Adel Hafiane
Self-supervised structured object representation learning
Aug 27, 2025Abstract:Self-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged as a powerful technique for learning visual representations. While recent SSL approaches achieve strong results in global image understanding, they are limited in capturing the structured representation in scenes. In this work, we propose a self-supervised approach that progressively builds structured visual representations by combining semantic grouping, instance level separation, and hierarchical structuring. Our approach, based on a novel ProtoScale module, captures visual elements across multiple spatial scales. Unlike common strategies like DINO that rely on random cropping and global embeddings, we preserve full scene context across augmented views to improve performance in dense prediction tasks. We validate our method on downstream object detection tasks using a combined subset of multiple datasets (COCO and UA-DETRAC). Experimental results show that our method learns object centric representations that enhance supervised object detection and outperform the state-of-the-art methods, even when trained with limited annotated data and fewer fine-tuning epochs.
WGAST: Weakly-Supervised Generative Network for Daily 10 m Land Surface Temperature Estimation via Spatio-Temporal Fusion
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Urbanization, climate change, and agricultural stress are increasing the demand for precise and timely environmental monitoring. Land Surface Temperature (LST) is a key variable in this context and is retrieved from remote sensing satellites. However, these systems face a trade-off between spatial and temporal resolution. While spatio-temporal fusion methods offer promising solutions, few have addressed the estimation of daily LST at 10 m resolution. In this study, we present WGAST, a Weakly-Supervised Generative Network for Daily 10 m LST Estimation via Spatio-Temporal Fusion of Terra MODIS, Landsat 8, and Sentinel-2. WGAST is the first end-to-end deep learning framework designed for this task. It adopts a conditional generative adversarial architecture, with a generator composed of four stages: feature extraction, fusion, LST reconstruction, and noise suppression. The first stage employs a set of encoders to extract multi-level latent representations from the inputs, which are then fused in the second stage using cosine similarity, normalization, and temporal attention mechanisms. The third stage decodes the fused features into high-resolution LST, followed by a Gaussian filter to suppress high-frequency noise. Training follows a weakly supervised strategy based on physical averaging principles and reinforced by a PatchGAN discriminator. Experiments demonstrate that WGAST outperforms existing methods in both quantitative and qualitative evaluations. Compared to the best-performing baseline, on average, WGAST reduces RMSE by 17.18% and improves SSIM by 11.00%. Furthermore, WGAST is robust to cloud-induced LST and effectively captures fine-scale thermal patterns, as validated against 33 ground-based sensors. The code is available at https://github.com/Sofianebouaziz1/WGAST.git.
Loss-Guided Model Sharing and Local Learning Correction in Decentralized Federated Learning for Crop Disease Classification
May 29, 2025Abstract:Crop disease detection and classification is a critical challenge in agriculture, with major implications for productivity, food security, and environmental sustainability. While deep learning models such as CNN and ViT have shown excellent performance in classifying plant diseases from images, their large-scale deployment is often limited by data privacy concerns. Federated Learning (FL) addresses this issue, but centralized FL remains vulnerable to single-point failures and scalability limits. In this paper, we introduce a novel Decentralized Federated Learning (DFL) framework that uses validation loss (Loss_val) both to guide model sharing between peers and to correct local training via an adaptive loss function controlled by weighting parameter. We conduct extensive experiments using PlantVillage datasets with three deep learning architectures (ResNet50, VGG16, and ViT_B16), analyzing the impact of weighting parameter, the number of shared models, the number of clients, and the use of Loss_val versus Loss_train of other clients. Results demonstrate that our DFL approach not only improves accuracy and convergence speed, but also ensures better generalization and robustness across heterogeneous data environments making it particularly well-suited for privacy-preserving agricultural applications.
Enhancing knowledge retention for continual learning with domain-specific adapters and features gating
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Continual learning empowers models to learn from a continuous stream of data while preserving previously acquired knowledge, effectively addressing the challenge of catastrophic forgetting. In this study, we propose a new approach that integrates adapters within the self-attention mechanisms of Vision Transformers to enhance knowledge retention when sequentially adding datasets from different domains. Unlike previous methods that continue learning with only one dataset, our approach introduces domain-specific output heads and feature gating, allowing the model to maintain high accuracy on previously learned tasks while incorporating only the essential information from multiple domains. The proposed method is compared to prominent parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods in the current state of the art. The results provide evidence that our method effectively alleviates the limitations of previous works. Furthermore, we conduct a comparative analysis using three datasets, CIFAR-100, Flowers102, and DTD, each representing a distinct domain, to investigate the impact of task order on model performance. Our findings underscore the critical role of dataset sequencing in shaping learning outcomes, demonstrating that strategic ordering can significantly improve the model's ability to adapt to evolving data distributions over time while preserving the integrity of previously learned knowledge.
Enhancing DeepLabV3+ to Fuse Aerial and Satellite Images for Semantic Segmentation
Mar 28, 2025Abstract:Aerial and satellite imagery are inherently complementary remote sensing sources, offering high-resolution detail alongside expansive spatial coverage. However, the use of these sources for land cover segmentation introduces several challenges, prompting the development of a variety of segmentation methods. Among these approaches, the DeepLabV3+ architecture is considered as a promising approach in the field of single-source image segmentation. However, despite its reliable results for segmentation, there is still a need to increase its robustness and improve its performance. This is particularly crucial for multimodal image segmentation, where the fusion of diverse types of information is essential. An interesting approach involves enhancing this architectural framework through the integration of novel components and the modification of certain internal processes. In this paper, we enhance the DeepLabV3+ architecture by introducing a new transposed conventional layers block for upsampling a second entry to fuse it with high level features. This block is designed to amplify and integrate information from satellite images, thereby enriching the segmentation process through fusion with aerial images. For experiments, we used the LandCover.ai (Land Cover from Aerial Imagery) dataset for aerial images, alongside the corresponding dataset sourced from Sentinel 2 data. Through the fusion of both sources, the mean Intersection over Union (mIoU) achieved a total mIoU of 84.91% without data augmentation.
Deep Learning for Spatio-Temporal Fusion in Land Surface Temperature Estimation: A Comprehensive Survey, Experimental Analysis, and Future Trends
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:The rapid advancements in satellite remote sensing have enhanced the capability to monitor and analyze the Earth's surface. Among the many variables captured through satellite sensors, Land Surface Temperature (LST) plays a critical role in understanding key environmental processes. However, obtaining high-resolution LST data remains a challenge, as satellite sensors often face a trade-off between spatial and temporal resolutions. In response, Spatio-Temporal Fusion (STF) has emerged as a powerful method to integrate two satellite data sources, one providing high spatial but low temporal resolution, and the other offering high temporal but low spatial resolution. Although a range of STF techniques have been proposed, from traditional methods to cutting-edge deep learning (DL) models, most have focused on surface reflectance, with limited application to LST estimation. DL approaches, in particular, show promise in improving the spatial and temporal resolutions of LST by capturing complex, non-linear relationships between input and output LST data. This paper offers a comprehensive review of the latest advancements in DL-based STF techniques for LST estimation. We analyze key research developments, mathematically formulate the STF problem, and introduce a novel taxonomy for DL-based STF methods. Furthermore, we discuss the challenges faced by current methods and highlight future research directions. In addition, we present the first open-source benchmark STF dataset for LST estimation, consisting of 51 pairs of MODIS-Landsat images spanning from 2013 to 2024. To support our findings, we conduct extensive experiments on state-of-the-art methods and present both quantitative and qualitative assessments. This is the first survey paper focused on DL-based STF for LST estimation. We hope it serves as a valuable reference for researchers and paves the way for future research in this field.
Fusion of Satellite Images and Weather Data with Transformer Networks for Downy Mildew Disease Detection
Sep 06, 2022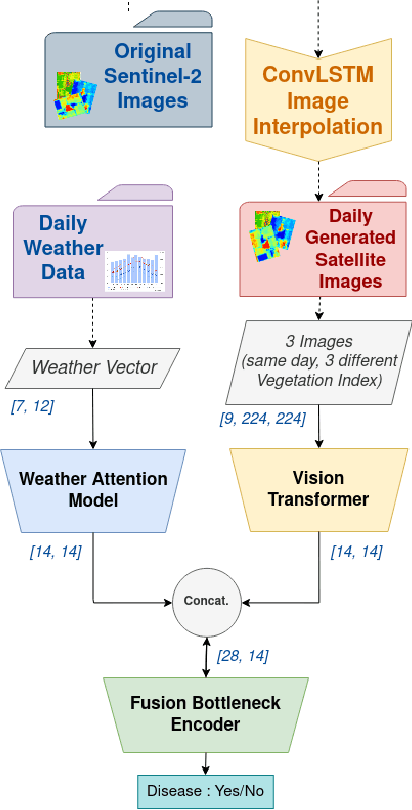
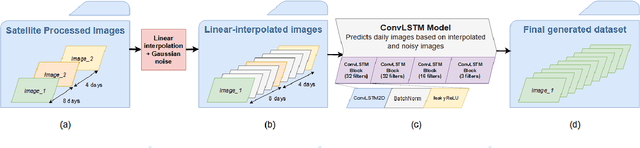
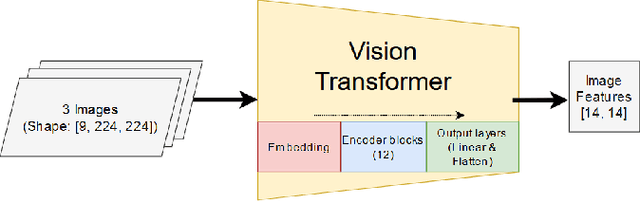
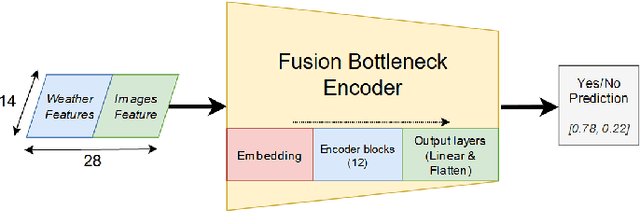
Abstract:Crop diseases significantly affect the quantity and quality of agricultural production. In a context where the goal of precision agriculture is to minimize or even avoid the use of pesticides, weather and remote sensing data with deep learning can play a pivotal role in detecting crop diseases, allowing localized treatment of crops. However, combining heterogeneous data such as weather and images remains a hot topic and challenging task. Recent developments in transformer architectures have shown the possibility of fusion of data from different domains, for instance text-image. The current trend is to custom only one transformer to create a multimodal fusion model. Conversely, we propose a new approach to realize data fusion using three transformers. In this paper, we first solved the missing satellite images problem, by interpolating them with a ConvLSTM model. Then, proposed a multimodal fusion architecture that jointly learns to process visual and weather information. The architecture is built from three main components, a Vision Transformer and two transformer-encoders, allowing to fuse both image and weather modalities. The results of the proposed method are promising achieving 97\% overall accuracy.
Generative models-based data labeling for deep networks regression: application to seed maturity estimation from UAV multispectral images
Aug 09, 2022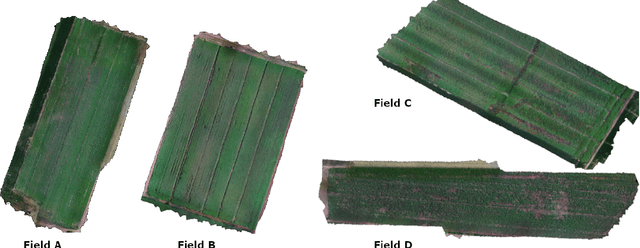

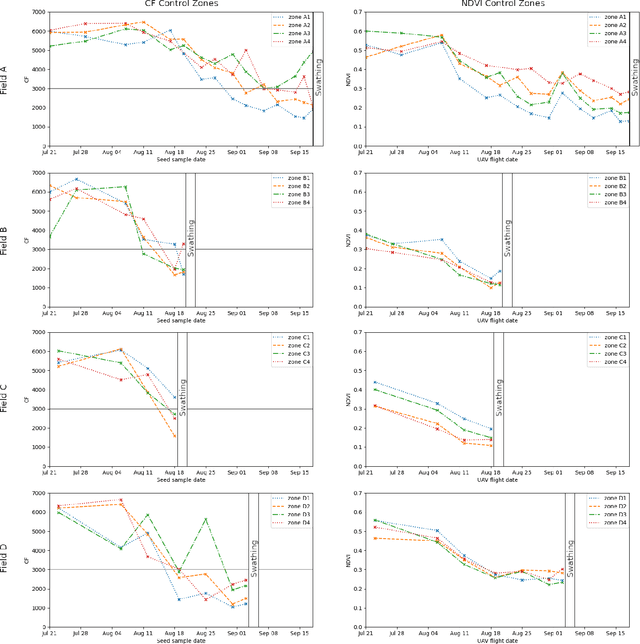
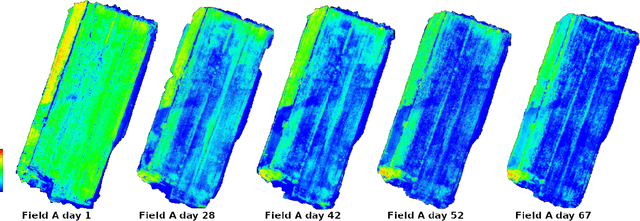
Abstract:Monitoring seed maturity is an increasing challenge in agriculture due to climate change and more restrictive practices. Seeds monitoring in the field is essential to optimize the farming process and to guarantee yield quality through high germination. Traditional methods are based on limited sampling in the field and analysis in laboratory. Moreover, they are time consuming and only allow monitoring sub-sections of the crop field. This leads to a lack of accuracy on the condition of the crop as a whole due to intra-field heterogeneities. Multispectral imagery by UAV allows uniform scan of fields and better capture of crop maturity information. On the other hand, deep learning methods have shown tremendous potential in estimating agronomic parameters, especially maturity. However, they require large labeled datasets. Although large sets of aerial images are available, labeling them with ground truth is a tedious, if not impossible task. In this paper, we propose a method for estimating parsley seed maturity using multispectral UAV imagery, with a new approach for automatic data labeling. This approach is based on parametric and non-parametric models to provide weak labels. We also consider the data acquisition protocol and the performance evaluation of the different steps of the method. Results show good performance, and the non-parametric kernel density estimator model can improve neural network generalization when used as a labeling method, leading to more robust and better performing deep neural models.
Vision Transformers For Weeds and Crops Classification Of High Resolution UAV Images
Sep 06, 2021
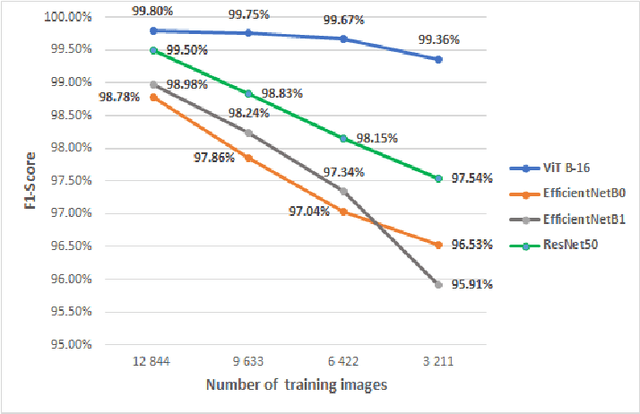
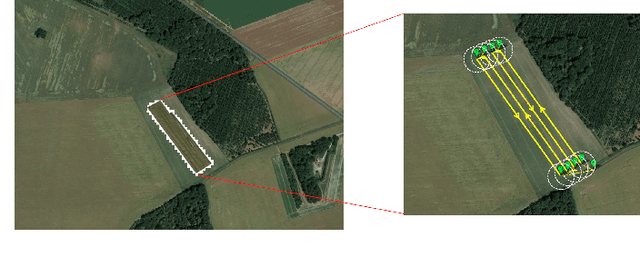
Abstract:Crop and weed monitoring is an important challenge for agriculture and food production nowadays. Thanks to recent advances in data acquisition and computation technologies, agriculture is evolving to a more smart and precision farming to meet with the high yield and high quality crop production. Classification and recognition in Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) images are important phases for crop monitoring. Advances in deep learning models relying on Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) have achieved high performances in image classification in the agricultural domain. Despite the success of this architecture, CNN still faces many challenges such as high computation cost, the need of large labelled datasets, ... Natural language processing's transformer architecture can be an alternative approach to deal with CNN's limitations. Making use of the self-attention paradigm, Vision Transformer (ViT) models can achieve competitive or better results without applying any convolution operations. In this paper, we adopt the self-attention mechanism via the ViT models for plant classification of weeds and crops: red beet, off-type beet (green leaves), parsley and spinach. Our experiments show that with small set of labelled training data, ViT models perform better compared to state-of-the-art CNN-based models EfficientNet and ResNet, with a top accuracy of 99.8\% achieved by the ViT model.
A deep learning based multiscale approach to segment cancer area in liver whole slide image
Jul 25, 2020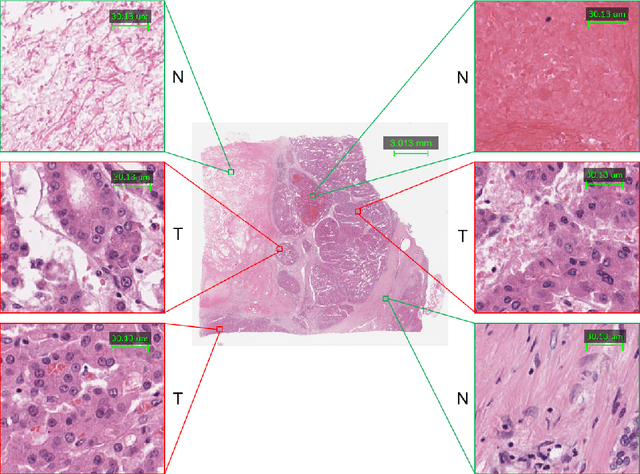
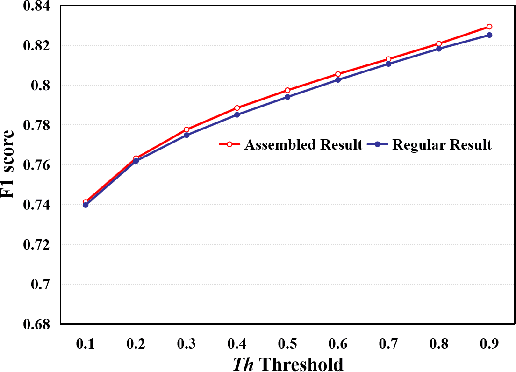
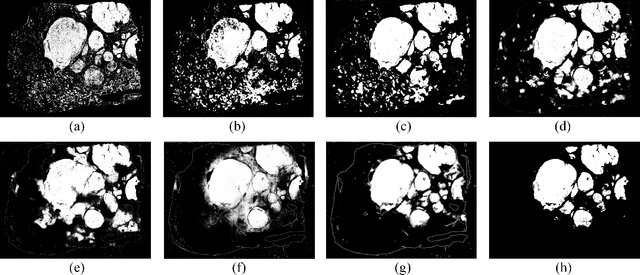
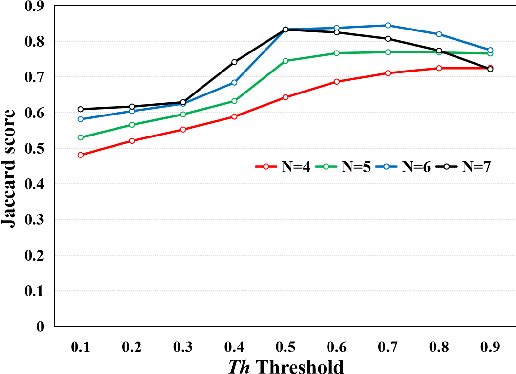
Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of liver cancer segmentation in Whole Slide Image (WSI). We propose a multi-scale image processing method based on automatic end-to-end deep neural network algorithm for segmentation of cancer area. A seven-levels gaussian pyramid representation of the histopathological image was built to provide the texture information in different scales. In this work, several neural architectures were compared using the original image level for the training procedure. The proposed method is based on U-Net applied to seven levels of various resolutions (pyramidal subsumpling). The predictions in different levels are combined through a voting mechanism. The final segmentation result is generated at the original image level. Partial color normalization and weighted overlapping method were applied in preprocessing and prediction separately. The results show the effectiveness of the proposed multi-scales approach achieving better scores compared to the state-of-the-art.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge