Ali Sydney
The infrastructure powering IBM's Gen AI model development
Jul 07, 2024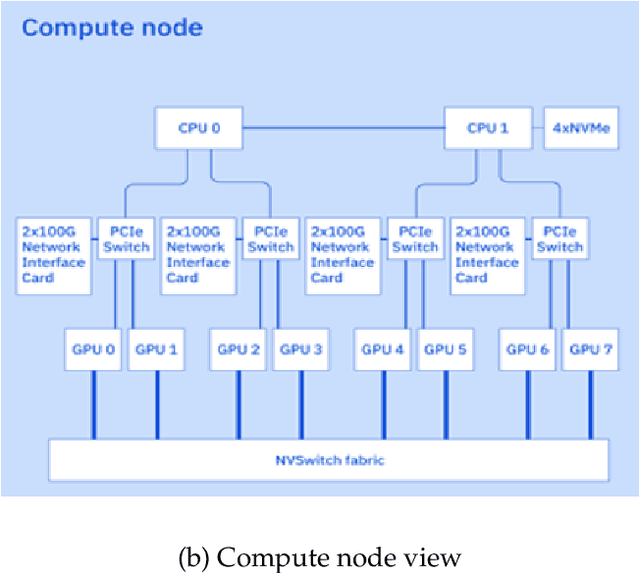
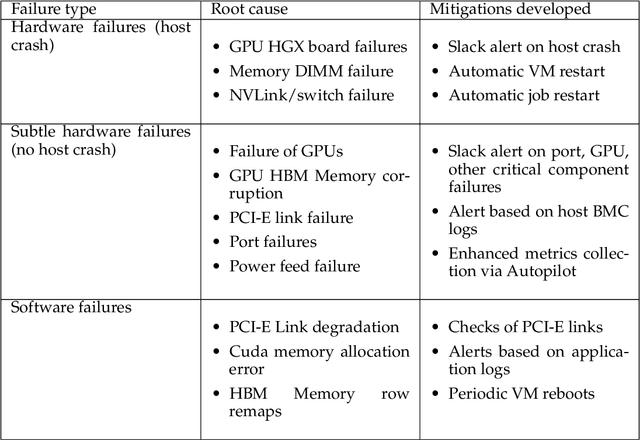
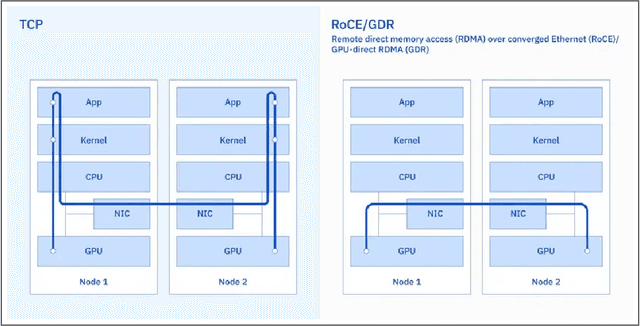
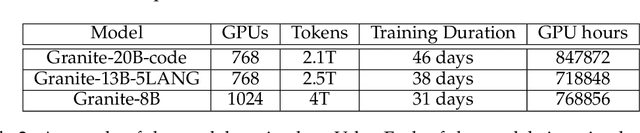
Abstract:AI Infrastructure plays a key role in the speed and cost-competitiveness of developing and deploying advanced AI models. The current demand for powerful AI infrastructure for model training is driven by the emergence of generative AI and foundational models, where on occasion thousands of GPUs must cooperate on a single training job for the model to be trained in a reasonable time. Delivering efficient and high-performing AI training requires an end-to-end solution that combines hardware, software and holistic telemetry to cater for multiple types of AI workloads. In this report, we describe IBM's hybrid cloud infrastructure that powers our generative AI model development. This infrastructure includes (1) Vela: an AI-optimized supercomputing capability directly integrated into the IBM Cloud, delivering scalable, dynamic, multi-tenant and geographically distributed infrastructure for large-scale model training and other AI workflow steps and (2) Blue Vela: a large-scale, purpose-built, on-premises hosting environment that is optimized to support our largest and most ambitious AI model training tasks. Vela provides IBM with the dual benefit of high performance for internal use along with the flexibility to adapt to an evolving commercial landscape. Blue Vela provides us with the benefits of rapid development of our largest and most ambitious models, as well as future-proofing against the evolving model landscape in the industry. Taken together, they provide IBM with the ability to rapidly innovate in the development of both AI models and commercial offerings.
GymFG: A Framework with a Gym Interface for FlightGear
Apr 26, 2020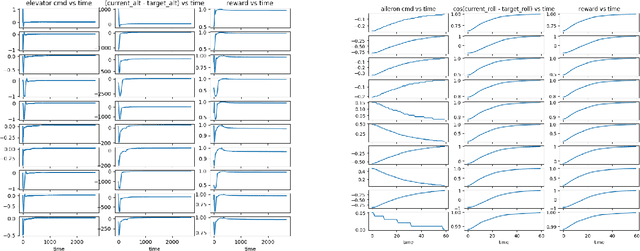
Abstract:Over the past decades, progress in deployable autonomous flight systems has slowly stagnated. This is reflected in today's production air-crafts, where pilots only enable simple physics-based systems such as autopilot for takeoff, landing, navigation, and terrain/traffic avoidance. Evidently, autonomy has not gained the trust of the community where higher problem complexity and cognitive workload are required. To address trust, we must revisit the process for developing autonomous capabilities: modeling and simulation. Given the prohibitive costs for live tests, we need to prototype and evaluate autonomous aerial agents in a high fidelity flight simulator with autonomous learning capabilities applicable to flight systems: such a open-source development platform is not available. As a result, we have developed GymFG: GymFG couples and extends a high fidelity, open-source flight simulator and a robust agent learning framework to facilitate learning of more complex tasks. Furthermore, we have demonstrated the use of GymFG to train an autonomous aerial agent using Imitation Learning. With GymFG, we can now deploy innovative ideas to address complex problems and build the trust necessary to move prototypes to the real-world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge