Alireza Darvishy
Deep Learning-Powered Visual SLAM Aimed at Assisting Visually Impaired Navigation
Oct 23, 2025



Abstract:Despite advancements in SLAM technologies, robust operation under challenging conditions such as low-texture, motion-blur, or challenging lighting remains an open challenge. Such conditions are common in applications such as assistive navigation for the visually impaired. These challenges undermine localization accuracy and tracking stability, reducing navigation reliability and safety. To overcome these limitations, we present SELM-SLAM3, a deep learning-enhanced visual SLAM framework that integrates SuperPoint and LightGlue for robust feature extraction and matching. We evaluated our framework using TUM RGB-D, ICL-NUIM, and TartanAir datasets, which feature diverse and challenging scenarios. SELM-SLAM3 outperforms conventional ORB-SLAM3 by an average of 87.84% and exceeds state-of-the-art RGB-D SLAM systems by 36.77%. Our framework demonstrates enhanced performance under challenging conditions, such as low-texture scenes and fast motion, providing a reliable platform for developing navigation aids for the visually impaired.
InCrowd-VI: A Realistic Visual-Inertial Dataset for Evaluating SLAM in Indoor Pedestrian-Rich Spaces for Human Navigation
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) techniques can be used to navigate the visually impaired, but the development of robust SLAM solutions for crowded spaces is limited by the lack of realistic datasets. To address this, we introduce InCrowd-VI, a novel visual-inertial dataset specifically designed for human navigation in indoor pedestrian-rich environments. Recorded using Meta Aria Project glasses, it captures realistic scenarios without environmental control. InCrowd-VI features 58 sequences totaling a 5 km trajectory length and 1.5 hours of recording time, including RGB, stereo images, and IMU measurements. The dataset captures important challenges such as pedestrian occlusions, varying crowd densities, complex layouts, and lighting changes. Ground-truth trajectories, accurate to approximately 2 cm, are provided in the dataset, originating from the Meta Aria project machine perception SLAM service. In addition, a semi-dense 3D point cloud of scenes is provided for each sequence. The evaluation of state-of-the-art visual odometry (VO) and SLAM algorithms on InCrowd-VI revealed severe performance limitations in these realistic scenarios, demonstrating the need and value of the new dataset to advance SLAM research for visually impaired navigation in complex indoor environments.
MathNet: A Data-Centric Approach for Printed Mathematical Expression Recognition
Apr 21, 2024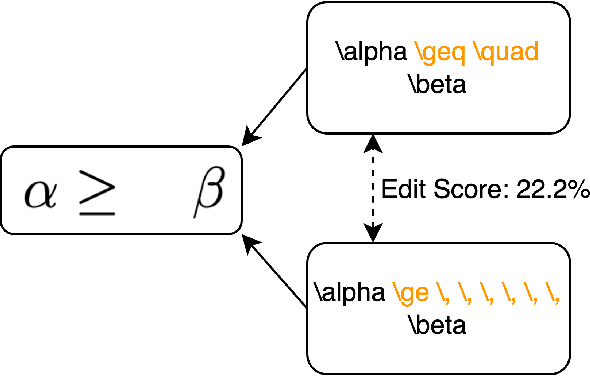
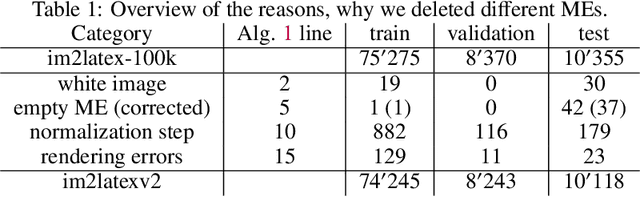
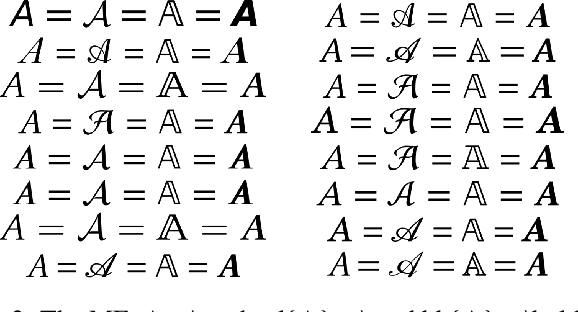
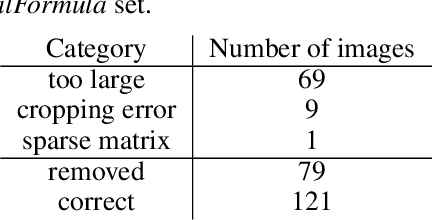
Abstract:Printed mathematical expression recognition (MER) models are usually trained and tested using LaTeX-generated mathematical expressions (MEs) as input and the LaTeX source code as ground truth. As the same ME can be generated by various different LaTeX source codes, this leads to unwanted variations in the ground truth data that bias test performance results and hinder efficient learning. In addition, the use of only one font to generate the MEs heavily limits the generalization of the reported results to realistic scenarios. We propose a data-centric approach to overcome this problem, and present convincing experimental results: Our main contribution is an enhanced LaTeX normalization to map any LaTeX ME to a canonical form. Based on this process, we developed an improved version of the benchmark dataset im2latex-100k, featuring 30 fonts instead of one. Second, we introduce the real-world dataset realFormula, with MEs extracted from papers. Third, we developed a MER model, MathNet, based on a convolutional vision transformer, with superior results on all four test sets (im2latex-100k, im2latexv2, realFormula, and InftyMDB-1), outperforming the previous state of the art by up to 88.3%.
SLAM for Visually Impaired People: A Survey
Dec 09, 2022Abstract:In recent decades, several assistive technologies for visually impaired and blind (VIB) people have been developed to improve their ability to navigate independently and safely. At the same time, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) techniques have become sufficiently robust and efficient to be adopted in the development of assistive technologies. In this paper, we first report the results of an anonymous survey conducted with VIB people to understand their experience and needs; we focus on digital assistive technologies that help them with indoor and outdoor navigation. Then, we present a literature review of assistive technologies based on SLAM. We discuss proposed approaches and indicate their pros and cons. We conclude by presenting future opportunities and challenges in this domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge