firms. so that, pricing strategies has recently attracted many researchers. Since game theory can handle such competing well this concern is addressed by designing a normal form game between providers in current research. A committee is considered in which providers register for improving their competition based pricing policies. The functionality of game theory is applied to design dynamic pricing policies. The usage of the committee makes the game a complete information one, in which each player is aware of every others payoff functions. The players enhance their pricing policies to maximize their profits. The contribution of this paper is the quantitative modeling of Cloud marketplaces in form of a game to provide novel dynamic pricing strategies; the model is validated by proving the existence and the uniqueness of Nash equilibrium of the game.
A Cost-Aware Mechanism for Optimized Resource Provisioning in Cloud Computing
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Due to the recent wide use of computational resources in cloud computing, new resource provisioning challenges have been emerged. Resource provisioning techniques must keep total costs to a minimum while meeting the requirements of the requests. According to widely usage of cloud services, it seems more challenging to develop effective schemes for provisioning services cost-effectively; we have proposed a novel learning based resource provisioning approach that achieves cost-reduction guarantees of demands. The contributions of our optimized resource provisioning (ORP) approach are as follows. Firstly, it is designed to provide a cost-effective method to efficiently handle the provisioning of requested applications; while most of the existing models allow only workflows in general which cares about the dependencies of the tasks, ORP performs based on services of which applications comprised and cares about their efficient provisioning totally. Secondly, it is a learning automata-based approach which selects the most proper resources for hosting each service of the demanded application; our approach considers both cost and service requirements together for deploying applications. Thirdly, a comprehensive evaluation is performed for three typical workloads: data-intensive, process-intensive and normal applications. The experimental results show that our method adapts most of the requirements efficiently, and furthermore the resulting performance meets our design goals.
A Comparative Study on Transfer Learning and Distance Metrics in Semantic Clustering over the COVID-19 Tweets
Nov 16, 2021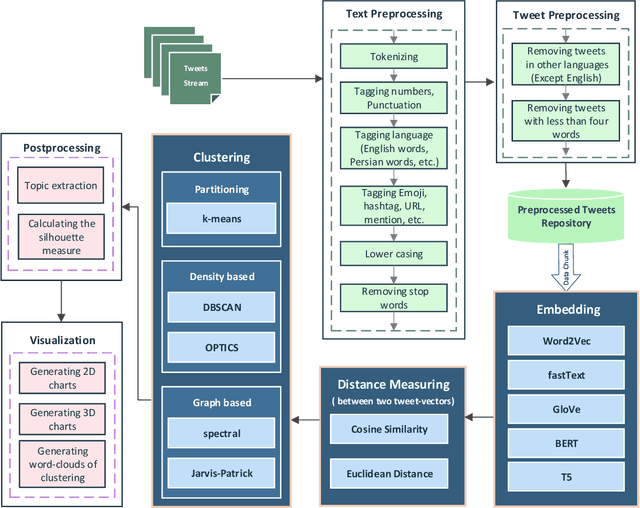

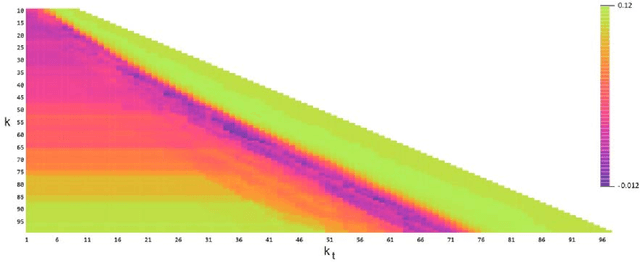
Abstract:This paper is a comparison study in the context of Topic Detection on COVID-19 data. There are various approaches for Topic Detection, among which the Clustering approach is selected in this paper. Clustering requires distance and calculating distance needs embedding. The aim of this research is to simultaneously study the three factors of embedding methods, distance metrics and clustering methods and their interaction. A dataset including one-month tweets collected with COVID-19-related hashtags is used for this study. Five methods, from earlier to new methods, are selected among the embedding methods: Word2Vec, fastText, GloVe, BERT and T5. Five clustering methods are investigated in this paper that are: k-means, DBSCAN, OPTICS, spectral and Jarvis-Patrick. Euclidian distance and Cosine distance as the most important distance metrics in this field are also examined. First, more than 7,500 tests are performed to tune the parameters. Then, all the different combinations of embedding methods with distance metrics and clustering methods are investigated by silhouette metric. The number of these combinations is 50 cases. First, the results of these 50 tests are examined. Then, the rank of each method is taken into account in all the tests of that method. Finally, the major variables of the research (embedding methods, distance metrics and clustering methods) are studied separately. Averaging is performed over the control variables to neutralize their effect. The experimental results show that T5 strongly outperforms other embedding methods in terms of silhouette metric. In terms of distance metrics, cosine distance is weakly better. DBSCAN is also superior to other methods in terms of clustering methods.
A New Clustering Approach based on Page's Path Similarity for Navigation Patterns Mining
Mar 07, 2010



Abstract:In recent years, predicting the user's next request in web navigation has received much attention. An information source to be used for dealing with such problem is the left information by the previous web users stored at the web access log on the web servers. Purposed systems for this problem work based on this idea that if a large number of web users request specific pages of a website on a given session, it can be concluded that these pages are satisfying similar information needs, and therefore they are conceptually related. In this study, a new clustering approach is introduced that employs logical path storing of a website pages as another parameter which is regarded as a similarity parameter and conceptual relation between web pages. The results of simulation have shown that the proposed approach is more than others precise in determining the clusters.
* Pages IEEE format, International Journal of Computer Science and Information Security, IJCSIS February 2010, ISSN 1947 5500, http://sites.google.com/site/ijcsis/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge