Alireza Moradi
Copula-Based Aggregation and Context-Aware Conformal Prediction for Reliable Renewable Energy Forecasting
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:The rapid growth of renewable energy penetration has intensified the need for reliable probabilistic forecasts to support grid operations at aggregated (fleet or system) levels. In practice, however, system operators often lack access to fleet-level probabilistic models and instead rely on site-level forecasts produced by heterogeneous third-party providers. Constructing coherent and calibrated fleet-level probabilistic forecasts from such inputs remains challenging due to complex cross-site dependencies and aggregation-induced miscalibration. This paper proposes a calibrated probabilistic aggregation framework that directly converts site-level probabilistic forecasts into reliable fleet-level forecasts in settings where system-level models cannot be trained or maintained. The framework integrates copula-based dependence modeling to capture cross-site correlations with Context-Aware Conformal Prediction (CACP) to correct miscalibration at the aggregated level. This combination enables dependence-aware aggregation while providing valid coverage and maintaining sharp prediction intervals. Experiments on large-scale solar generation datasets from MISO, ERCOT, and SPP demonstrate that the proposed Copula+CACP approach consistently achieves near-nominal coverage with significantly sharper intervals than uncalibrated aggregation baselines.
Informed Forecasting: Leveraging Auxiliary Knowledge to Boost LLM Performance on Time Series Forecasting
May 15, 2025Abstract:With the widespread adoption of Large Language Models (LLMs), there is a growing need to establish best practices for leveraging their capabilities beyond traditional natural language tasks. In this paper, a novel cross-domain knowledge transfer framework is proposed to enhance the performance of LLMs in time series forecasting -- a task of increasing relevance in fields such as energy systems, finance, and healthcare. The approach systematically infuses LLMs with structured temporal information to improve their forecasting accuracy. This study evaluates the proposed method on a real-world time series dataset and compares it to a naive baseline where the LLM receives no auxiliary information. Results show that knowledge-informed forecasting significantly outperforms the uninformed baseline in terms of predictive accuracy and generalization. These findings highlight the potential of knowledge transfer strategies to bridge the gap between LLMs and domain-specific forecasting tasks.
MCTS with Refinement for Proposals Selection Games in Scene Understanding
Jul 07, 2022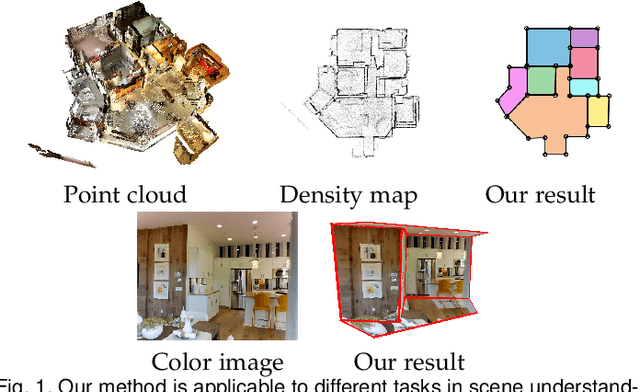
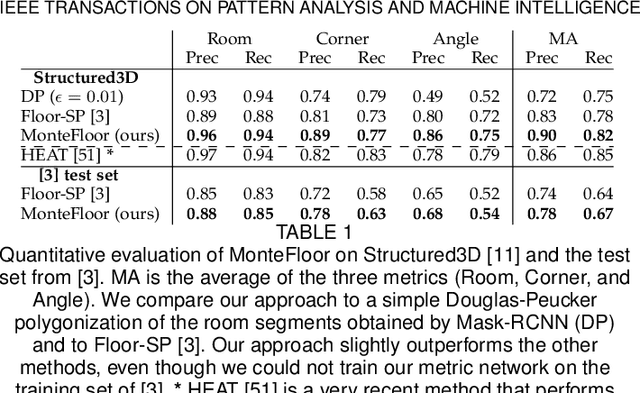
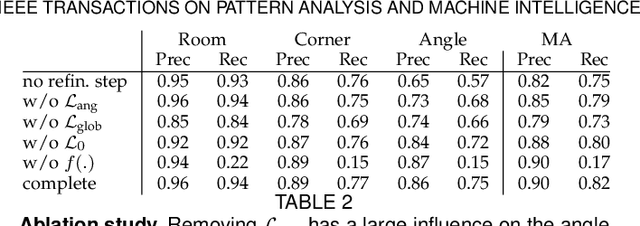
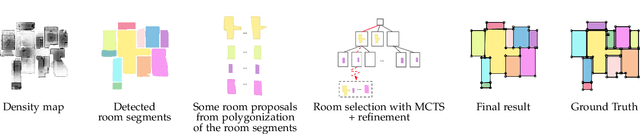
Abstract:We propose a novel method applicable in many scene understanding problems that adapts the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) algorithm, originally designed to learn to play games of high-state complexity. From a generated pool of proposals, our method jointly selects and optimizes proposals that minimize the objective term. In our first application for floor plan reconstruction from point clouds, our method selects and refines the room proposals, modelled as 2D polygons, by optimizing on an objective function combining the fitness as predicted by a deep network and regularizing terms on the room shapes. We also introduce a novel differentiable method for rendering the polygonal shapes of these proposals. Our evaluations on the recent and challenging Structured3D and Floor-SP datasets show significant improvements over the state-of-the-art, without imposing hard constraints nor assumptions on the floor plan configurations. In our second application, we extend our approach to reconstruct general 3D room layouts from a color image and obtain accurate room layouts. We also show that our differentiable renderer can easily be extended for rendering 3D planar polygons and polygon embeddings. Our method shows high performance on the Matterport3D-Layout dataset, without introducing hard constraints on room layout configurations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge