Alexandra Gallyas-Sanhueza
LoFi User Scheduling for Multiuser MIMO Wireless Systems
Jan 08, 2024



Abstract:We propose new low-fidelity (LoFi) user equipment (UE) scheduling algorithms for multiuser multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) wireless communication systems. The proposed methods rely on an efficient guess-and-check procedure that, given an objective function, performs paired comparisons between random subsets of UEs that should be scheduled in certain time slots. The proposed LoFi scheduling methods are computationally efficient, highly parallelizable, and gradient-free, which enables the use of almost arbitrary, non-differentiable objective functions. System simulations in a millimeter-wave (mmWave) multiuser MIMO scenario demonstrate that the proposed LoFi schedulers outperform a range of state-of-the-art user scheduling algorithms in terms of bit error-rate and/or computational complexity.
Low-Complexity Blind Parameter Estimation in Wireless Systems with Noisy Sparse Signals
Feb 27, 2023Abstract:Baseband processing algorithms often require knowledge of the noise power, signal power, or signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In practice, these parameters are typically unknown and must be estimated. Furthermore, the mean-square error (MSE) is a desirable metric to be minimized in a variety of estimation and signal recovery algorithms. However, the MSE cannot directly be used as it depends on the true signal that is generally unknown to the estimator. In this paper, we propose novel blind estimators for the average noise power, average receive signal power, SNR, and MSE. The proposed estimators can be computed at low complexity and solely rely on the large-dimensional and sparse nature of the processed data. Our estimators can be used (i) to quickly track some of the key system parameters while avoiding additional pilot overhead, (ii) to design low-complexity nonparametric algorithms that require such quantities, and (iii) to accelerate more sophisticated estimation or recovery algorithms. We conduct a theoretical analysis of the proposed estimators for a Bernoulli complex Gaussian (BCG) prior, and we demonstrate their efficacy via synthetic experiments. We also provide three application examples that deviate from the BCG prior in millimeter-wave multi-antenna and cell-free wireless systems for which we develop nonparametric denoising algorithms that improve channel-estimation accuracy with a performance comparable to denoisers that assume perfect knowledge of the system parameters.
Hardware-Aware Beamspace Precoding for All-Digital mmWave Massive MU-MIMO
Aug 13, 2021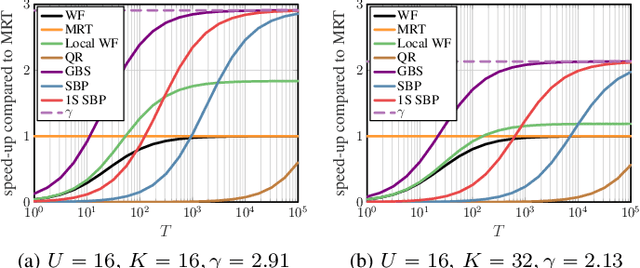
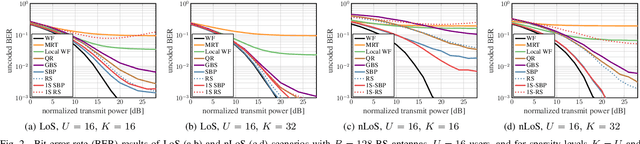

Abstract:Massive multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MU-MIMO) wireless systems operating at millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies enable simultaneous wideband data transmission to a large number of users. In order to reduce the complexity of MU precoding in all-digital basestation architectures, we propose a two-stage precoding architecture that first performs precoding using a sparse matrix in the beamspace domain, followed by an inverse fast Fourier transform that converts the result to the antenna domain. The sparse precoding matrix requires a small number of multipliers and enables regular hardware architectures, which allows the design of hardware-efficient all-digital precoders. Simulation results demonstrate that our methods approach the error-rate of conventional Wiener filter precoding with more than 2x reduced complexity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge