Ailong Ma
EarthVL: A Progressive Earth Vision-Language Understanding and Generation Framework
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Earth vision has achieved milestones in geospatial object recognition but lacks exploration in object-relational reasoning, limiting comprehensive scene understanding. To address this, a progressive Earth vision-language understanding and generation framework is proposed, including a multi-task dataset (EarthVLSet) and a semantic-guided network (EarthVLNet). Focusing on city planning applications, EarthVLSet includes 10.9k sub-meter resolution remote sensing images, land-cover masks, and 761.5k textual pairs involving both multiple-choice and open-ended visual question answering (VQA) tasks. In an object-centric way, EarthVLNet is proposed to progressively achieve semantic segmentation, relational reasoning, and comprehensive understanding. The first stage involves land-cover segmentation to generate object semantics for VQA guidance. Guided by pixel-wise semantics, the object awareness based large language model (LLM) performs relational reasoning and knowledge summarization to generate the required answers. As for optimization, the numerical difference loss is proposed to dynamically add difference penalties, addressing the various objects' statistics. Three benchmarks, including semantic segmentation, multiple-choice, and open-ended VQA demonstrated the superiorities of EarthVLNet, yielding three future directions: 1) segmentation features consistently enhance VQA performance even in cross-dataset scenarios; 2) multiple-choice tasks show greater sensitivity to the vision encoder than to the language decoder; and 3) open-ended tasks necessitate advanced vision encoders and language decoders for an optimal performance. We believe this dataset and method will provide a beneficial benchmark that connects ''image-mask-text'', advancing geographical applications for Earth vision.
Single-Temporal Supervised Learning for Universal Remote Sensing Change Detection
Jun 22, 2024Abstract:Bitemporal supervised learning paradigm always dominates remote sensing change detection using numerous labeled bitemporal image pairs, especially for high spatial resolution (HSR) remote sensing imagery. However, it is very expensive and labor-intensive to label change regions in large-scale bitemporal HSR remote sensing image pairs. In this paper, we propose single-temporal supervised learning (STAR) for universal remote sensing change detection from a new perspective of exploiting changes between unpaired images as supervisory signals. STAR enables us to train a high-accuracy change detector only using unpaired labeled images and can generalize to real-world bitemporal image pairs. To demonstrate the flexibility and scalability of STAR, we design a simple yet unified change detector, termed ChangeStar2, capable of addressing binary change detection, object change detection, and semantic change detection in one architecture. ChangeStar2 achieves state-of-the-art performances on eight public remote sensing change detection datasets, covering above two supervised settings, multiple change types, multiple scenarios. The code is available at https://github.com/Z-Zheng/pytorch-change-models.
EarthVQA: Towards Queryable Earth via Relational Reasoning-Based Remote Sensing Visual Question Answering
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:Earth vision research typically focuses on extracting geospatial object locations and categories but neglects the exploration of relations between objects and comprehensive reasoning. Based on city planning needs, we develop a multi-modal multi-task VQA dataset (EarthVQA) to advance relational reasoning-based judging, counting, and comprehensive analysis. The EarthVQA dataset contains 6000 images, corresponding semantic masks, and 208,593 QA pairs with urban and rural governance requirements embedded. As objects are the basis for complex relational reasoning, we propose a Semantic OBject Awareness framework (SOBA) to advance VQA in an object-centric way. To preserve refined spatial locations and semantics, SOBA leverages a segmentation network for object semantics generation. The object-guided attention aggregates object interior features via pseudo masks, and bidirectional cross-attention further models object external relations hierarchically. To optimize object counting, we propose a numerical difference loss that dynamically adds difference penalties, unifying the classification and regression tasks. Experimental results show that SOBA outperforms both advanced general and remote sensing methods. We believe this dataset and framework provide a strong benchmark for Earth vision's complex analysis. The project page is at https://Junjue-Wang.github.io/homepage/EarthVQA.
Scalable Multi-Temporal Remote Sensing Change Data Generation via Simulating Stochastic Change Process
Sep 29, 2023Abstract:Understanding the temporal dynamics of Earth's surface is a mission of multi-temporal remote sensing image analysis, significantly promoted by deep vision models with its fuel -- labeled multi-temporal images. However, collecting, preprocessing, and annotating multi-temporal remote sensing images at scale is non-trivial since it is expensive and knowledge-intensive. In this paper, we present a scalable multi-temporal remote sensing change data generator via generative modeling, which is cheap and automatic, alleviating these problems. Our main idea is to simulate a stochastic change process over time. We consider the stochastic change process as a probabilistic semantic state transition, namely generative probabilistic change model (GPCM), which decouples the complex simulation problem into two more trackable sub-problems, \ie, change event simulation and semantic change synthesis. To solve these two problems, we present the change generator (Changen), a GAN-based GPCM, enabling controllable object change data generation, including customizable object property, and change event. The extensive experiments suggest that our Changen has superior generation capability, and the change detectors with Changen pre-training exhibit excellent transferability to real-world change datasets.
AutoLC: Search Lightweight and Top-Performing Architecture for Remote Sensing Image Land-Cover Classification
May 11, 2022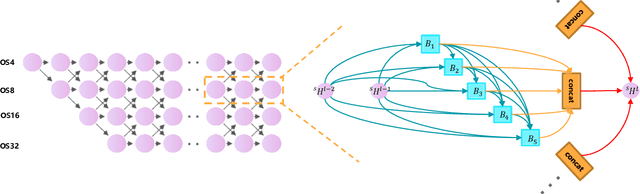
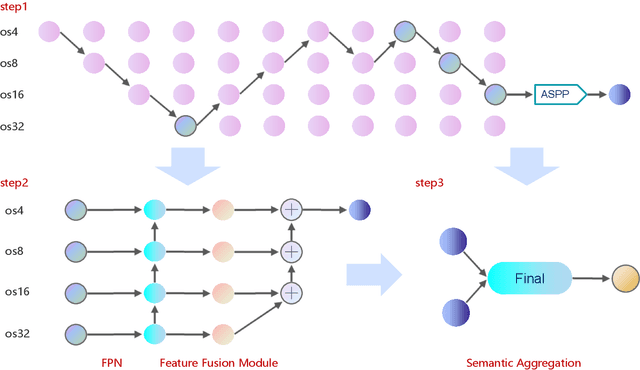
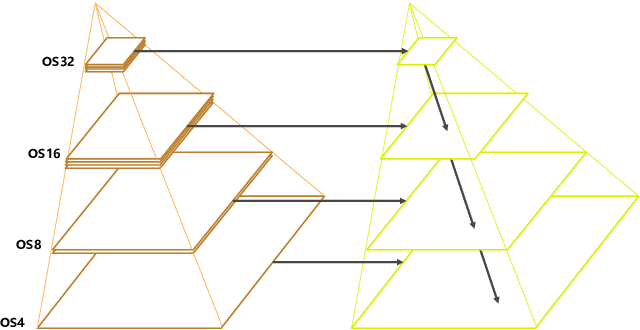

Abstract:Land-cover classification has long been a hot and difficult challenge in remote sensing community. With massive High-resolution Remote Sensing (HRS) images available, manually and automatically designed Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have already shown their great latent capacity on HRS land-cover classification in recent years. Especially, the former can achieve better performance while the latter is able to generate lightweight architecture. Unfortunately, they both have shortcomings. On the one hand, because manual CNNs are almost proposed for natural image processing, it becomes very redundant and inefficient to process HRS images. On the other hand, nascent Neural Architecture Search (NAS) techniques for dense prediction tasks are mainly based on encoder-decoder architecture, and just focus on the automatic design of the encoder, which makes it still difficult to recover the refined mapping when confronting complicated HRS scenes. To overcome their defects and tackle the HRS land-cover classification problems better, we propose AutoLC which combines the advantages of two methods. First, we devise a hierarchical search space and gain the lightweight encoder underlying gradient-based search strategy. Second, we meticulously design a lightweight but top-performing decoder that is adaptive to the searched encoder of itself. Finally, experimental results on the LoveDA land-cover dataset demonstrate that our AutoLC method outperforms the state-of-art manual and automatic methods with much less computational consumption.
LoveDA: A Remote Sensing Land-Cover Dataset for Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation
Oct 24, 2021



Abstract:Deep learning approaches have shown promising results in remote sensing high spatial resolution (HSR) land-cover mapping. However, urban and rural scenes can show completely different geographical landscapes, and the inadequate generalizability of these algorithms hinders city-level or national-level mapping. Most of the existing HSR land-cover datasets mainly promote the research of learning semantic representation, thereby ignoring the model transferability. In this paper, we introduce the Land-cOVEr Domain Adaptive semantic segmentation (LoveDA) dataset to advance semantic and transferable learning. The LoveDA dataset contains 5987 HSR images with 166768 annotated objects from three different cities. Compared to the existing datasets, the LoveDA dataset encompasses two domains (urban and rural), which brings considerable challenges due to the: 1) multi-scale objects; 2) complex background samples; and 3) inconsistent class distributions. The LoveDA dataset is suitable for both land-cover semantic segmentation and unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) tasks. Accordingly, we benchmarked the LoveDA dataset on eleven semantic segmentation methods and eight UDA methods. Some exploratory studies including multi-scale architectures and strategies, additional background supervision, and pseudo-label analysis were also carried out to address these challenges. The code and data are available at https://github.com/Junjue-Wang/LoveDA.
Change is Everywhere: Single-Temporal Supervised Object Change Detection in Remote Sensing Imagery
Aug 16, 2021



Abstract:For high spatial resolution (HSR) remote sensing images, bitemporal supervised learning always dominates change detection using many pairwise labeled bitemporal images. However, it is very expensive and time-consuming to pairwise label large-scale bitemporal HSR remote sensing images. In this paper, we propose single-temporal supervised learning (STAR) for change detection from a new perspective of exploiting object changes in unpaired images as supervisory signals. STAR enables us to train a high-accuracy change detector only using \textbf{unpaired} labeled images and generalize to real-world bitemporal images. To evaluate the effectiveness of STAR, we design a simple yet effective change detector called ChangeStar, which can reuse any deep semantic segmentation architecture by the ChangeMixin module. The comprehensive experimental results show that ChangeStar outperforms the baseline with a large margin under single-temporal supervision and achieves superior performance under bitemporal supervision. Code is available at https://github.com/Z-Zheng/ChangeStar
Foreground-Aware Relation Network for Geospatial Object Segmentation in High Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing Imagery
Nov 19, 2020



Abstract:Geospatial object segmentation, as a particular semantic segmentation task, always faces with larger-scale variation, larger intra-class variance of background, and foreground-background imbalance in the high spatial resolution (HSR) remote sensing imagery. However, general semantic segmentation methods mainly focus on scale variation in the natural scene, with inadequate consideration of the other two problems that usually happen in the large area earth observation scene. In this paper, we argue that the problems lie on the lack of foreground modeling and propose a foreground-aware relation network (FarSeg) from the perspectives of relation-based and optimization-based foreground modeling, to alleviate the above two problems. From perspective of relation, FarSeg enhances the discrimination of foreground features via foreground-correlated contexts associated by learning foreground-scene relation. Meanwhile, from perspective of optimization, a foreground-aware optimization is proposed to focus on foreground examples and hard examples of background during training for a balanced optimization. The experimental results obtained using a large scale dataset suggest that the proposed method is superior to the state-of-the-art general semantic segmentation methods and achieves a better trade-off between speed and accuracy. Code has been made available at: \url{https://github.com/Z-Zheng/FarSeg}.
FPGA: Fast Patch-Free Global Learning Framework for Fully End-to-End Hyperspectral Image Classification
Nov 11, 2020



Abstract:Deep learning techniques have provided significant improvements in hyperspectral image (HSI) classification. The current deep learning based HSI classifiers follow a patch-based learning framework by dividing the image into overlapping patches. As such, these methods are local learning methods, which have a high computational cost. In this paper, a fast patch-free global learning (FPGA) framework is proposed for HSI classification. In FPGA, an encoder-decoder based FCN is utilized to consider the global spatial information by processing the whole image, which results in fast inference. However, it is difficult to directly utilize the encoder-decoder based FCN for HSI classification as it always fails to converge due to the insufficiently diverse gradients caused by the limited training samples. To solve the divergence problem and maintain the abilities of FCN of fast inference and global spatial information mining, a global stochastic stratified sampling strategy is first proposed by transforming all the training samples into a stochastic sequence of stratified samples. This strategy can obtain diverse gradients to guarantee the convergence of the FCN in the FPGA framework. For a better design of FCN architecture, FreeNet, which is a fully end-to-end network for HSI classification, is proposed to maximize the exploitation of the global spatial information and boost the performance via a spectral attention based encoder and a lightweight decoder. A lateral connection module is also designed to connect the encoder and decoder, fusing the spatial details in the encoder and the semantic features in the decoder. The experimental results obtained using three public benchmark datasets suggest that the FPGA framework is superior to the patch-based framework in both speed and accuracy for HSI classification. Code has been made available at: https://github.com/Z-Zheng/FreeNet.
Hi-UCD: A Large-scale Dataset for Urban Semantic Change Detection in Remote Sensing Imagery
Nov 11, 2020


Abstract:With the acceleration of the urban expansion, urban change detection (UCD), as a significant and effective approach, can provide the change information with respect to geospatial objects for dynamical urban analysis. However, existing datasets suffer from three bottlenecks: (1) lack of high spatial resolution images; (2) lack of semantic annotation; (3) lack of long-range multi-temporal images. In this paper, we propose a large scale benchmark dataset, termed Hi-UCD. This dataset uses aerial images with a spatial resolution of 0.1 m provided by the Estonia Land Board, including three-time phases, and semantically annotated with nine classes of land cover to obtain the direction of ground objects change. It can be used for detecting and analyzing refined urban changes. We benchmark our dataset using some classic methods in binary and multi-class change detection. Experimental results show that Hi-UCD is challenging yet useful. We hope the Hi-UCD can become a strong benchmark accelerating future research.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge