Aleksandr Artemenkov
NUQ: Nonparametric Uncertainty Quantification for Deterministic Neural Networks
Feb 07, 2022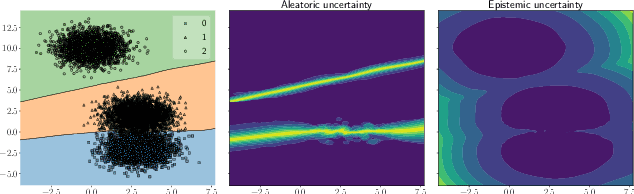
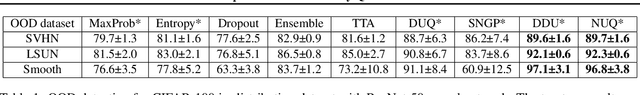
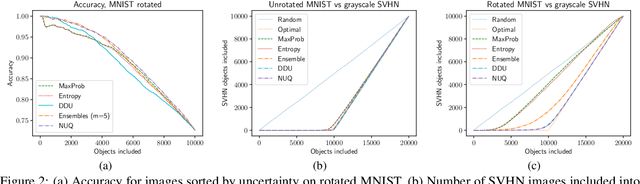

Abstract:This paper proposes a fast and scalable method for uncertainty quantification of machine learning models' predictions. First, we show the principled way to measure the uncertainty of predictions for a classifier based on Nadaraya-Watson's nonparametric estimate of the conditional label distribution. Importantly, the approach allows to disentangle explicitly aleatoric and epistemic uncertainties. The resulting method works directly in the feature space. However, one can apply it to any neural network by considering an embedding of the data induced by the network. We demonstrate the strong performance of the method in uncertainty estimation tasks on a variety of real-world image datasets, such as MNIST, SVHN, CIFAR-100 and several versions of ImageNet.
NCVis: Noise Contrastive Approach for Scalable Visualization
Jan 30, 2020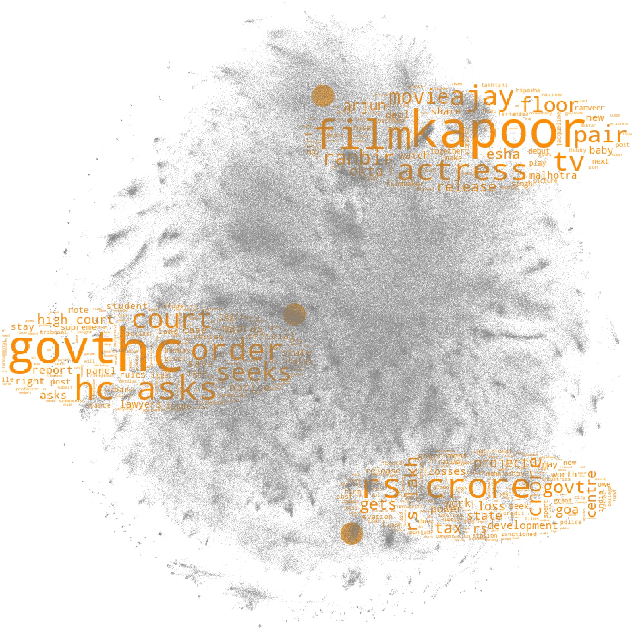

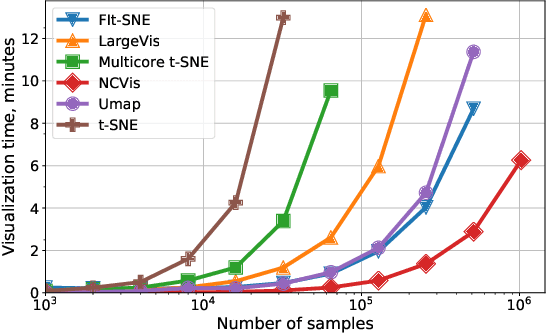

Abstract:Modern methods for data visualization via dimensionality reduction, such as t-SNE, usually have performance issues that prohibit their application to large amounts of high-dimensional data. In this work, we propose NCVis -- a high-performance dimensionality reduction method built on a sound statistical basis of noise contrastive estimation. We show that NCVis outperforms state-of-the-art techniques in terms of speed while preserving the representation quality of other methods. In particular, the proposed approach successfully proceeds a large dataset of more than 1 million news headlines in several minutes and presents the underlying structure in a human-readable way. Moreover, it provides results consistent with classical methods like t-SNE on more straightforward datasets like images of hand-written digits. We believe that the broader usage of such software can significantly simplify the large-scale data analysis and lower the entry barrier to this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge