Airlie Chapman
An Event-Triggered Framework for Trust-Mediated Human-Autonomy Interaction
Dec 12, 2024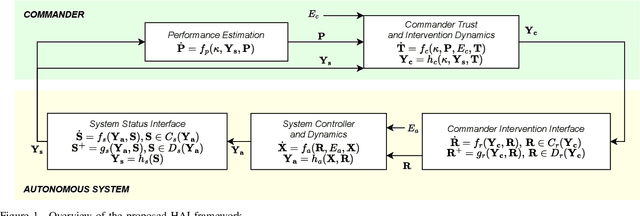
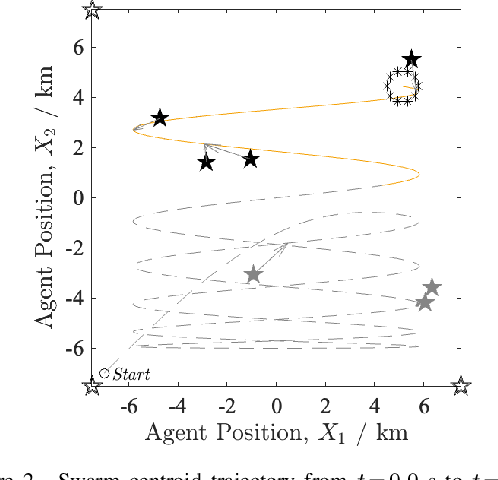
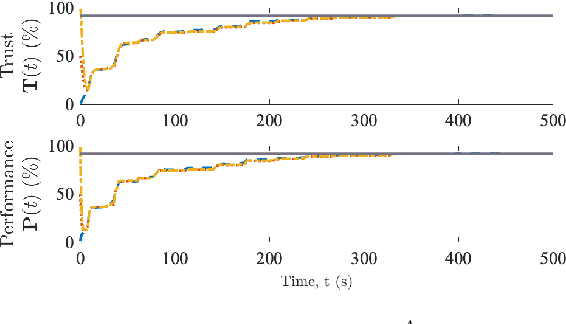
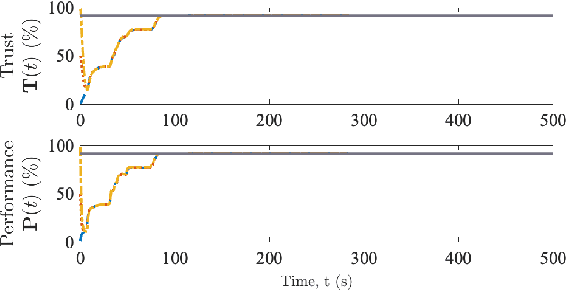
Abstract:Inspired by the increased cooperation between humans and autonomous systems, we present a new hybrid systems framework capturing the interconnected dynamics underlying these interactions. The framework accommodates models arising from both the autonomous systems and cognitive psychology literature in order to represent key elements such as human trust in the autonomous system. The intermittent nature of human interactions are incorporated by asynchronous event-triggered sampling at the framework's human-autonomous system interfaces. We illustrate important considerations for tuning framework parameters by investigating a practical application to an autonomous robotic swarm search and rescue scenario. In this way, we demonstrate how the proposed framework may assist in designing more efficient and effective interactions between humans and autonomous systems.
Mitigating Challenges of the Space Environment for Onboard Artificial Intelligence: Design Overview of the Imaging Payload on SpIRIT
Apr 12, 2024



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) and autonomous edge computing in space are emerging areas of interest to augment capabilities of nanosatellites, where modern sensors generate orders of magnitude more data than can typically be transmitted to mission control. Here, we present the hardware and software design of an onboard AI subsystem hosted on SpIRIT. The system is optimised for on-board computer vision experiments based on visible light and long wave infrared cameras. This paper highlights the key design choices made to maximise the robustness of the system in harsh space conditions, and their motivation relative to key mission requirements, such as limited compute resources, resilience to cosmic radiation, extreme temperature variations, distribution shifts, and very low transmission bandwidths. The payload, called Loris, consists of six visible light cameras, three infrared cameras, a camera control board and a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) system-on-module. Loris enables the execution of AI models with on-orbit fine-tuning as well as a next-generation image compression algorithm, including progressive coding. This innovative approach not only enhances the data processing capabilities of nanosatellites but also lays the groundwork for broader applications to remote sensing from space.
Online Distributed Optimization on Dynamic Networks
Dec 22, 2014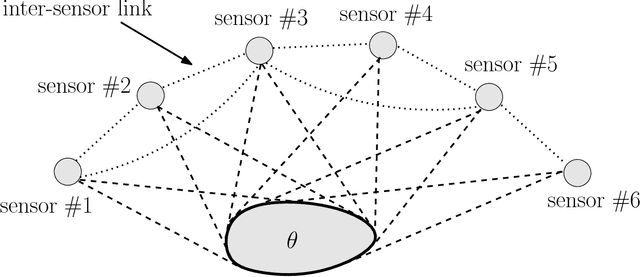

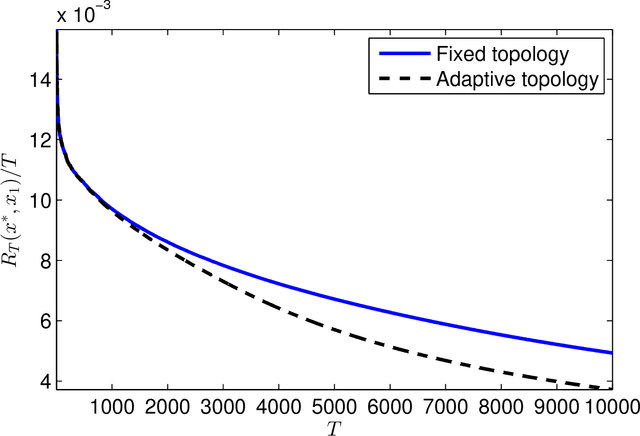
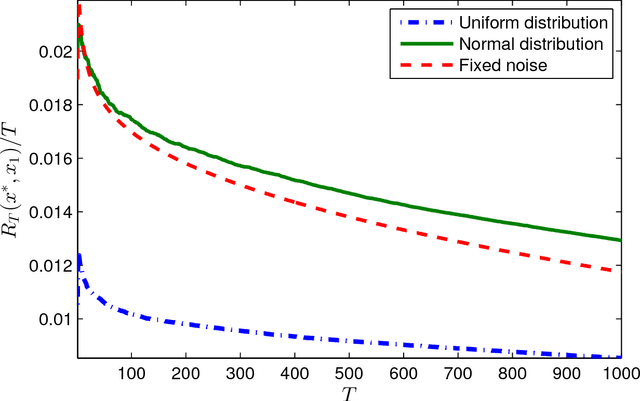
Abstract:This paper presents a distributed optimization scheme over a network of agents in the presence of cost uncertainties and over switching communication topologies. Inspired by recent advances in distributed convex optimization, we propose a distributed algorithm based on a dual sub-gradient averaging. The objective of this algorithm is to minimize a cost function cooperatively. Furthermore, the algorithm changes the weights on the communication links in the network to adapt to varying reliability of neighboring agents. A convergence rate analysis as a function of the underlying network topology is then presented, followed by simulation results for representative classes of sensor networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge