Aditi Sharma
IndicEval-XL: Bridging Linguistic Diversity in Code Generation Across Indic Languages
Feb 26, 2025



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in code generation from natural language prompts, revolutionizing software development workflows. As we advance towards agent-based development paradigms, these models form the cornerstone of next-generation software development lifecycles. However, current benchmarks for evaluating multilingual code generation capabilities are predominantly English-centric, limiting their applicability across the global developer community. To address this limitation, we present IndicEval-XL, a comprehensive benchmark for code generation that incorporates 6 major Indic languages, collectively spoken by approximately 14\% of the world's population. Our benchmark bridges these languages with 12 programming languages, creating a robust evaluation framework. This work is particularly significant given India's representation of one-eighth of the global population and the crucial role Indic languages play in Indian society. IndicEval-XL represents a significant step toward expanding the linguistic diversity in code generation systems and evaluation frameworks. By developing resources that support multiple languages, we aim to make AI-powered development tools more inclusive and accessible to developers of various linguistic backgrounds. To facilitate further research and development in this direction, we make our dataset and evaluation benchmark publicly available at https://github.com/telekom/IndicEval-XL
AI Guide Dog: Egocentric Path Prediction on Smartphone
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:This paper introduces AI Guide Dog (AIGD), a lightweight egocentric navigation assistance system for visually impaired individuals, designed for real-time deployment on smartphones. AIGD addresses key challenges in blind navigation by employing a vision-only, multi-label classification approach to predict directional commands, ensuring safe traversal across diverse environments. We propose a novel technique to enable goal-based outdoor navigation by integrating GPS signals and high-level directions, while also addressing uncertain multi-path predictions for destination-free indoor navigation. Our generalized model is the first navigation assistance system to handle both goal-oriented and exploratory navigation scenarios across indoor and outdoor settings, establishing a new state-of-the-art in blind navigation. We present methods, datasets, evaluations, and deployment insights to encourage further innovations in assistive navigation systems.
Software Effort Estimation using Neuro Fuzzy Inference System: Past and Present
Dec 26, 2019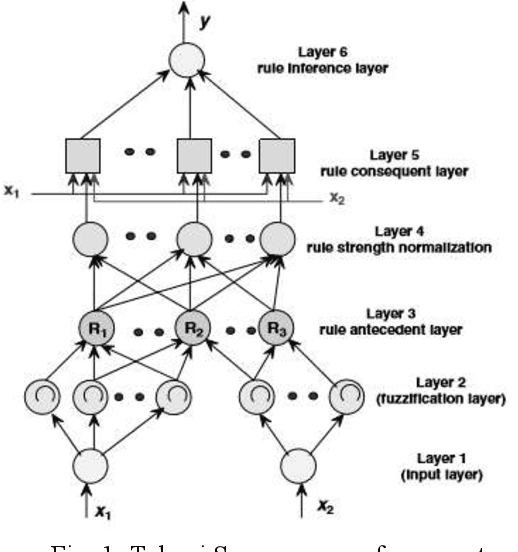
Abstract:Most important reason for project failure is poor effort estimation. Software development effort estimation is needed for assigning appropriate team members for development, allocating resources for software development, binding etc. Inaccurate software estimation may lead to delay in project, over-budget or cancellation of the project. But the effort estimation models are not very efficient. In this paper, we are analyzing the new approach for estimation i.e. Neuro Fuzzy Inference System (NFIS). It is a mixture model that consolidates the components of artificial neural network with fuzzy logic for giving a better estimation.
Anxious Depression Prediction in Real-time Social Data
Mar 25, 2019
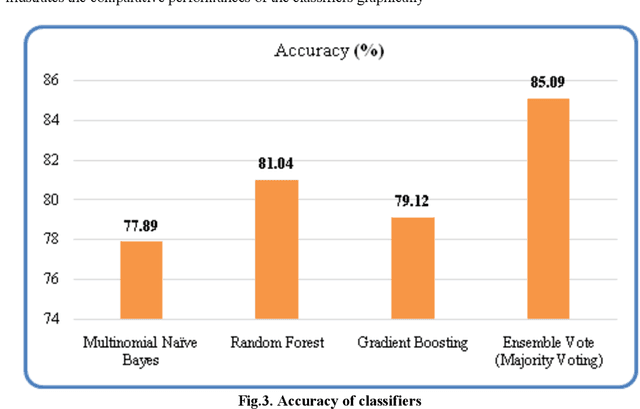
Abstract:Mental well-being and social media have been closely related domains of study. In this research a novel model, AD prediction model, for anxious depression prediction in real-time tweets is proposed. This mixed anxiety-depressive disorder is a predominantly associated with erratic thought process, restlessness and sleeplessness. Based on the linguistic cues and user posting patterns, the feature set is defined using a 5-tuple vector <word, timing, frequency, sentiment, contrast>. An anxiety-related lexicon is built to detect the presence of anxiety indicators. Time and frequency of tweet is analyzed for irregularities and opinion polarity analytics is done to find inconsistencies in posting behaviour. The model is trained using three classifiers (multinomial na\"ive bayes, gradient boosting, and random forest) and majority voting using an ensemble voting classifier is done. Preliminary results are evaluated for tweets of sampled 100 users and the proposed model achieves a classification accuracy of 85.09%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge