Amartya Hatua
Machine Unlearning using Forgetting Neural Networks
Oct 29, 2024Abstract:Modern computer systems store vast amounts of personal data, enabling advances in AI and ML but risking user privacy and trust. For privacy reasons, it is desired sometimes for an ML model to forget part of the data it was trained on. This paper presents a new approach to machine unlearning using forgetting neural networks (FNN). FNNs are neural networks with specific forgetting layers, that take inspiration from the processes involved when a human brain forgets. While FNNs had been proposed as a theoretical construct, they have not been previously used as a machine unlearning method. We describe four different types of forgetting layers and study their properties. In our experimental evaluation, we report our results on the MNIST handwritten digit recognition and fashion datasets. The effectiveness of the unlearned models was tested using Membership Inference Attacks (MIA). Successful experimental results demonstrate the great potential of our proposed method for dealing with the machine unlearning problem.
Machine Unlearning using a Multi-GAN based Model
Jul 26, 2024Abstract:This article presents a new machine unlearning approach that utilizes multiple Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) based models. The proposed method comprises two phases: i) data reorganization in which synthetic data using the GAN model is introduced with inverted class labels of the forget datasets, and ii) fine-tuning the pre-trained model. The GAN models consist of two pairs of generators and discriminators. The generator discriminator pairs generate synthetic data for the retain and forget datasets. Then, a pre-trained model is utilized to get the class labels of the synthetic datasets. The class labels of synthetic and original forget datasets are inverted. Finally, all combined datasets are used to fine-tune the pre-trained model to get the unlearned model. We have performed the experiments on the CIFAR-10 dataset and tested the unlearned models using Membership Inference Attacks (MIA). The inverted class labels procedure and synthetically generated data help to acquire valuable information that enables the model to outperform state-of-the-art models and other standard unlearning classifiers.
AI-Enhanced Data Processing and Discovery Crowd Sourcing for Meteor Shower Mapping
Aug 02, 2023Abstract:The Cameras for Allsky Meteor Surveillance (CAMS) project, funded by NASA starting in 2010, aims to map our meteor showers by triangulating meteor trajectories detected in low-light video cameras from multiple locations across 16 countries in both the northern and southern hemispheres. Its mission is to validate, discover, and predict the upcoming returns of meteor showers. Our research aimed to streamline the data processing by implementing an automated cloud-based AI-enabled pipeline and improve the data visualization to improve the rate of discoveries by involving the public in monitoring the meteor detections. This article describes the process of automating the data ingestion, processing, and insight generation using an interpretable Active Learning and AI pipeline. This work also describes the development of an interactive web portal (the NASA Meteor Shower portal) to facilitate the visualization of meteor radiant maps. To date, CAMS has discovered over 200 new meteor showers and has validated dozens of previously reported showers.
Claim Verification using a Multi-GAN based Model
Mar 24, 2021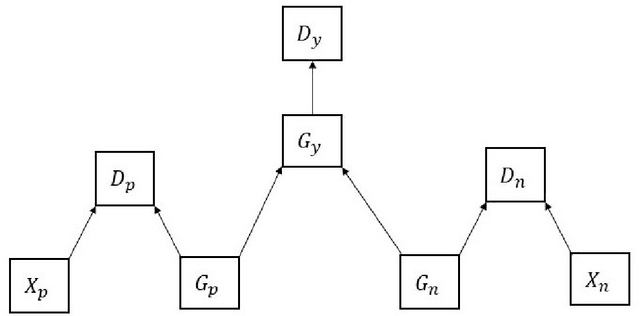
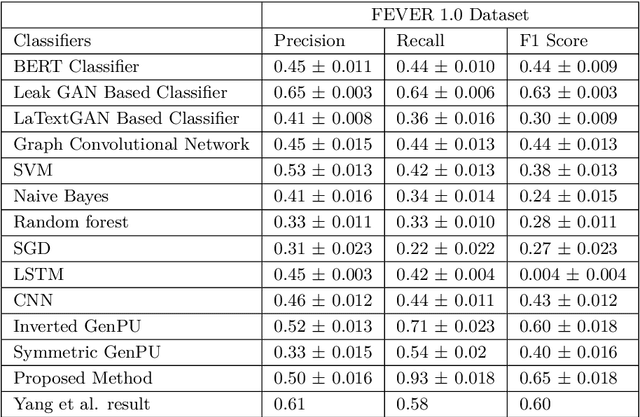
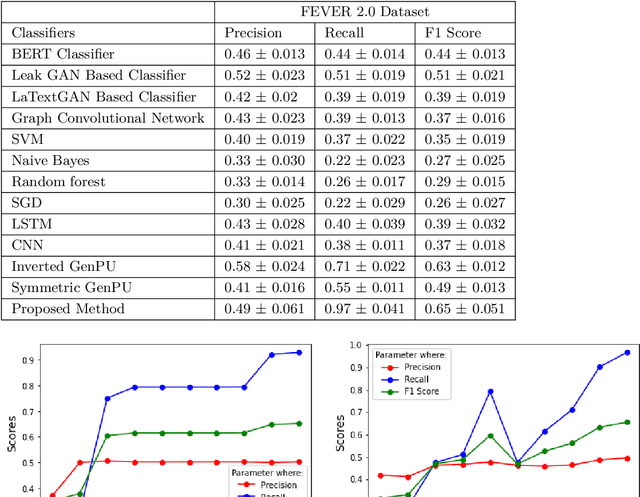
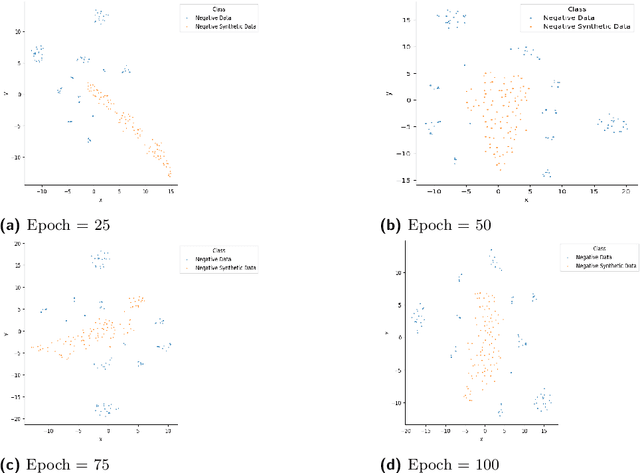
Abstract:This article describes research on claim verification carried out using a multiple GAN-based model. The proposed model consists of three pairs of generators and discriminators. The generator and discriminator pairs are responsible for generating synthetic data for supported and refuted claims and claim labels. A theoretical discussion about the proposed model is provided to validate the equilibrium state of the model. The proposed model is applied to the FEVER dataset, and a pre-trained language model is used for the input text data. The synthetically generated data helps to gain information which helps the model to perform better than state of the art models and other standard classifiers.
Optimal Feature Selection from VMware ESXi 5.1 Feature Set
Oct 18, 2014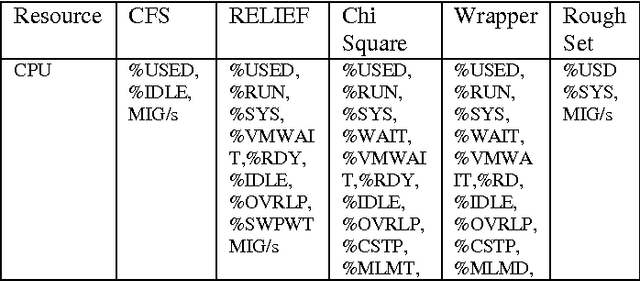
Abstract:A study of VMware ESXi 5.1 server has been carried out to find the optimal set of parameters which suggest usage of different resources of the server. Feature selection algorithms have been used to extract the optimum set of parameters of the data obtained from VMware ESXi 5.1 server using esxtop command. Multiple virtual machines (VMs) are running in the mentioned server. K-means algorithm is used for clustering the VMs. The goodness of each cluster is determined by Davies Bouldin index and Dunn index respectively. The best cluster is further identified by the determined indices. The features of the best cluster are considered into a set of optimal parameters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge