Alessio Mascolini
Neuro-symbolic Empowered Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models for Real-time Anomaly Detection in Industry 4.0
Jul 18, 2023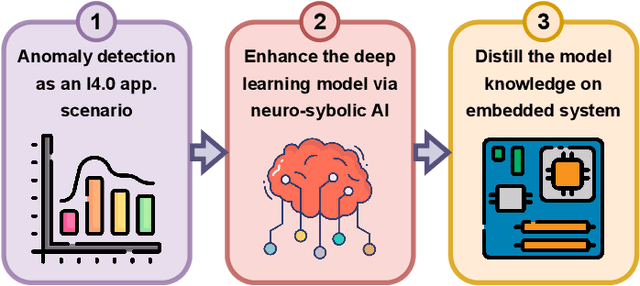
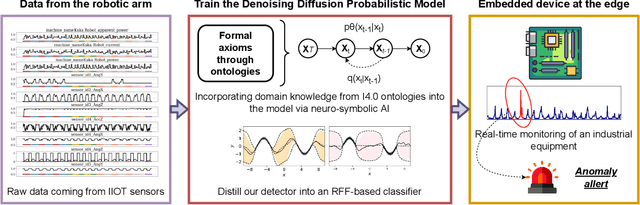
Abstract:Industry 4.0 involves the integration of digital technologies, such as IoT, Big Data, and AI, into manufacturing and industrial processes to increase efficiency and productivity. As these technologies become more interconnected and interdependent, Industry 4.0 systems become more complex, which brings the difficulty of identifying and stopping anomalies that may cause disturbances in the manufacturing process. This paper aims to propose a diffusion-based model for real-time anomaly prediction in Industry 4.0 processes. Using a neuro-symbolic approach, we integrate industrial ontologies in the model, thereby adding formal knowledge on smart manufacturing. Finally, we propose a simple yet effective way of distilling diffusion models through Random Fourier Features for deployment on an embedded system for direct integration into the manufacturing process. To the best of our knowledge, this approach has never been explored before.
Exploiting generative self-supervised learning for the assessment of biological images with lack of annotations: a COVID-19 case-study
Jul 26, 2021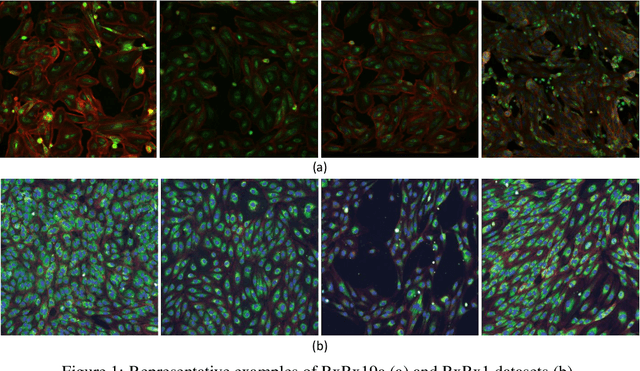
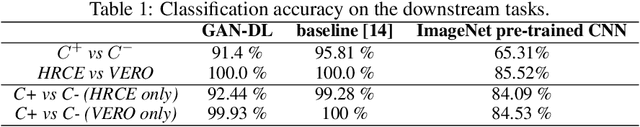
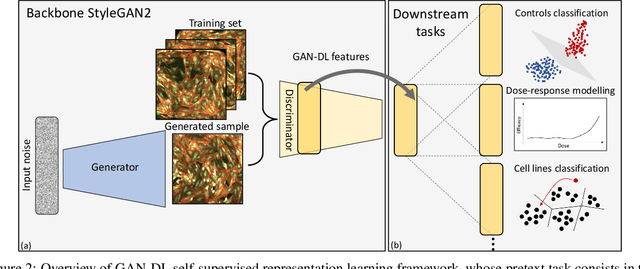
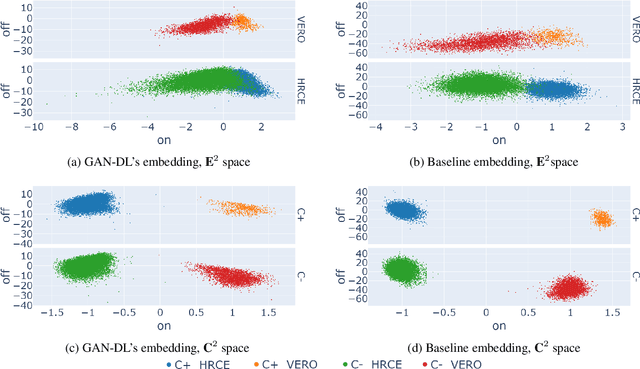
Abstract:Computer-aided analysis of biological images typically requires extensive training on large-scale annotated datasets, which is not viable in many situations. In this paper we present GAN-DL, a Discriminator Learner based on the StyleGAN2 architecture, which we employ for self-supervised image representation learning in the case of fluorescent biological images. We show that Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Networks combined with linear Support Vector Machines enable high-throughput compound screening based on raw images. We demonstrate this by classifying active and inactive compounds tested for the inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection in VERO and HRCE cell lines. In contrast to previous methods, our deep learning based approach does not require any annotation besides the one that is normally collected during the sample preparation process. We test our technique on the RxRx19a Sars-CoV-2 image collection. The dataset consists of fluorescent images that were generated to assess the ability of regulatory-approved or in late-stage clinical trials compound to modulate the in vitro infection from SARS-CoV-2 in both VERO and HRCE cell lines. We show that our technique can be exploited not only for classification tasks, but also to effectively derive a dose response curve for the tested treatments, in a self-supervised manner. Lastly, we demonstrate its generalization capabilities by successfully addressing a zero-shot learning task, consisting in the categorization of four different cell types of the RxRx1 fluorescent images collection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge