Aleksei Gonnochenko
Comparison of modern open-source visual SLAM approaches
Aug 03, 2021



Abstract:SLAM is one of the most fundamental areas of research in robotics and computer vision. State of the art solutions has advanced significantly in terms of accuracy and stability. Unfortunately, not all the approaches are available as open-source solutions and free to use. The results of some of them are difficult to reproduce, and there is a lack of comparison on common datasets. In our work, we make a comparative analysis of state of the art open-source methods. We assess the algorithms based on accuracy, computational performance, robustness, and fault tolerance. Moreover, we present a comparison of datasets as well as an analysis of algorithms from a practical point of view. The findings of the work raise several crucial questions for SLAM researchers.
Coinbot: Intelligent Robotic Coin Bag Manipulation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning And Machine Teaching
Dec 02, 2020
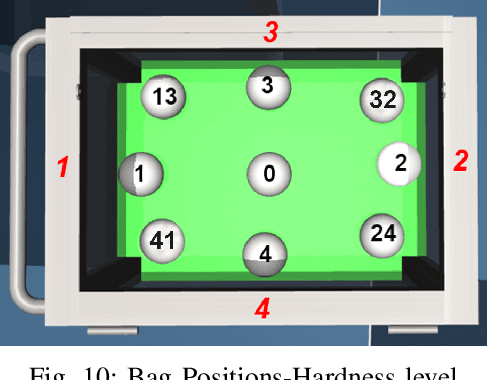
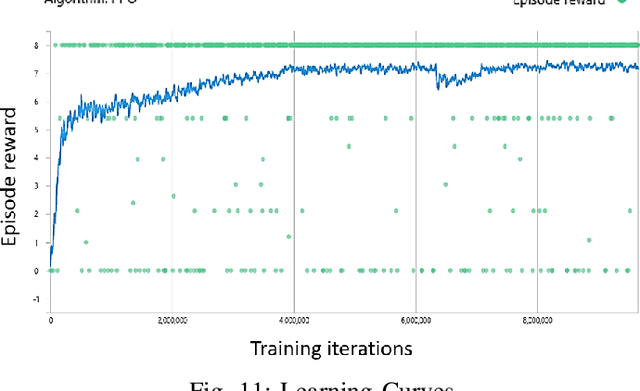
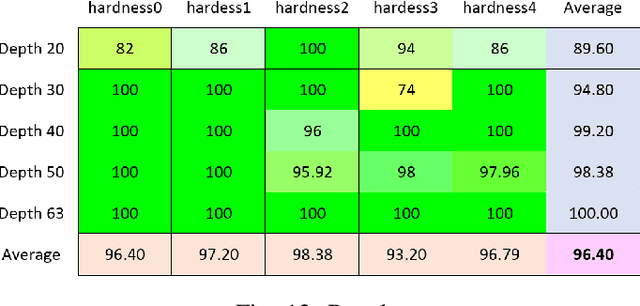
Abstract:Given the laborious difficulty of moving heavy bags of physical currency in the cash center of the bank, there is a large demand for training and deploying safe autonomous systems capable of conducting such tasks in a collaborative workspace. However, the deformable properties of the bag along with the large quantity of rigid-body coins contained within it, significantly increases the challenges of bag detection, grasping and manipulation by a robotic gripper and arm. In this paper, we apply deep reinforcement learning and machine learning techniques to the task of controlling a collaborative robot to automate the unloading of coin bags from a trolley. To accomplish the task-specific process of gripping flexible materials like coin bags where the center of the mass changes during manipulation, a special gripper was implemented in simulation and designed in physical hardware. Leveraging a depth camera and object detection using deep learning, a bag detection and pose estimation has been done for choosing the optimal point of grasping. An intelligent approach based on deep reinforcement learning has been introduced to propose the best configuration of the robot end-effector to maximize successful grasping. A boosted motion planning is utilized to increase the speed of motion planning during robot operation. Real-world trials with the proposed pipeline have demonstrated success rates over 96\% in a real-world setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge