Alain Riou
Zero-shot Musical Stem Retrieval with Joint-Embedding Predictive Architectures
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we tackle the task of musical stem retrieval. Given a musical mix, it consists in retrieving a stem that would fit with it, i.e., that would sound pleasant if played together. To do so, we introduce a new method based on Joint-Embedding Predictive Architectures, where an encoder and a predictor are jointly trained to produce latent representations of a context and predict latent representations of a target. In particular, we design our predictor to be conditioned on arbitrary instruments, enabling our model to perform zero-shot stem retrieval. In addition, we discover that pretraining the encoder using contrastive learning drastically improves the model's performance. We validate the retrieval performances of our model using the MUSDB18 and MoisesDB datasets. We show that it significantly outperforms previous baselines on both datasets, showcasing its ability to support more or less precise (and possibly unseen) conditioning. We also evaluate the learned embeddings on a beat tracking task, demonstrating that they retain temporal structure and local information.
Stem-JEPA: A Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture for Musical Stem Compatibility Estimation
Aug 05, 2024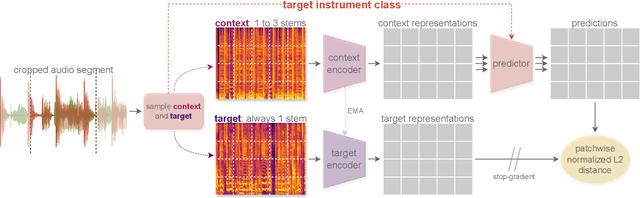
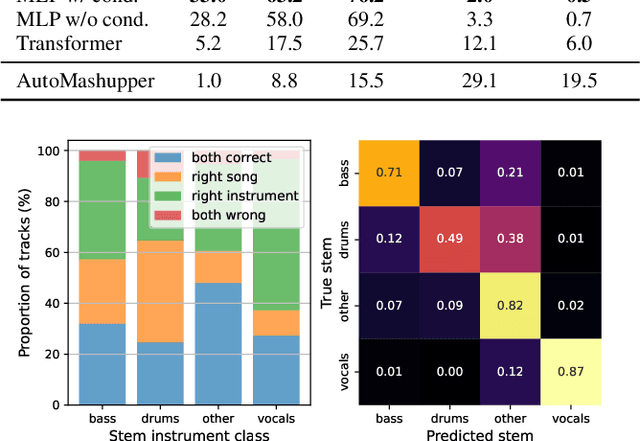
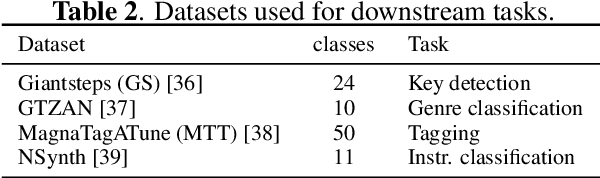
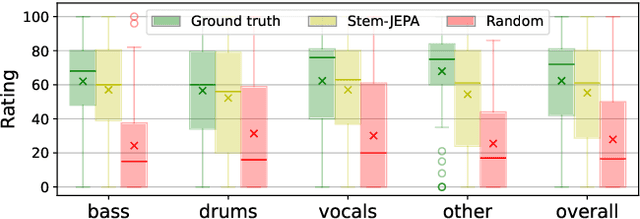
Abstract:This paper explores the automated process of determining stem compatibility by identifying audio recordings of single instruments that blend well with a given musical context. To tackle this challenge, we present Stem-JEPA, a novel Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (JEPA) trained on a multi-track dataset using a self-supervised learning approach. Our model comprises two networks: an encoder and a predictor, which are jointly trained to predict the embeddings of compatible stems from the embeddings of a given context, typically a mix of several instruments. Training a model in this manner allows its use in estimating stem compatibility - retrieving, aligning, or generating a stem to match a given mix - or for downstream tasks such as genre or key estimation, as the training paradigm requires the model to learn information related to timbre, harmony, and rhythm. We evaluate our model's performance on a retrieval task on the MUSDB18 dataset, testing its ability to find the missing stem from a mix and through a subjective user study. We also show that the learned embeddings capture temporal alignment information and, finally, evaluate the representations learned by our model on several downstream tasks, highlighting that they effectively capture meaningful musical features.
Investigating Design Choices in Joint-Embedding Predictive Architectures for General Audio Representation Learning
May 14, 2024


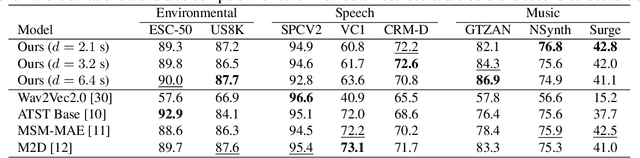
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of self-supervised general-purpose audio representation learning. We explore the use of Joint-Embedding Predictive Architectures (JEPA) for this task, which consists of splitting an input mel-spectrogram into two parts (context and target), computing neural representations for each, and training the neural network to predict the target representations from the context representations. We investigate several design choices within this framework and study their influence through extensive experiments by evaluating our models on various audio classification benchmarks, including environmental sounds, speech and music downstream tasks. We focus notably on which part of the input data is used as context or target and show experimentally that it significantly impacts the model's quality. In particular, we notice that some effective design choices in the image domain lead to poor performance on audio, thus highlighting major differences between these two modalities.
PESTO: Pitch Estimation with Self-supervised Transposition-equivariant Objective
Sep 05, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of pitch estimation using Self Supervised Learning (SSL). The SSL paradigm we use is equivariance to pitch transposition, which enables our model to accurately perform pitch estimation on monophonic audio after being trained only on a small unlabeled dataset. We use a lightweight ($<$ 30k parameters) Siamese neural network that takes as inputs two different pitch-shifted versions of the same audio represented by its Constant-Q Transform. To prevent the model from collapsing in an encoder-only setting, we propose a novel class-based transposition-equivariant objective which captures pitch information. Furthermore, we design the architecture of our network to be transposition-preserving by introducing learnable Toeplitz matrices. We evaluate our model for the two tasks of singing voice and musical instrument pitch estimation and show that our model is able to generalize across tasks and datasets while being lightweight, hence remaining compatible with low-resource devices and suitable for real-time applications. In particular, our results surpass self-supervised baselines and narrow the performance gap between self-supervised and supervised methods for pitch estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge