Alexandru Rinciog
Reinforcement Learning for AMR Charging Decisions: The Impact of Reward and Action Space Design
May 16, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel reinforcement learning (RL) design to optimize the charging strategy for autonomous mobile robots in large-scale block stacking warehouses. RL design involves a wide array of choices that can mostly only be evaluated through lengthy experimentation. Our study focuses on how different reward and action space configurations, ranging from flexible setups to more guided, domain-informed design configurations, affect the agent performance. Using heuristic charging strategies as a baseline, we demonstrate the superiority of flexible, RL-based approaches in terms of service times. Furthermore, our findings highlight a trade-off: While more open-ended designs are able to discover well-performing strategies on their own, they may require longer convergence times and are less stable, whereas guided configurations lead to a more stable learning process but display a more limited generalization potential. Our contributions are threefold. First, we extend SLAPStack, an open-source, RL-compatible simulation-framework to accommodate charging strategies. Second, we introduce a novel RL design for tackling the charging strategy problem. Finally, we introduce several novel adaptive baseline heuristics and reproducibly evaluate the design using a Proximal Policy Optimization agent and varying different design configurations, with a focus on reward.
MachineLearnAthon: An Action-Oriented Machine Learning Didactic Concept
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:Machine Learning (ML) techniques are encountered nowadays across disciplines, from social sciences, through natural sciences to engineering. The broad application of ML and the accelerated pace of its evolution lead to an increasing need for dedicated teaching concepts aimed at making the application of this technology more reliable and responsible. However, teaching ML is a daunting task. Aside from the methodological complexity of ML algorithms, both with respect to theory and implementation, the interdisciplinary and empirical nature of the field need to be taken into consideration. This paper introduces the MachineLearnAthon format, an innovative didactic concept designed to be inclusive for students of different disciplines with heterogeneous levels of mathematics, programming and domain expertise. At the heart of the concept lie ML challenges, which make use of industrial data sets to solve real-world problems. These cover the entire ML pipeline, promoting data literacy and practical skills, from data preparation, through deployment, to evaluation.
Towards Standardizing Reinforcement Learning Approaches for Stochastic Production Scheduling
Apr 16, 2021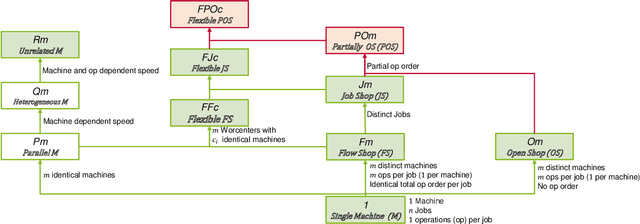
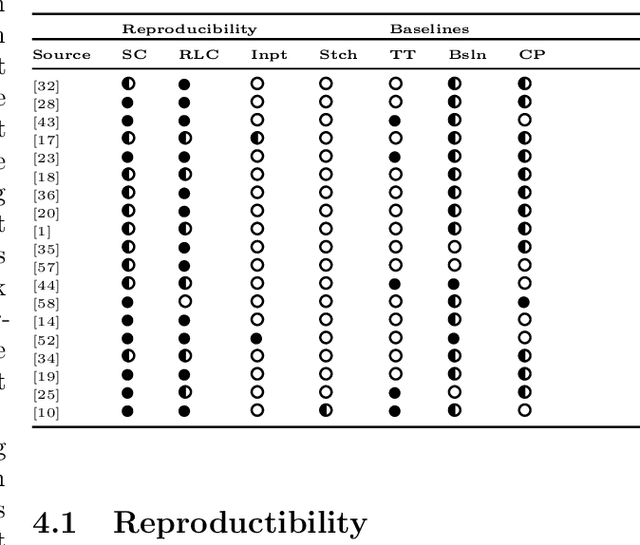
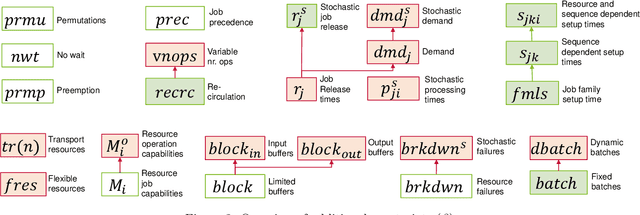
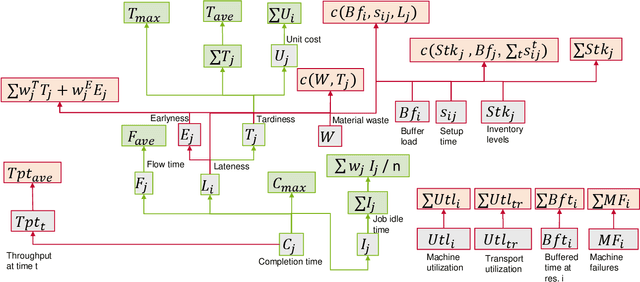
Abstract:Recent years have seen a rise in interest in terms of using machine learning, particularly reinforcement learning (RL), for production scheduling problems of varying degrees of complexity. The general approach is to break down the scheduling problem into a Markov Decision Process (MDP), whereupon a simulation implementing the MDP is used to train an RL agent. Since existing studies rely on (sometimes) complex simulations for which the code is unavailable, the experiments presented are hard, or, in the case of stochastic environments, impossible to reproduce accurately. Furthermore, there is a vast array of RL designs to choose from. To make RL methods widely applicable in production scheduling and work out their strength for the industry, the standardization of model descriptions - both production setup and RL design - and validation scheme are a prerequisite. Our contribution is threefold: First, we standardize the description of production setups used in RL studies based on established nomenclature. Secondly, we classify RL design choices from existing publications. Lastly, we propose recommendations for a validation scheme focusing on reproducibility and sufficient benchmarking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge