Alvaro Lopez Pellicer
ProtoMedX: Towards Explainable Multi-Modal Prototype Learning for Bone Health Classification
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Bone health studies are crucial in medical practice for the early detection and treatment of Osteopenia and Osteoporosis. Clinicians usually make a diagnosis based on densitometry (DEXA scans) and patient history. The applications of AI in this field are ongoing research. Most successful methods rely on deep learning models that use vision alone (DEXA/X-ray imagery) and focus on prediction accuracy, while explainability is often disregarded and left to post hoc assessments of input contributions. We propose ProtoMedX, a multi-modal model that uses both DEXA scans of the lumbar spine and patient records. ProtoMedX's prototype-based architecture is explainable by design, which is crucial for medical applications, especially in the context of the upcoming EU AI Act, as it allows explicit analysis of model decisions, including incorrect ones. ProtoMedX demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in bone health classification while also providing explanations that can be visually understood by clinicians. Using a dataset of 4,160 real NHS patients, the proposed ProtoMedX achieves 87.58% accuracy in vision-only tasks and 89.8% in its multi-modal variant, both surpassing existing published methods.
UNICAD: A Unified Approach for Attack Detection, Noise Reduction and Novel Class Identification
Jun 24, 2024



Abstract:As the use of Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) becomes pervasive, their vulnerability to adversarial attacks and limitations in handling unseen classes poses significant challenges. The state-of-the-art offers discrete solutions aimed to tackle individual issues covering specific adversarial attack scenarios, classification or evolving learning. However, real-world systems need to be able to detect and recover from a wide range of adversarial attacks without sacrificing classification accuracy and to flexibly act in {\bf unseen} scenarios. In this paper, UNICAD, is proposed as a novel framework that integrates a variety of techniques to provide an adaptive solution. For the targeted image classification, UNICAD achieves accurate image classification, detects unseen classes, and recovers from adversarial attacks using Prototype and Similarity-based DNNs with denoising autoencoders. Our experiments performed on the CIFAR-10 dataset highlight UNICAD's effectiveness in adversarial mitigation and unseen class classification, outperforming traditional models.
Federated Adversarial Learning for Robust Autonomous Landing Runway Detection
Jun 22, 2024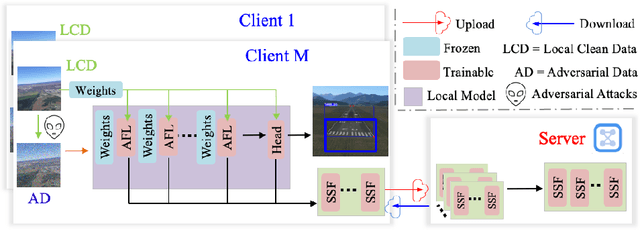
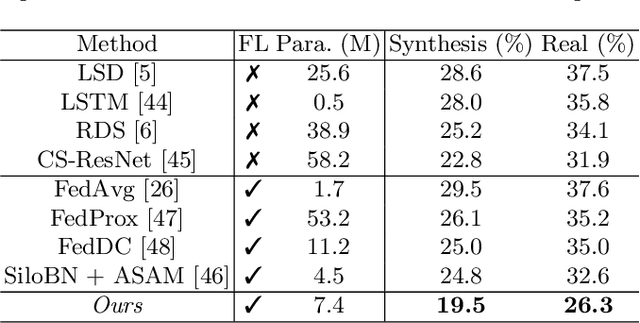
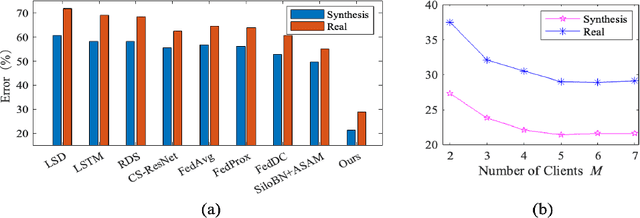
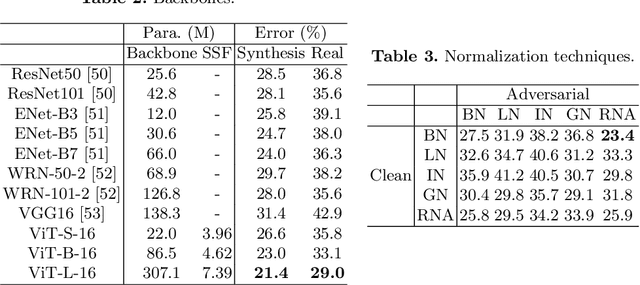
Abstract:As the development of deep learning techniques in autonomous landing systems continues to grow, one of the major challenges is trust and security in the face of possible adversarial attacks. In this paper, we propose a federated adversarial learning-based framework to detect landing runways using paired data comprising of clean local data and its adversarial version. Firstly, the local model is pre-trained on a large-scale lane detection dataset. Then, instead of exploiting large instance-adaptive models, we resort to a parameter-efficient fine-tuning method known as scale and shift deep features (SSF), upon the pre-trained model. Secondly, in each SSF layer, distributions of clean local data and its adversarial version are disentangled for accurate statistics estimation. To the best of our knowledge, this marks the first instance of federated learning work that address the adversarial sample problem in landing runway detection. Our experimental evaluations over both synthesis and real images of Landing Approach Runway Detection (LARD) dataset consistently demonstrate good performance of the proposed federated adversarial learning and robust to adversarial attacks.
* ICANN2024
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge