Ali Sharifi-Zarchi
Infinity and Beyond: Compositional Alignment in VAR and Diffusion T2I Models
Dec 12, 2025



Abstract:Achieving compositional alignment between textual descriptions and generated images - covering objects, attributes, and spatial relationships - remains a core challenge for modern text-to-image (T2I) models. Although diffusion-based architectures have been widely studied, the compositional behavior of emerging Visual Autoregressive (VAR) models is still largely unexamined. We benchmark six diverse T2I systems - SDXL, PixArt-$α$, Flux-Dev, Flux-Schnell, Infinity-2B, and Infinity-8B - across the full T2I-CompBench++ and GenEval suites, evaluating alignment in color and attribute binding, spatial relations, numeracy, and complex multi-object prompts. Across both benchmarks, Infinity-8B achieves the strongest overall compositional alignment, while Infinity-2B also matches or exceeds larger diffusion models in several categories, highlighting favorable efficiency-performance trade-offs. In contrast, SDXL and PixArt-$α$ show persistent weaknesses in attribute-sensitive and spatial tasks. These results provide the first systematic comparison of VAR and diffusion approaches to compositional alignment and establish unified baselines for the future development of the T2I model.
Novel Pipeline for Diagnosing Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Sensitive to Related Biomarkers
Jul 11, 2023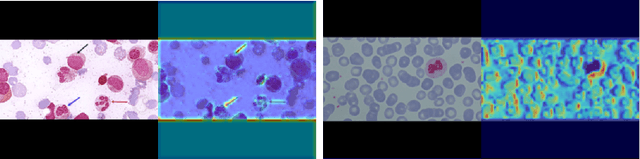
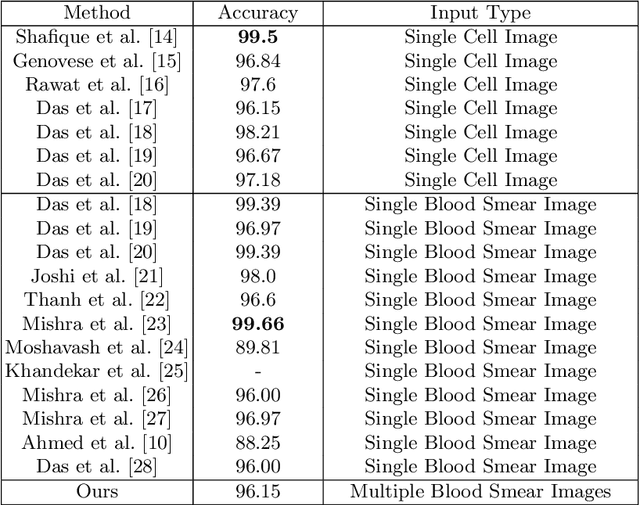
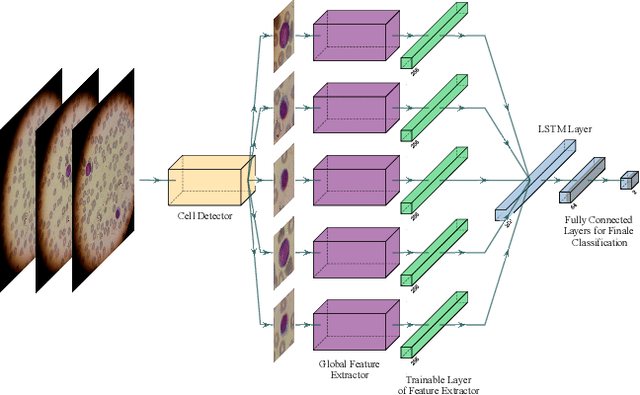
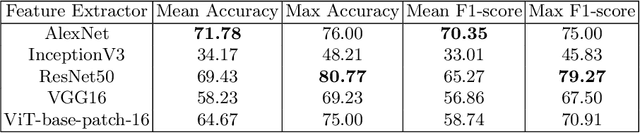
Abstract:Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is one of the most common types of childhood blood cancer. The quick start of the treatment process is critical to saving the patient's life, and for this reason, early diagnosis of this disease is essential. Examining the blood smear images of these patients is one of the methods used by expert doctors to diagnose this disease. Deep learning-based methods have numerous applications in medical fields, as they have significantly advanced in recent years. ALL diagnosis is not an exception in this field, and several machine learning-based methods for this problem have been proposed. In previous methods, high diagnostic accuracy was reported, but our work showed that this alone is not sufficient, as it can lead to models taking shortcuts and not making meaningful decisions. This issue arises due to the small size of medical training datasets. To address this, we constrained our model to follow a pipeline inspired by experts' work. We also demonstrated that, since a judgement based on only one image is insufficient, redefining the problem as a multiple-instance learning problem is necessary for achieving a practical result. Our model is the first to provide a solution to this problem in a multiple-instance learning setup. We introduced a novel pipeline for diagnosing ALL that approximates the process used by hematologists, is sensitive to disease biomarkers, and achieves an accuracy of 96.15%, an F1-score of 94.24%, a sensitivity of 97.56%, and a specificity of 90.91% on ALL IDB 1. Our method was further evaluated on an out-of-distribution dataset, which posed a challenging test and had acceptable performance. Notably, our model was trained on a relatively small dataset, highlighting the potential for our approach to be applied to other medical datasets with limited data availability.
Inferring Molecular Pathology and micro-RNA Transcriptome from mRNA Profiles of Cancer Biopsies through Deep Multi-Task Learning
Aug 07, 2018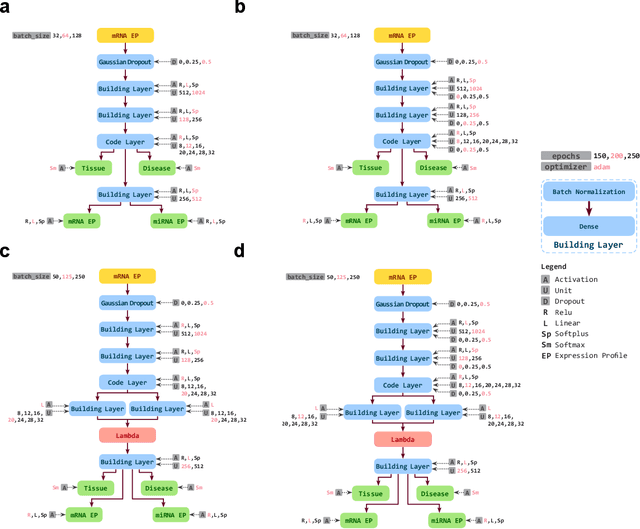
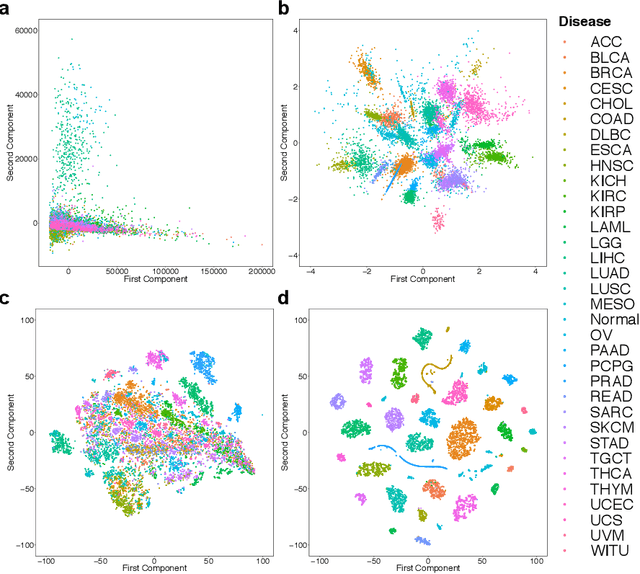
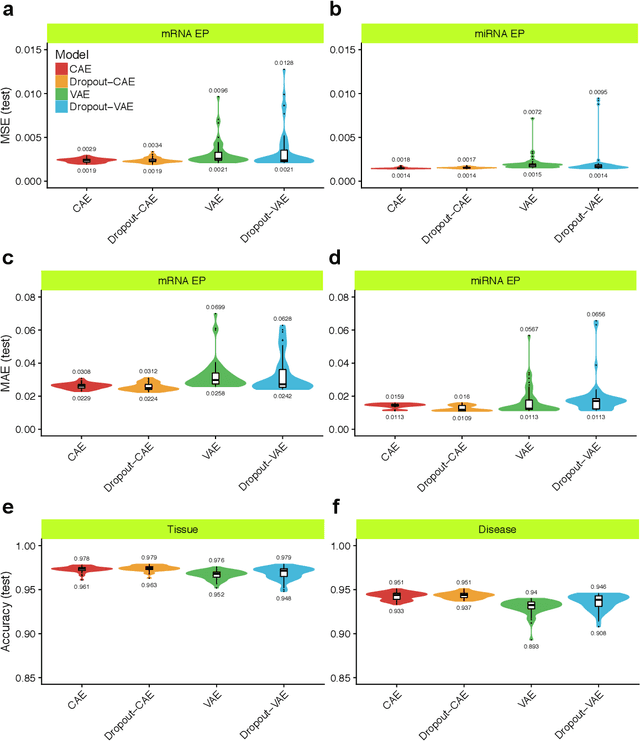
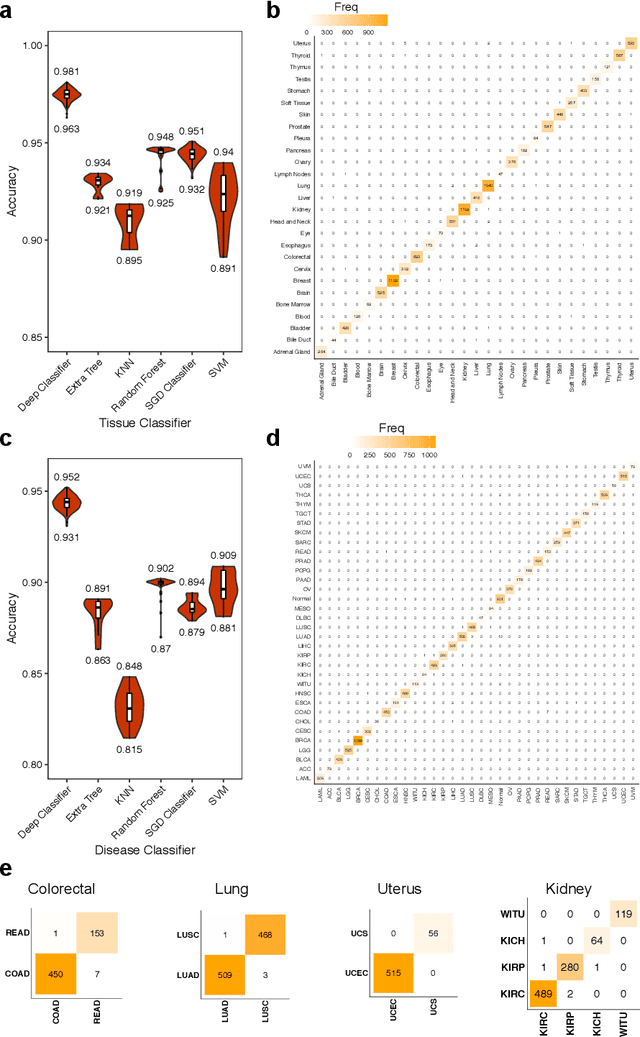
Abstract:Despite great advances, molecular cancer pathology is often limited to use a small number of biomarkers rather than the whole transcriptome, partly due to the computational challenges. Here, we introduce a novel architecture of DNNs that is capable of simultaneous inference of various properties of biological samples, through multi-task and transfer learning. We employed this architecture on mRNA transcription profiles of 10787 clinical samples from 34 classes (one healthy and 33 different types of cancer) from 27 tissues. Our system significantly outperforms prior works and classical machine learning approaches in predicting tissue-of-origin, normal or disease state and cancer type of each sample. Furthermore, it can predict miRNA transcription profile of each sample, which enables performing miRNA expression research when only mRNA transcriptome data are available. We also show this system is very robust against noise and missing values. Collectively, our results highlight applications of artificial intelligence in molecular cancer pathology and oncological research.
Cell Identity Codes: Understanding Cell Identity from Gene Expression Profiles using Deep Neural Networks
Jun 13, 2018Abstract:Understanding cell identity is an important task in many biomedical areas. Expression patterns of specific marker genes have been used to characterize some limited cell types, but exclusive markers are not available for many cell types. A second approach is to use machine learning to discriminate cell types based on the whole gene expression profiles (GEPs). The accuracies of simple classification algorithms such as linear discriminators or support vector machines are limited due to the complexity of biological systems. We used deep neural networks to analyze 1040 GEPs from 16 different human tissues and cell types. After comparing different architectures, we identified a specific structure of deep autoencoders that can encode a GEP into a vector of 30 numeric values, which we call the cell identity code (CIC). The original GEP can be reproduced from the CIC with an accuracy comparable to technical replicates of the same experiment. Although we use an unsupervised approach to train the autoencoder, we show different values of the CIC are connected to different biological aspects of the cell, such as different pathways or biological processes. This network can use CIC to reproduce the GEP of the cell types it has never seen during the training. It also can resist some noise in the measurement of the GEP. Furthermore, we introduce classifier autoencoder, an architecture that can accurately identify cell type based on the GEP or the CIC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge