Alexandre Cochet
ICMUB laboratory, UMR CNRS 6302, Universite de Bourgogne Europe, Dijon, France, Nuclear Medicine Department, Centre Georges-Francois Leclerc, Dijon, France
Automatic quantification of breast cancer biomarkers from multiple 18F-FDG PET image segmentation
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) has become a standard clinical practice for tumor downsizing in breast cancer with 18F-FDG Positron Emission Tomography (PET). Our work aims to leverage PET imaging for the segmentation of breast lesions. The focus is on developing an automated system that accurately segments primary tumor regions and extracts key biomarkers from these areas to provide insights into the evolution of breast cancer following the first course of NAC. 243 baseline 18F-FDG PET scans (PET_Bl) and 180 follow-up 18F-FDG PET scans (PET_Fu) were acquired before and after the first course of NAC, respectively. Firstly, a deep learning-based breast tumor segmentation method was developed. The optimal baseline model (model trained on baseline exams) was fine-tuned on 15 follow-up exams and adapted using active learning to segment tumor areas in PET_Fu. The pipeline computes biomarkers such as maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), metabolic tumor volume (MTV), and total lesion glycolysis (TLG) to evaluate tumor evolution between PET_Fu and PET_Bl. Quality control measures were employed to exclude aberrant outliers. The nnUNet deep learning model outperformed in tumor segmentation on PET_Bl, achieved a Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) of 0.89 and a Hausdorff distance (HD) of 3.52 mm. After fine-tuning, the model demonstrated a DSC of 0.78 and a HD of 4.95 mm on PET_Fu exams. Biomarkers analysis revealed very strong correlations whatever the biomarker between manually segmented and automatically predicted regions. The significant average decrease of SUVmax, MTV and TLG were 5.22, 11.79 cm3 and 19.23 cm3, respectively. The presented approach demonstrates an automated system for breast tumor segmentation from 18F-FDG PET. Thanks to the extracted biomarkers, our method enables the automatic assessment of cancer progression.
Segmentation of the Myocardium on Late-Gadolinium Enhanced MRI based on 2.5 D Residual Squeeze and Excitation Deep Learning Model
May 27, 2020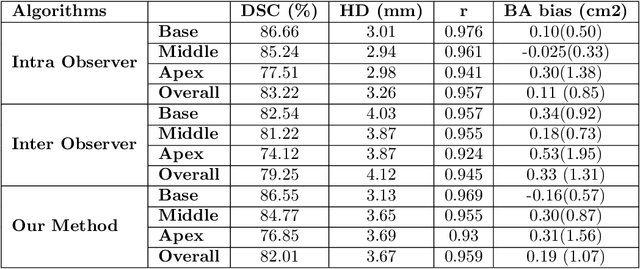
Abstract:Cardiac left ventricular (LV) segmentation from short-axis MRI acquired 10 minutes after the injection of a contrast agent (LGE-MRI) is a necessary step in the processing allowing the identification and diagnosis of cardiac diseases such as myocardial infarction. However, this segmentation is challenging due to high variability across subjects and the potential lack of contrast between structures. Then, the main objective of this work is to develop an accurate automatic segmentation method based on deep learning models for the myocardial borders on LGE-MRI. To this end, 2.5 D residual neural network integrated with a squeeze and excitation blocks in encoder side with specialized convolutional has been proposed. Late fusion has been used to merge the output of the best trained proposed models from a different set of hyperparameters. A total number of 320 exams (with a mean number of 6 slices per exam) were used for training and 28 exams used for testing. The performance analysis of the proposed ensemble model in the basal and middle slices was similar as compared to intra-observer study and slightly lower at apical slices. The overall Dice score was 82.01% by our proposed method as compared to Dice score of 83.22% obtained from the intra observer study. The proposed model could be used for the automatic segmentation of myocardial border that is a very important step for accurate quantification of no-reflow, myocardial infarction, myocarditis, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, among others.
Myocardial Infarction Quantification From Late Gadolinium Enhancement MRI Using Top-hat Transforms and Neural Networks
Jan 09, 2019



Abstract:Significance: Late gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (LGE-MRI) is the gold standard technique for myocardial viability assessment. Although the technique accurately reflects the damaged tissue, there is no clinical standard for quantifying myocardial infarction (MI), demanding most algorithms to be expert dependent. Objectives and Methods: In this work a new automatic method for MI quantification from LGE-MRI is proposed. Our novel segmentation approach is devised for accurately detecting not only hyper-enhanced lesions, but also microvascular-obstructed areas. Moreover, it includes a myocardial disease detection step which extends the algorithm for working under healthy scans. The method is based on a cascade approach where firstly, diseased slices are identified by a convolutional neural network (CNN). Secondly, by means of morphological operations a fast coarse scar segmentation is obtained. Thirdly, the segmentation is refined by a boundary-voxel reclassification strategy using an ensemble of CNNs. For its validation, reproducibility and further comparison against other methods, we tested the method on a big multi-field expert annotated LGE-MRI database including healthy and diseased cases. Results and Conclusion: In an exhaustive comparison against nine reference algorithms, the proposal achieved state-of-the-art segmentation performances and showed to be the only method agreeing in volumetric scar quantification with the expert delineations. Moreover, the method was able to reproduce the intra- and inter-observer variability ranges. It is concluded that the method could suitably be transferred to clinical scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge