Abdelkader Nasreddine Belkacem
Transformer-based Image and Video Inpainting: Current Challenges and Future Directions
Jun 28, 2024



Abstract:Image inpainting is currently a hot topic within the field of computer vision. It offers a viable solution for various applications, including photographic restoration, video editing, and medical imaging. Deep learning advancements, notably convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs), have significantly enhanced the inpainting task with an improved capability to fill missing or damaged regions in an image or video through the incorporation of contextually appropriate details. These advancements have improved other aspects, including efficiency, information preservation, and achieving both realistic textures and structures. Recently, visual transformers have been exploited and offer some improvements to image or video inpainting. The advent of transformer-based architectures, which were initially designed for natural language processing, has also been integrated into computer vision tasks. These methods utilize self-attention mechanisms that excel in capturing long-range dependencies within data; therefore, they are particularly effective for tasks requiring a comprehensive understanding of the global context of an image or video. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive review of the current image or video inpainting approaches, with a specific focus on transformer-based techniques, with the goal to highlight the significant improvements and provide a guideline for new researchers in the field of image or video inpainting using visual transformers. We categorized the transformer-based techniques by their architectural configurations, types of damage, and performance metrics. Furthermore, we present an organized synthesis of the current challenges, and suggest directions for future research in the field of image or video inpainting.
NewsGPT: ChatGPT Integration for Robot-Reporter
Nov 11, 2023
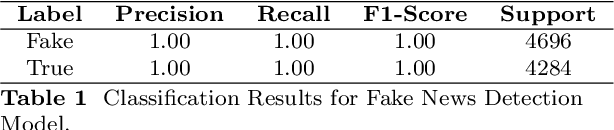
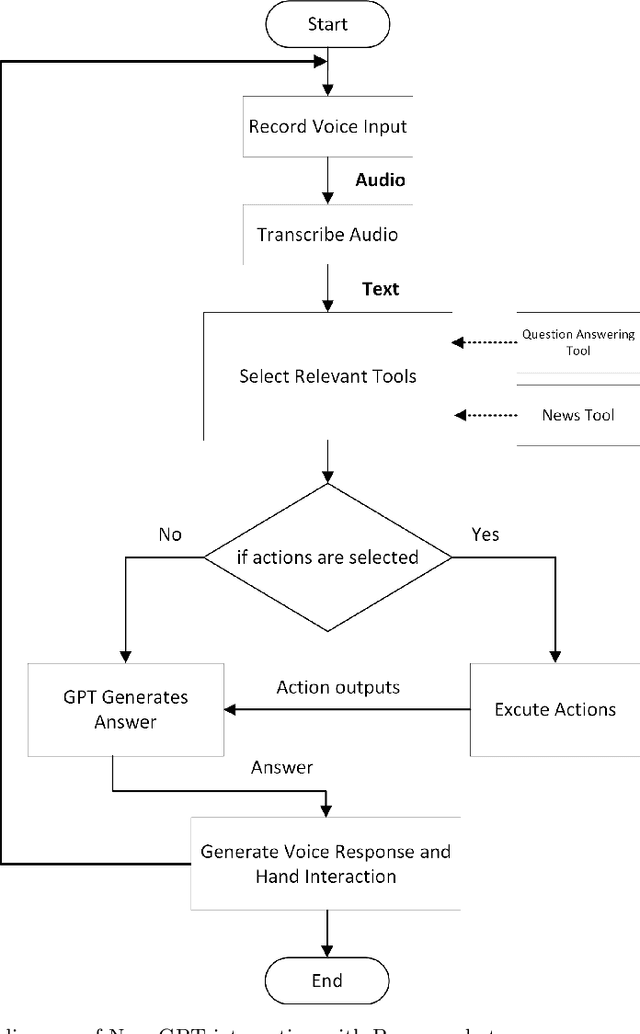
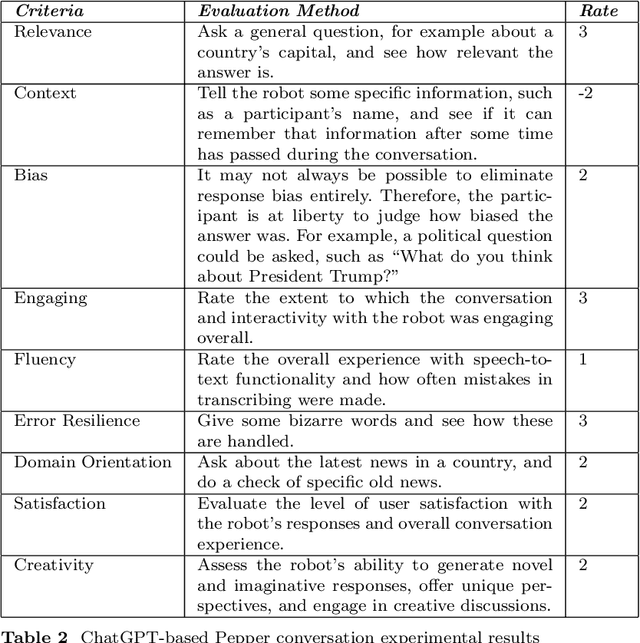
Abstract:The integration of large language models (LLMs) with social robots has emerged as a promising avenue for enhancing human-robot interactions at a time when news reports generated by artificial intelligence (AI) are gaining in credibility. This integration is expected to intensify and become a more productive resource for journalism, media, communication, and education. In this paper a novel system is proposed that integrates AI's generative pretrained transformer (GPT) model with the Pepper robot, with the aim of improving the robot's natural language understanding and response generation capabilities for enhanced social interactions. By leveraging GPT's powerful language processing capabilities, this system offers a comprehensive pipeline that incorporates voice input recording, speech-to-text transcription, context analysis, and text-to-speech synthesis action generation. The Pepper robot is enabled to comprehend user queries, generate informative responses with general knowledge, maintain contextually relevant conversations, and act as a more domain-oriented news reporter. It is also linked with a news resource and powered with a Google search capability. To evaluate the performance of the framework, experiments were conducted involving a set of diverse questions. The robot's responses were assessed on the basis of eight criteria, including relevance, context, and fluency. Despite some identified limitations, this system contributes to the field of journalism and human-robot interaction by showcasing the potential of integrating LLMs with social robots. The proposed framework opens up opportunities for improving the conversational capabilities of robots, enabling interactions that are smoother, more engaging, and more context aware.
End-to-End AI-Based Point-of-Care Diagnosis System for Classifying Respiratory Illnesses and Early Detection of COVID-19
Jun 28, 2020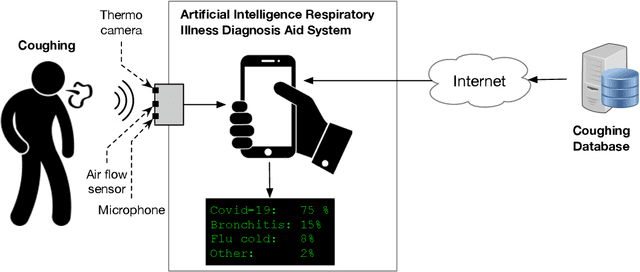
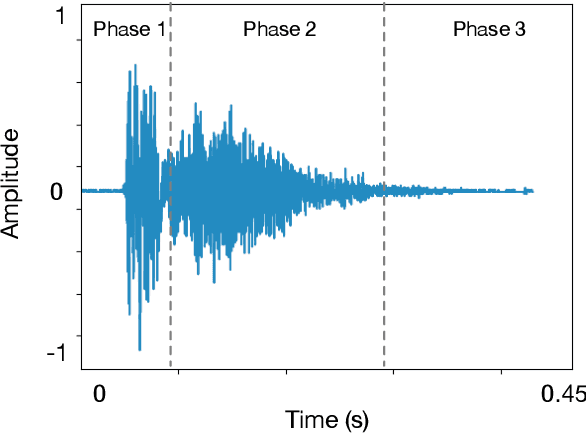
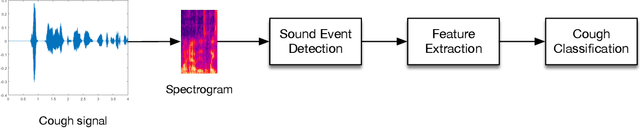

Abstract:Respiratory symptoms can be a caused by different underlying conditions, and are often caused by viral infections, such as Influenza-like illnesses or other emerging viruses like the Coronavirus. These respiratory viruses, often, have common symptoms, including coughing, high temperature, congested nose, and difficulty breathing. However, early diagnosis of the type of the virus, can be crucial, especially in cases such as the recent COVID-19 pandemic. One of the factors that contributed to the spread of the pandemic, was the late diagnosis or confusing it with regular flu-like symptoms. Science has proved that one of the possible differentiators of the underlying causes of these different respiratory diseases is coughing, which comes in different types and forms. Therefore, a reliable lab-free tool for early and more accurate diagnosis that can differentiate between different respiratory diseases is very much needed. This paper proposes an end-to-end portable system that can record data from patients with symptom, including coughs (voluntary or involuntary) and translate them into health data for diagnosis, and with the aid of machine learning, classify them into different respiratory illnesses, including COVID-19. With the ongoing efforts to stop the spread of the COVID-19 disease everywhere today, and against similar diseases in the future, our proposed low cost and user-friendly solution can play an important part in the early diagnosis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge