Ahmed Karam Eldaly
Direct low-field MRI super-resolution using undersampled k-space
Feb 28, 2026Abstract:Low-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) provides affordable access to diagnostic imaging but suffers from prolonged acquisition and limited image quality. Accelerated imaging can be achieved with k-space undersampling, while super-resolution (SR) and image quality transfer (IQT) methods typically rely on spatial-domain post-processing. In this work, we propose a novel framework for reconstructing high-field MR like images directly from undersampled low-field k-space. Our approach employs a k-space dual channel U-Net that processes the real and imaginary components of undersampled k-space to restore missing frequency content. Experiments on low-field brain MRI demonstrate that our k-space-driven image enhancement consistently outperforms the counterpart spatial-domain method. Furthermore, reconstructions from undersampled k-space achieve image quality comparable to full k-space acquisitions. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that investigates low-field MRI SR/IQT directly from undersampled k-space.
Low-Field Magnetic Resonance Image Quality Enhancement using a Conditional Flow Matching Model
Oct 14, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces a novel framework for image quality transfer based on conditional flow matching (CFM). Unlike conventional generative models that rely on iterative sampling or adversarial objectives, CFM learns a continuous flow between a noise distribution and target data distributions through the direct regression of an optimal velocity field. We evaluate this approach in the context of low-field magnetic resonance imaging (LF-MRI), a rapidly emerging modality that offers affordable and portable scanning but suffers from inherently low signal-to-noise ratio and reduced diagnostic quality. Our framework is designed to reconstruct high-field-like MR images from their corresponding low-field inputs, thereby bridging the quality gap without requiring expensive infrastructure. Experiments demonstrate that CFM not only achieves state-of-the-art performance, but also generalizes robustly to both in-distribution and out-of-distribution data. Importantly, it does so while utilizing significantly fewer parameters than competing deep learning methods. These results underline the potential of CFM as a powerful and scalable tool for MRI reconstruction, particularly in resource-limited clinical environments.
Towards Human-AI Collaboration System for the Detection of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma in Histopathology Images
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC) is the most prevalent form of breast cancer, and early, accurate diagnosis is critical to improving patient survival rates by guiding treatment decisions. Combining medical expertise with artificial intelligence (AI) holds significant promise for enhancing the precision and efficiency of IDC detection. In this work, we propose a human-in-the-loop (HITL) deep learning system designed to detect IDC in histopathology images. The system begins with an initial diagnosis provided by a high-performance EfficientNetV2S model, offering feedback from AI to the human expert. Medical professionals then review the AI-generated results, correct any misclassified images, and integrate the revised labels into the training dataset, forming a feedback loop from the human back to the AI. This iterative process refines the model's performance over time. The EfficientNetV2S model itself achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to existing methods in the literature, with an overall accuracy of 93.65\%. Incorporating the human-in-the-loop system further improves the model's accuracy using four experimental groups with misclassified images. These results demonstrate the potential of this collaborative approach to enhance AI performance in diagnostic systems. This work contributes to advancing automated, efficient, and highly accurate methods for IDC detection through human-AI collaboration, offering a promising direction for future AI-assisted medical diagnostics.
Alternative Learning Paradigms for Image Quality Transfer
Nov 08, 2024



Abstract:Image Quality Transfer (IQT) aims to enhance the contrast and resolution of low-quality medical images, e.g. obtained from low-power devices, with rich information learned from higher quality images. In contrast to existing IQT methods which adopt supervised learning frameworks, in this work, we propose two novel formulations of the IQT problem. The first approach uses an unsupervised learning framework, whereas the second is a combination of both supervised and unsupervised learning. The unsupervised learning approach considers a sparse representation (SRep) and dictionary learning model, which we call IQT-SRep, whereas the combination of supervised and unsupervised learning approach is based on deep dictionary learning (DDL), which we call IQT-DDL. The IQT-SRep approach trains two dictionaries using a SRep model using pairs of low- and high-quality volumes. Subsequently, the SRep of a low-quality block, in terms of the low-quality dictionary, can be directly used to recover the corresponding high-quality block using the high-quality dictionary. On the other hand, the IQT-DDL approach explicitly learns a high-resolution dictionary to upscale the input volume, while the entire network, including high dictionary generator, is simultaneously optimised to take full advantage of deep learning methods. The two models are evaluated using a low-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) application aiming to recover high-quality images akin to those obtained from high-field scanners. Experiments comparing the proposed approaches against state-of-the-art supervised deep learning IQT method (IQT-DL) identify that the two novel formulations of the IQT problem can avoid bias associated with supervised methods when tested using out-of-distribution data that differs from the distribution of the data the model was trained on. This highlights the potential benefit of these novel paradigms for IQT.
* Accepted for publication at the Journal of Machine Learning for Biomedical Imaging (MELBA) https://melba-journal.org/2024:027
Patch-based Sparse Representation For Bacterial Detection
Oct 29, 2018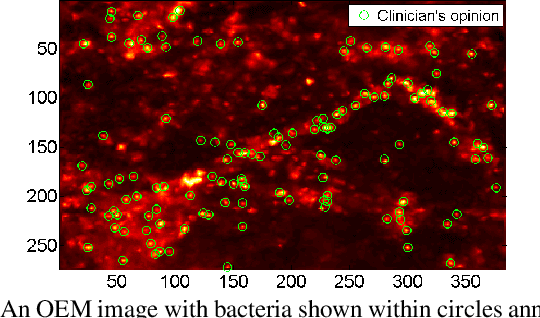
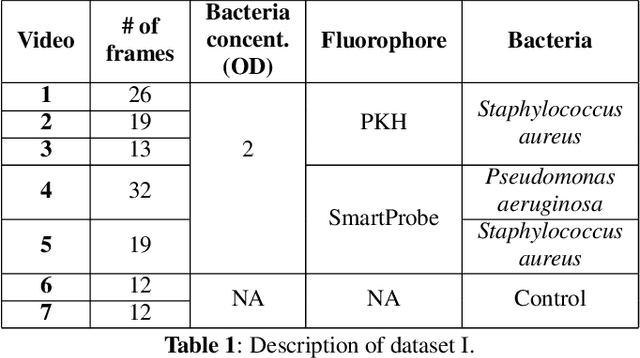
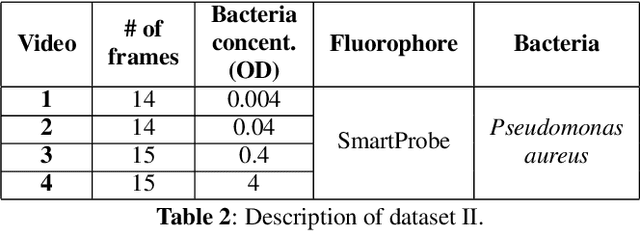

Abstract:In this paper, we propose a supervised approach for bacterial detection in optical endomicroscopy images. This approach splits each image into a set of overlapping patches and assumes that observed intensities are linear combinations of the actual intensity values associated with background image structures, corrupted by additive Gaussian noise and potentially by a sparse outlier term modelling anomalies (which are considered to be candidate bacteria). The actual intensity term representing background structures is modelled as a linear combination of a few atoms drawn from a dictionary which is learned from bacteria-free data and then fixed while analyzing new images. The bacteria detection task is formulated as a minimization problem and an Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) is then used to estimate the unknown parameters. Simulations conducted using two ex vivo lung datasets show good detection and correlation performance between bacteria counts identified by a trained clinician and those of the proposed method.
Deconvolution and Restoration of Optical Endomicroscopy Images
Aug 28, 2018



Abstract:Optical endomicroscopy (OEM) is an emerging technology platform with preclinical and clinical imaging applications. Pulmonary OEM via fibre bundles has the potential to provide in vivo, in situ molecular signatures of disease such as infection and inflammation. However, enhancing the quality of data acquired by this technique for better visualization and subsequent analysis remains a challenging problem. Cross coupling between fiber cores and sparse sampling by imaging fiber bundles are the main reasons for image degradation, and poor detection performance (i.e., inflammation, bacteria, etc.). In this work, we address the problem of deconvolution and restoration of OEM data. We propose a hierarchical Bayesian model to solve this problem and compare three estimation algorithms to exploit the resulting joint posterior distribution. The first method is based on Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods, however, it exhibits a relatively long computational time. The second and third algorithms deal with this issue and are based on a variational Bayes (VB) approach and an alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) algorithm respectively. Results on both synthetic and real datasets illustrate the effectiveness of the proposed methods for restoration of OEM images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge