Abdullah Cheema
Classification of Potholes Based on Surface Area Using Pre-Trained Models of Convolutional Neural Network
Sep 29, 2023



Abstract:Potholes are fatal and can cause severe damage to vehicles as well as can cause deadly accidents. In South Asian countries, pavement distresses are the primary cause due to poor subgrade conditions, lack of subsurface drainage, and excessive rainfalls. The present research compares the performance of three pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) models, i.e., ResNet 50, ResNet 18, and MobileNet. At first, pavement images are classified to find whether images contain potholes, i.e., Potholes or Normal. Secondly, pavements images are classi-fied into three categories, i.e., Small Pothole, Large Pothole, and Normal. Pavement images are taken from 3.5 feet (waist height) and 2 feet. MobileNet v2 has an accuracy of 98% for detecting a pothole. The classification of images taken at the height of 2 feet has an accuracy value of 87.33%, 88.67%, and 92% for classifying the large, small, and normal pavement, respectively. Similarly, the classification of the images taken from full of waist (FFW) height has an accuracy value of 98.67%, 98.67%, and 100%.
Dynamic Visual Analytics for Elicitation Meetings with ELICA
Jul 10, 2018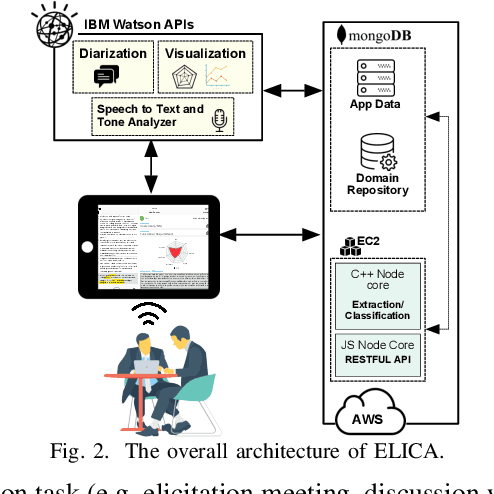
Abstract:Requirements elicitation can be very challenging in projects that require deep domain knowledge about the system at hand. As analysts have the full control over the elicitation process, their lack of knowledge about the system under study inhibits them from asking related questions and reduces the accuracy of requirements provided by stakeholders. We present ELICA, a generic interactive visual analytics tool to assist analysts during requirements elicitation process. ELICA uses a novel information extraction algorithm based on a combination of Weighted Finite State Transducers (WFSTs) (generative model) and SVMs (discriminative model). ELICA presents the extracted relevant information in an interactive GUI (including zooming, panning, and pinching) that allows analysts to explore which parts of the ongoing conversation (or specification document) match with the extracted information. In this demonstration, we show that ELICA is usable and effective in practice, and is able to extract the related information in real-time. We also demonstrate how carefully designed features in ELICA facilitate the interactive and dynamic process of information extraction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge