Ahmed Sharshar
Bridging ASR and LLMs for Dysarthric Speech Recognition: Benchmarking Self-Supervised and Generative Approaches
Aug 11, 2025



Abstract:Speech Recognition (ASR) due to phoneme distortions and high variability. While self-supervised ASR models like Wav2Vec, HuBERT, and Whisper have shown promise, their effectiveness in dysarthric speech remains unclear. This study systematically benchmarks these models with different decoding strategies, including CTC, seq2seq, and LLM-enhanced decoding (BART,GPT-2, Vicuna). Our contributions include (1) benchmarking ASR architectures for dysarthric speech, (2) introducing LLM-based decoding to improve intelligibility, (3) analyzing generalization across datasets, and (4) providing insights into recognition errors across severity levels. Findings highlight that LLM-enhanced decoding improves dysarthric ASR by leveraging linguistic constraints for phoneme restoration and grammatical correction.
Not Only Grey Matter: OmniBrain for Robust Multimodal Classification of Alzheimer's Disease
Jul 28, 2025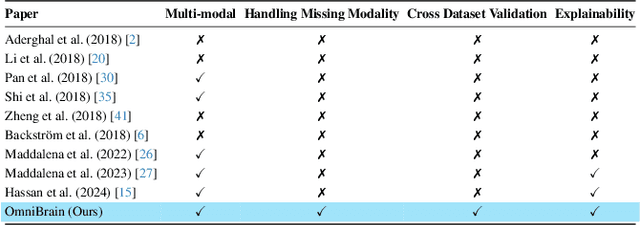
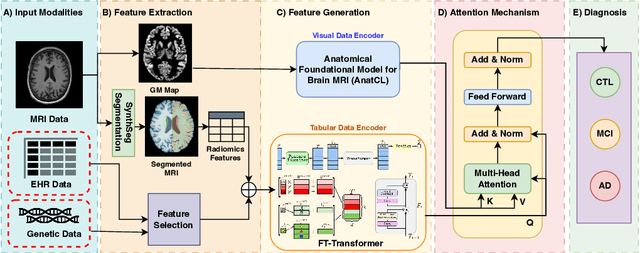
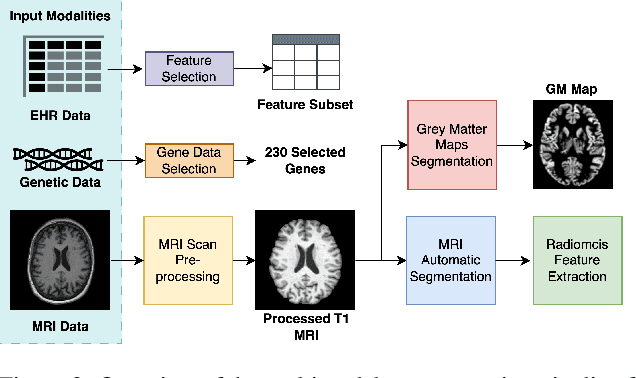
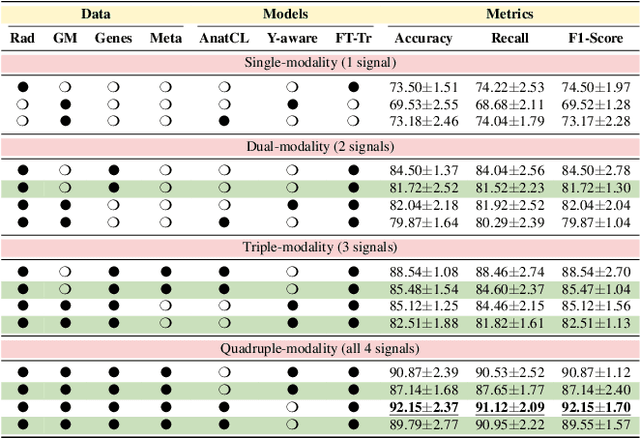
Abstract:Alzheimer's disease affects over 55 million people worldwide and is projected to more than double by 2050, necessitating rapid, accurate, and scalable diagnostics. However, existing approaches are limited because they cannot achieve clinically acceptable accuracy, generalization across datasets, robustness to missing modalities, and explainability all at the same time. This inability to satisfy all these requirements simultaneously undermines their reliability in clinical settings. We propose OmniBrain, a multimodal framework that integrates brain MRI, radiomics, gene expression, and clinical data using a unified model with cross-attention and modality dropout. OmniBrain achieves $92.2 \pm 2.4\%$accuracy on the ANMerge dataset and generalizes to the MRI-only ADNI dataset with $70.4 \pm 2.7\%$ accuracy, outperforming unimodal and prior multimodal approaches. Explainability analyses highlight neuropathologically relevant brain regions and genes, enhancing clinical trust. OmniBrain offers a robust, interpretable, and practical solution for real-world Alzheimer's diagnosis.
Vision-Language Models for Edge Networks: A Comprehensive Survey
Feb 11, 2025

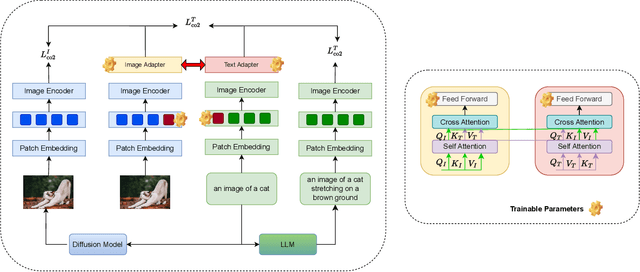
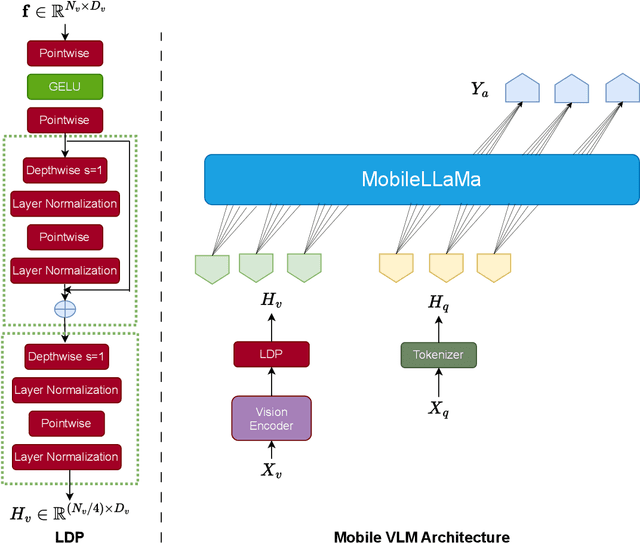
Abstract:Vision Large Language Models (VLMs) combine visual understanding with natural language processing, enabling tasks like image captioning, visual question answering, and video analysis. While VLMs show impressive capabilities across domains such as autonomous vehicles, smart surveillance, and healthcare, their deployment on resource-constrained edge devices remains challenging due to processing power, memory, and energy limitations. This survey explores recent advancements in optimizing VLMs for edge environments, focusing on model compression techniques, including pruning, quantization, knowledge distillation, and specialized hardware solutions that enhance efficiency. We provide a detailed discussion of efficient training and fine-tuning methods, edge deployment challenges, and privacy considerations. Additionally, we discuss the diverse applications of lightweight VLMs across healthcare, environmental monitoring, and autonomous systems, illustrating their growing impact. By highlighting key design strategies, current challenges, and offering recommendations for future directions, this survey aims to inspire further research into the practical deployment of VLMs, ultimately making advanced AI accessible in resource-limited settings.
PulmoFusion: Advancing Pulmonary Health with Efficient Multi-Modal Fusion
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:Traditional remote spirometry lacks the precision required for effective pulmonary monitoring. We present a novel, non-invasive approach using multimodal predictive models that integrate RGB or thermal video data with patient metadata. Our method leverages energy-efficient Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) for the regression of Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) and classification of Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV1) and Forced Vital Capacity (FVC), using lightweight CNNs to overcome SNN limitations in regression tasks. Multimodal data integration is improved with a Multi-Head Attention Layer, and we employ K-Fold validation and ensemble learning to boost robustness. Using thermal data, our SNN models achieve 92% accuracy on a breathing-cycle basis and 99.5% patient-wise. PEF regression models attain Relative RMSEs of 0.11 (thermal) and 0.26 (RGB), with an MAE of 4.52% for FEV1/FVC predictions, establishing state-of-the-art performance. Code and dataset can be found on https://github.com/ahmed-sharshar/RespiroDynamics.git
GeoLLaVA: Efficient Fine-Tuned Vision-Language Models for Temporal Change Detection in Remote Sensing
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:Detecting temporal changes in geographical landscapes is critical for applications like environmental monitoring and urban planning. While remote sensing data is abundant, existing vision-language models (VLMs) often fail to capture temporal dynamics effectively. This paper addresses these limitations by introducing an annotated dataset of video frame pairs to track evolving geographical patterns over time. Using fine-tuning techniques like Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA), quantized LoRA (QLoRA), and model pruning on models such as Video-LLaVA and LLaVA-NeXT-Video, we significantly enhance VLM performance in processing remote sensing temporal changes. Results show significant improvements, with the best performance achieving a BERT score of 0.864 and ROUGE-1 score of 0.576, demonstrating superior accuracy in describing land-use transformations.
Innovative Horizons in Aerial Imagery: LSKNet Meets DiffusionDet for Advanced Object Detection
Nov 21, 2023Abstract:In the realm of aerial image analysis, object detection plays a pivotal role, with significant implications for areas such as remote sensing, urban planning, and disaster management. This study addresses the inherent challenges in this domain, notably the detection of small objects, managing densely packed elements, and accounting for diverse orientations. We present an in-depth evaluation of an object detection model that integrates the Large Selective Kernel Network (LSKNet)as its backbone with the DiffusionDet head, utilizing the iSAID dataset for empirical analysis. Our approach encompasses the introduction of novel methodologies and extensive ablation studies. These studies critically assess various aspects such as loss functions, box regression techniques, and classification strategies to refine the model's precision in object detection. The paper details the experimental application of the LSKNet backbone in synergy with the DiffusionDet heads, a combination tailored to meet the specific challenges in aerial image object detection. The findings of this research indicate a substantial enhancement in the model's performance, especially in the accuracy-time tradeoff. The proposed model achieves a mean average precision (MAP) of approximately 45.7%, which is a significant improvement, outperforming the RCNN model by 4.7% on the same dataset. This advancement underscores the effectiveness of the proposed modifications and sets a new benchmark in aerial image analysis, paving the way for more accurate and efficient object detection methodologies. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/SashaMatsun/LSKDiffDet
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge