Abdelkrim Alahyane
LAAS-SARA, LAAS-RISC, LAAS
Optimizing Asynchronous Federated Learning: A Delicate Trade-Off Between Model-Parameter Staleness and Update Frequency
Feb 12, 2025



Abstract:Synchronous federated learning (FL) scales poorly with the number of clients due to the straggler effect. Algorithms like FedAsync and GeneralizedFedAsync address this limitation by enabling asynchronous communication between clients and the central server. In this work, we rely on stochastic modeling to better understand the impact of design choices in asynchronous FL algorithms, such as the concurrency level and routing probabilities, and we leverage this knowledge to optimize loss. We characterize in particular a fundamental trade-off for optimizing asynchronous FL: minimizing gradient estimation errors by avoiding model parameter staleness, while also speeding up the system by increasing the throughput of model updates. Our two main contributions can be summarized as follows. First, we prove a discrete variant of Little's law to derive a closed-form expression for relative delay, a metric that quantifies staleness. This allows us to efficiently minimize the average loss per model update, which has been the gold standard in literature to date. Second, we observe that naively optimizing this metric leads us to slow down the system drastically by overemphazing staleness at the detriment of throughput. This motivates us to introduce an alternative metric that also takes system speed into account, for which we derive a tractable upper-bound that can be minimized numerically. Extensive numerical results show that these optimizations enhance accuracy by 10% to 30%.
Open data for Moroccan license plates for OCR applications : data collection, labeling, and model construction
Apr 16, 2021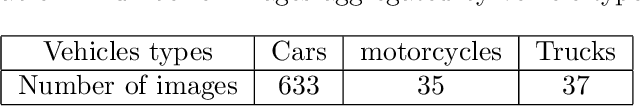

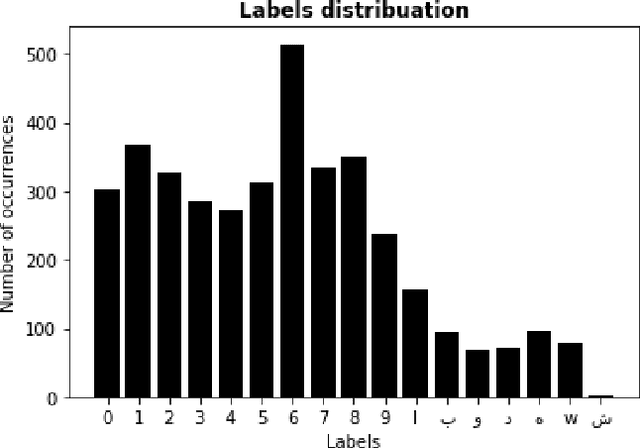
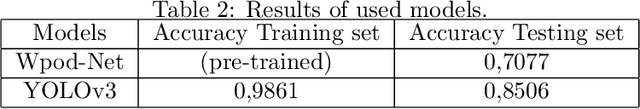
Abstract:Significant number of researches have been developed recently around intelligent system for traffic management, especially, OCR based license plate recognition, as it is considered as a main step for any automatic traffic management system. Good quality data sets are increasingly needed and produced by the research community to improve the performance of those algorithms. Furthermore, a special need of data is noted for countries having special characters on their licence plates, like Morocco, where Arabic Alphabet is used. In this work, we present a labeled open data set of circulation plates taken in Morocco, for different type of vehicles, namely cars, trucks and motorcycles. This data was collected manually and consists of 705 unique and different images. Furthermore this data was labeled for plate segmentation and for matriculation number OCR. Also, As we show in this paper, the data can be enriched using data augmentation techniques to create training sets with few thousands of images for different machine leaning and AI applications. We present and compare a set of models built on this data. Also, we publish this data as an open access data to encourage innovation and applications in the field of OCR and image processing for traffic control and other applications for transportation and heterogeneous vehicle management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge