Ajay Chawda
Unsupervised Anomaly Detection for Auditing Data and Impact of Categorical Encodings
Oct 26, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the Vehicle Claims dataset, consisting of fraudulent insurance claims for automotive repairs. The data belongs to the more broad category of Auditing data, which includes also Journals and Network Intrusion data. Insurance claim data are distinctively different from other auditing data (such as network intrusion data) in their high number of categorical attributes. We tackle the common problem of missing benchmark datasets for anomaly detection: datasets are mostly confidential, and the public tabular datasets do not contain relevant and sufficient categorical attributes. Therefore, a large-sized dataset is created for this purpose and referred to as Vehicle Claims (VC) dataset. The dataset is evaluated on shallow and deep learning methods. Due to the introduction of categorical attributes, we encounter the challenge of encoding them for the large dataset. As One Hot encoding of high cardinal dataset invokes the "curse of dimensionality", we experiment with GEL encoding and embedding layer for representing categorical attributes. Our work compares competitive learning, reconstruction-error, density estimation and contrastive learning approaches for Label, One Hot, GEL encoding and embedding layer to handle categorical values.
Dimensionality of datasets in object detection networks
Oct 13, 2022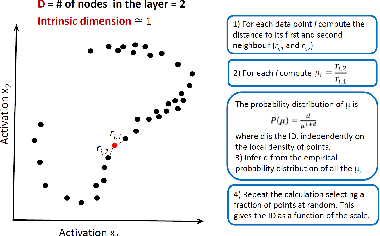
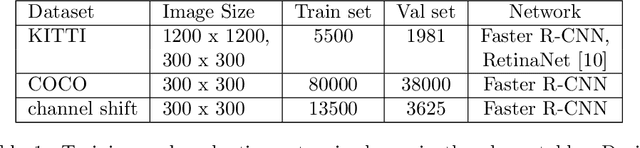
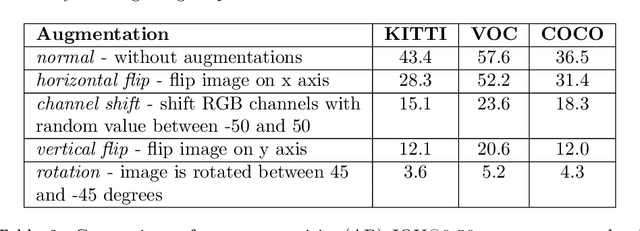
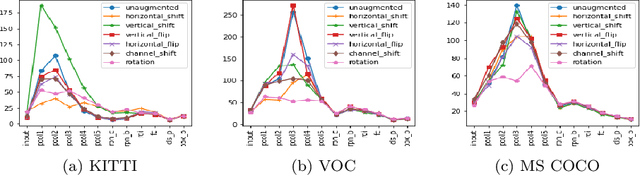
Abstract:In recent years, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are used in a large number of tasks in computer vision. One of them is object detection for autonomous driving. Although CNNs are used widely in many areas, what happens inside the network is still unexplained on many levels. Our goal is to determine the effect of Intrinsic dimension (i.e. minimum number of parameters required to represent data) in different layers on the accuracy of object detection network for augmented data sets. Our investigation determines that there is difference between the representation of normal and augmented data during feature extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge