Alexander Steen
An Encoding of Abstract Dialectical Frameworks into Higher-Order Logic
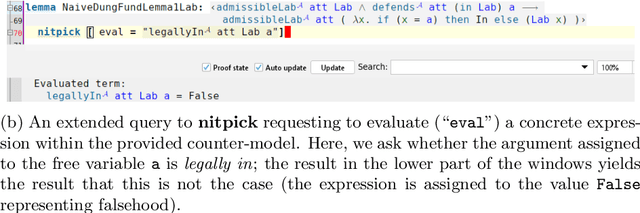
Dec 08, 2023Abstract:An approach for encoding abstract dialectical frameworks and their semantics into classical higher-order logic is presented. Important properties and semantic relationships are formally encoded and proven using the proof assistant Isabelle/HOL. This approach allows for the computer-assisted analysis of abstract dialectical frameworks using automated and interactive reasoning tools within a uniform logic environment. Exemplary applications include the formal analysis and verification of meta-theoretical properties, and the generation of interpretations and extensions under specific semantic constraints.
Solving QMLTP Problems by Translation to Higher-order Logic
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:This paper describes an evaluation of Automated Theorem Proving (ATP) systems on problems taken from the QMLTP library of first-order modal logic problems. Principally, the problems are translated to higher-order logic in the TPTP languages using an embedding approach, and solved using higher-order logic ATP systems. Additionally, the results from native modal logic ATP systems are considered, and compared with those from the embedding approach. The conclusions are that (i) The embedding process is reliable and successful. (ii) The choice of backend ATP system can significantly impact the performance of the embedding approach. (iii) Native modal logic ATP systems outperform the embedding approach. (iv) The embedding approach can cope with a wider range modal logics than the native modal systems considered.
Bridging between LegalRuleML and TPTP for Automated Normative Reasoning (extended version)
Sep 12, 2022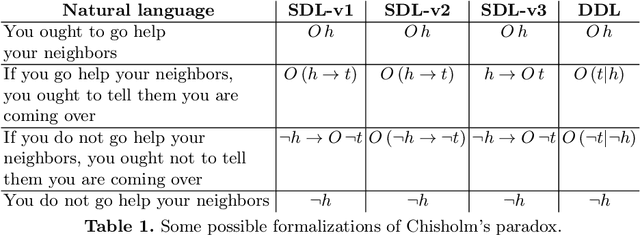
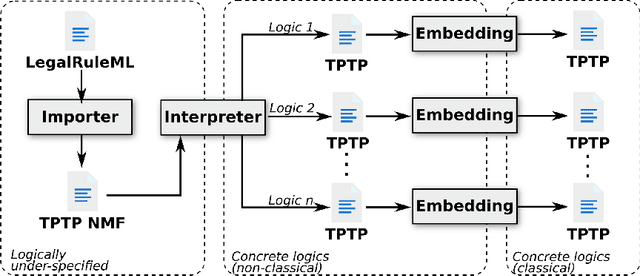

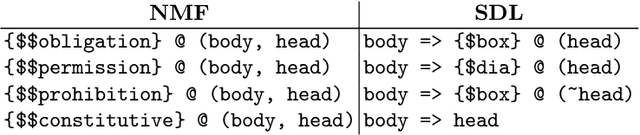
Abstract:LegalRuleML is a comprehensive XML-based representation framework for modeling and exchanging normative rules. The TPTP input and output formats, on the other hand, are general-purpose standards for the interaction with automated reasoning systems. In this paper we provide a bridge between the two communities by (i) defining a logic-pluralistic normative reasoning language based on the TPTP format, (ii) providing a translation scheme between relevant fragments of LegalRuleML and this language, and (iii) proposing a flexible architecture for automated normative reasoning based on this translation. We exemplarily instantiate and demonstrate the approach with three different normative logics.
Who Finds the Short Proof? An Exploration of Variants of Boolos' Curious Inference using Higher-order Automated Theorem Provers
Aug 22, 2022Abstract:This paper reports on an exploration of variants of Boolos' curious inference, using higher-order automated theorem provers (ATPs). Surprisingly, only a single shorthand notation had to be provided by hand. All higher-order lemmas required for obtaining short proof are automatically discovered by the ATPs. Given the observations and suggestions in this paper, full proof automation of Boolos' example on the speedup of proof lengths, and related examples, now seems to be within reach for higher-order ATPs.
An Extensible Logic Embedding Tool for Lightweight Non-Classical Reasoning
Mar 23, 2022

Abstract:The logic embedding tool provides a procedural encoding for non-classical reasoning problems into classical higher-order logic. It is extensible and can support an increasing number of different non-classical logics as reasoning targets. When used as a pre-processor or library for higher-order theorem provers, the tool admits off-the-shelf automation for logics for which otherwise few to none provers are currently available.
Automated Reasoning in Non-classical Logics in the TPTP World
Feb 20, 2022
Abstract:Non-classical logics are used in a wide spectrum of disciplines, including artificial intelligence, computer science, mathematics, and philosophy. The de-facto standard infrastructure for automated theorem proving, the TPTP World, currently supports only classical logics. Similar standards for non-classical logic reasoning do not exist (yet). This hampers practical development of reasoning systems, and limits their interoperability and application. This paper describes the latest extension of the TPTP World, which provides languages and infrastructure for reasoning in non-classical logics. The extensions integrate seamlessly with the existing TPTP World.
A Formalisation of Abstract Argumentation in Higher-Order Logic
Oct 18, 2021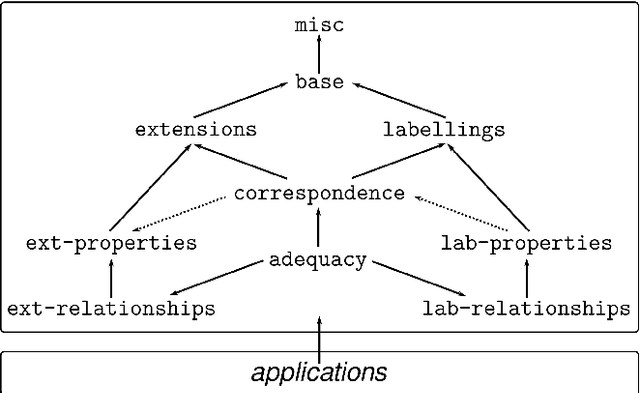
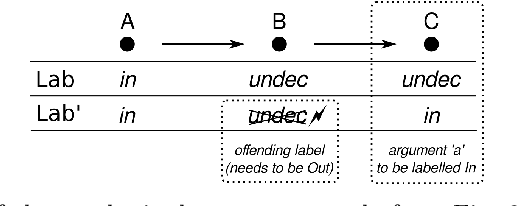
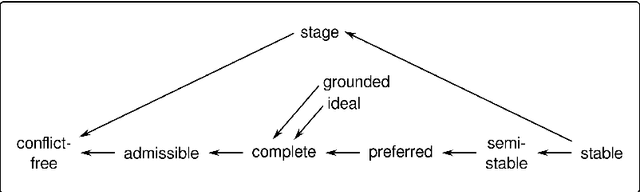
Abstract:We present an approach for representing abstract argumentation frameworks based on an encoding into classical higher-order logic. This provides a uniform framework for computer-assisted assessment of abstract argumentation frameworks using interactive and automated reasoning tools. This enables the formal analysis and verification of meta-theoretical properties as well as the flexible generation of extensions and labellings with respect to well-known argumentation semantics.
On Reductions of Hintikka Sets for Higher-Order Logic
Apr 16, 2020Abstract:Steen's (2018) Hintikka set properties for Church's type theory based on primitive equality are reduced to the Hintikka set properties of Benzm\"uller, Brown and Kohlhase (2004) which are based on the logical connectives negation, disjunction and universal quantification.
The NAI Suite -- Drafting and Reasoning over Legal Texts
Oct 15, 2019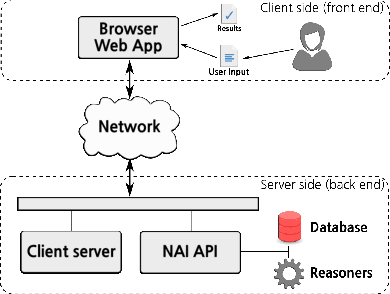

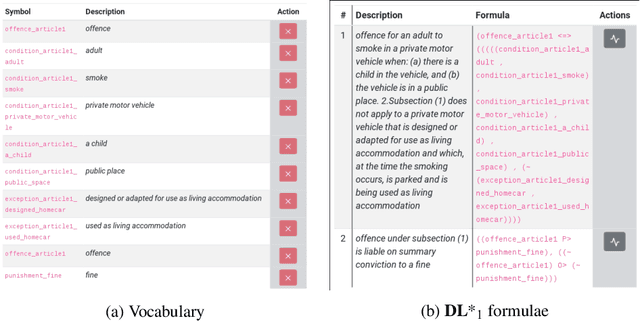

Abstract:A prototype for automated reasoning over legal texts, called NAI, is presented. As an input, NAI accepts formalized logical representations of such legal texts that can be created and curated using an integrated annotation interface. The prototype supports automated reasoning over the given text representation and multiple quality assurance procedures. The pragmatics of the NAI suite as well its feasibility in practical applications is studied on a fragment of the Smoking Prohibition (Children in Motor Vehicles) (Scotland) Act 2016 of the Scottish Parliament.
Extensional Higher-Order Paramodulation in Leo-III
Jul 26, 2019



Abstract:Leo-III is an automated theorem prover for extensional type theory with Henkin semantics and choice. Reasoning with primitive equality is enabled by adapting paramodulation-based proof search to higher-order logic. The prover may cooperate with multiple external specialist reasoning systems such as first-order provers and SMT solvers. Leo-III is compatible with the TPTP/TSTP framework for input formats, reporting results and proofs, and standardized communication between reasoning systems, enabling e.g. proof reconstruction from within proof assistants such as Isabelle/HOL. Leo-III supports reasoning in polymorphic first-order and higher-order logic, in all normal quantified modal logics, as well as in different deontic logics. Its development had initiated the ongoing extension of the TPTP infrastructure to reasoning within non-classical logics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge