Adam Ligocki
Computer Vision Approaches for Automated Bee Counting Application
Jun 13, 2024



Abstract:Many application from the bee colony health state monitoring could be efficiently solved using a computer vision techniques. One of such challenges is an efficient way for counting the number of incoming and outcoming bees, which could be used to further analyse many trends, such as the bee colony health state, blooming periods, or for investigating the effects of agricultural spraying. In this paper, we compare three methods for the automated bee counting over two own datasets. The best performing method is based on the ResNet-50 convolutional neural network classifier, which achieved accuracy of 87% over the BUT1 dataset and the accuracy of 93% over the BUT2 dataset.
Machine Learning and Computer Vision Techniques in Bee Monitoring Applications
Jul 29, 2022



Abstract:Machine learning and computer vision are dynamically growing fields, which have proven to be able to solve very complex tasks. They could also be used for the monitoring of the honeybee colonies and for the inspection of their health state, which could identify potentially dangerous states before the situation is critical, or to better plan periodic bee colony inspections and therefore save significant costs. In this paper, we present an overview of the state-of-the-art computer vision and machine learning applications used for bee monitoring. We also demonstrate the potential of those methods as an example of an automated bee counter algorithm. The paper is aimed at veterinary and apidology professionals and experts, who might not be familiar with machine learning to introduce to them its possibilities, therefore each family of applications is opened by a brief theoretical introduction and motivation related to its base method. We hope that this paper will inspire other scientists to use the machine learning techniques for other applications in bee monitoring.
Robotic Template Library
Jul 01, 2021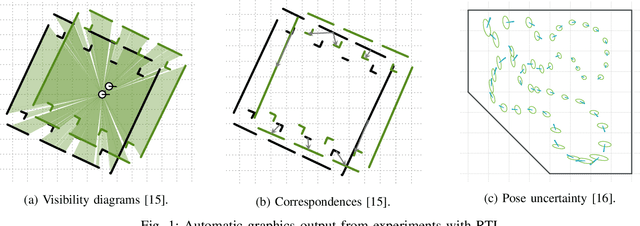
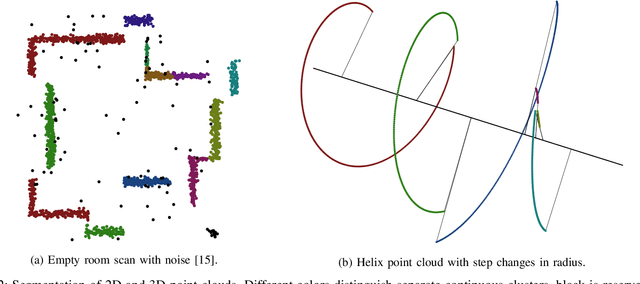
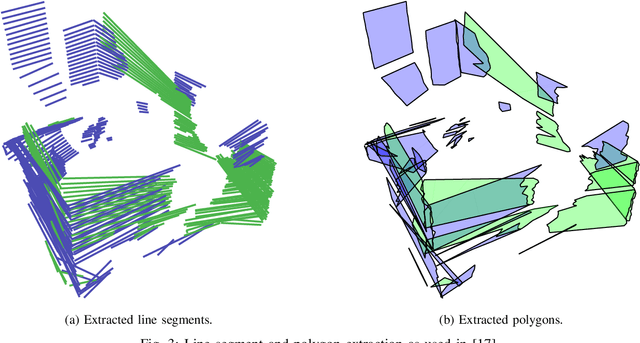

Abstract:Robotic Template Library (RTL) is a set of tools for dealing with geometry and point cloud processing, especially in robotic applications. The software package covers basic objects such as vectors, line segments, quaternions, rigid transformations, etc., however, its main contribution lies in the more advanced modules: The segmentation module for batch or stream clustering of point clouds, the fast vectorization module for approximation of continuous point clouds by geometric objects of higher grade and the LaTeX export module enabling automated generation of high-quality visual outputs. It is a header-only library written in C++17, uses the Eigen library as a linear algebra back-end, and is designed with high computational performance in mind. RTL can be used in all robotic tasks such as motion planning, map building, object recognition and many others, but the point cloud processing utilities are general enough to be employed in any field touching object reconstruction and computer vision applications as well.
Brno Urban Dataset: Winter Extention
Jun 05, 2021



Abstract:Research on autonomous driving is advancing dramatically and requires new data and techniques to progress even further. To reflect this pressure, we present an extension of our recent work - the Brno Urban Dataset (BUD). The new data focus on winter conditions in various snow-covered environments and feature additional LiDAR and radar sensors for object detection in front of the vehicle. The improvement affects the old data as well. We provide YOLO detection annotations for all old RGB images in the dataset. The detections are further also transferred by our original algorithm into the infra-red (IR) images, captured by the thermal camera. To our best knowledge, it makes this dataset the largest source of machine-annotated thermal images currently available. The dataset is published under MIT license on https://github.com/Robotics-BUT/Brno-Urban-Dataset.
Visual diagnosis of the Varroa destructor parasitic mite in honeybees using object detector techniques
Feb 26, 2021
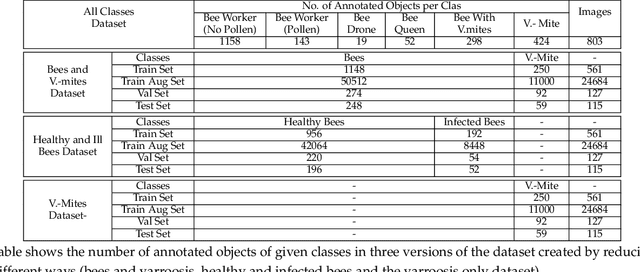
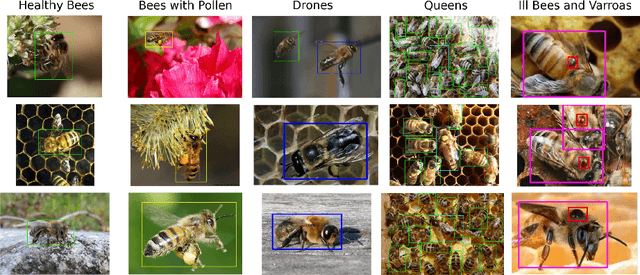
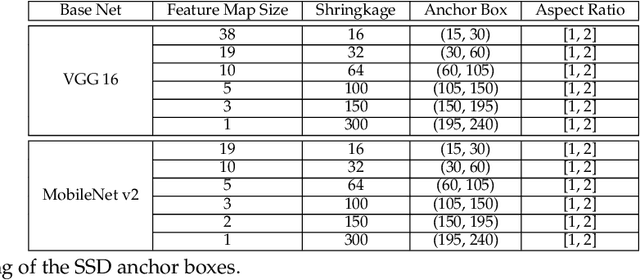
Abstract:The Varroa destructor mite is one of the most dangerous Honey Bee (Apis mellifera) parasites worldwide and the bee colonies have to be regularly monitored in order to control its spread. Here we present an object detector based method for health state monitoring of bee colonies. This method has the potential for online measurement and processing. In our experiment, we compare the YOLO and SSD object detectors along with the Deep SVDD anomaly detector. Based on the custom dataset with 600 ground-truth images of healthy and infected bees in various scenes, the detectors reached a high F1 score up to 0.874 in the infected bee detection and up to 0.727 in the detection of the Varroa Destructor mite itself. The results demonstrate the potential of this approach, which will be later used in the real-time computer vision based honey bee inspection system. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first one using object detectors for this purpose. We expect that performance of those object detectors will enable us to inspect the health status of the honey bee colonies.
Atlas Fusion -- Modern Framework for Autonomous Agent Sensor Data Fusion
Oct 22, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we present our new sensor fusion framework for self-driving cars and other autonomous robots. We have designed our framework as a universal and scalable platform for building up a robust 3D model of the agent's surrounding environment by fusing a wide range of various sensors into the data model that we can use as a basement for the decision making and planning algorithms. Our software currently covers the data fusion of the RGB and thermal cameras, 3D LiDARs, 3D IMU, and a GNSS positioning. The framework covers a complete pipeline from data loading, filtering, preprocessing, environment model construction, visualization, and data storage. The architecture allows the community to modify the existing setup or to extend our solution with new ideas. The entire software is fully compatible with ROS (Robotic Operation System), which allows the framework to cooperate with other ROS-based software. The source codes are fully available as an open-source under the MIT license. See https://github.com/Robotics-BUT/Atlas-Fusion.
Brno Urban Dataset -- The New Data for Self-Driving Agents and Mapping Tasks
Sep 15, 2019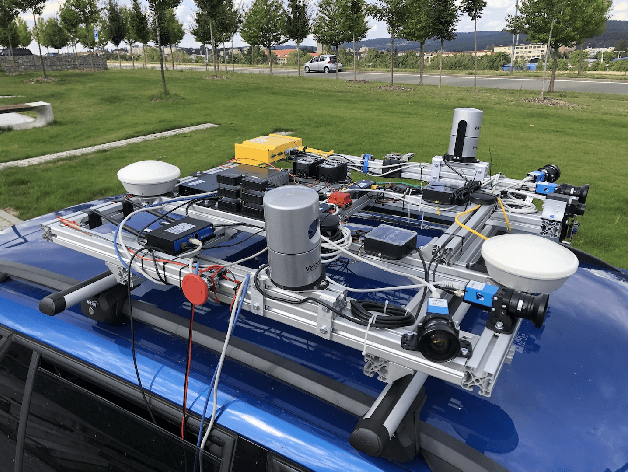



Abstract:Autonomous driving is a dynamically growing field of research, where quality and amount of experimental data is critical. Although several rich datasets are available these days, the demands of researchers and technical possibilities are evolving. Through this paper, we bring a new dataset recorded in Brno, Czech Republic. It offers data from four WUXGA cameras, two 3D LiDARs, inertial measurement unit, infrared camera and especially differential RTK GNSS receiver with centimetre accuracy which, to the best knowledge of the authors, is not available from any other public dataset so far. In addition, all the data are precisely timestamped with sub-millisecond precision to allow wider range of applications. At the time of publishing of this paper, recordings of more than 350 km of rides in varying environment are shared at: https: //github.com/RoboticsBUT/Brno-Urban-Dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge