Émilie Wirbel
Cross-modal Learning for Domain Adaptation in 3D Semantic Segmentation
Jan 18, 2021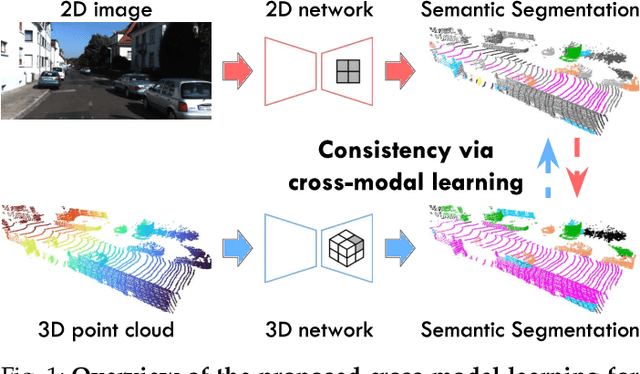
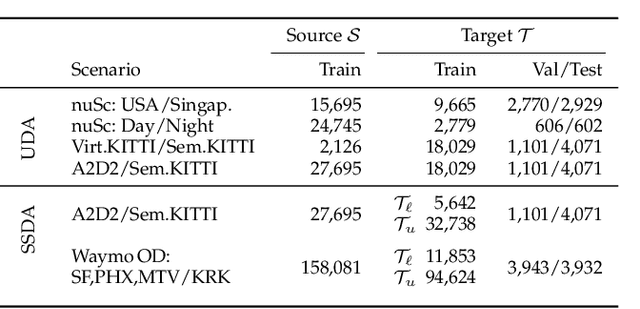
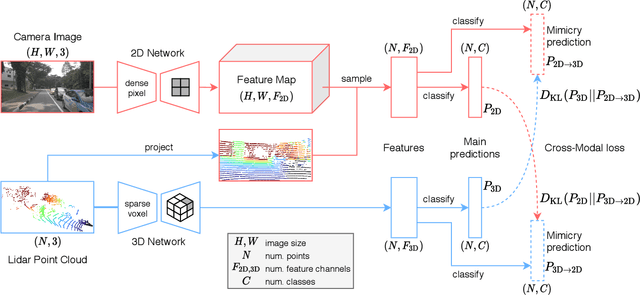
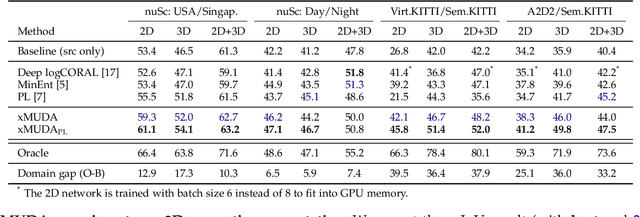
Abstract:Domain adaptation is an important task to enable learning when labels are scarce. While most works focus only on the image modality, there are many important multi-modal datasets. In order to leverage multi-modality for domain adaptation, we propose cross-modal learning, where we enforce consistency between the predictions of two modalities via mutual mimicking. We constrain our network to make correct predictions on labeled data and consistent predictions across modalities on unlabeled target-domain data. Experiments in unsupervised and semi-supervised domain adaptation settings prove the effectiveness of this novel domain adaptation strategy. Specifically, we evaluate on the task of 3D semantic segmentation using the image and point cloud modality. We leverage recent autonomous driving datasets to produce a wide variety of domain adaptation scenarios including changes in scene layout, lighting, sensor setup and weather, as well as the synthetic-to-real setup. Our method significantly improves over previous uni-modal adaptation baselines on all adaption scenarios. Code will be made available.
xMUDA: Cross-Modal Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for 3D Semantic Segmentation
Nov 28, 2019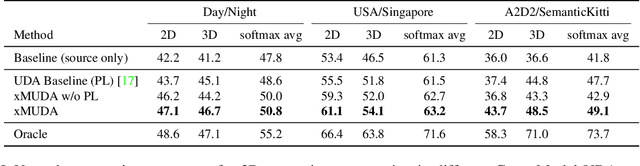
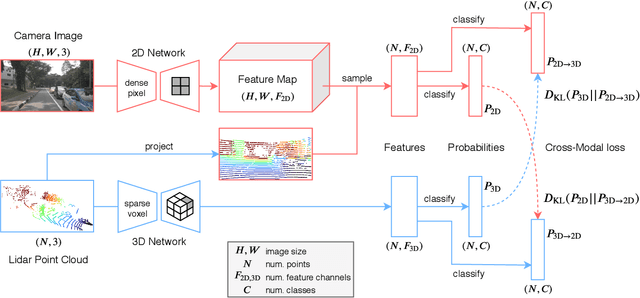

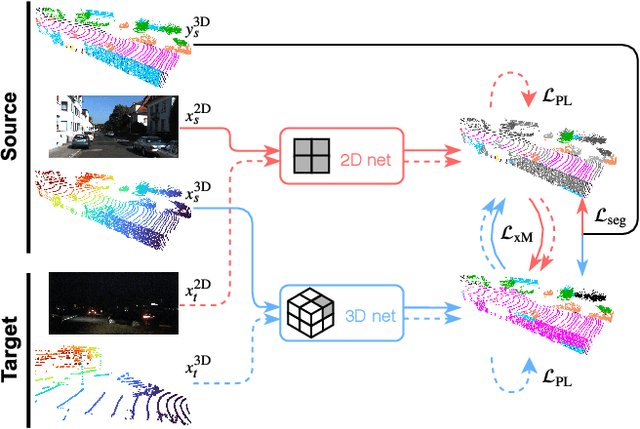
Abstract:Unsupervised Domain Adaptation (UDA) is crucial to tackle the lack of annotations in a new domain. There are many multi-modal datasets, but most UDA approaches are uni-modal. In this work, we explore how to learn from multi-modality and propose cross-modal UDA (xMUDA) where we assume the presence of 2D images and 3D point clouds for 3D semantic segmentation. This is challenging as the two input spaces are heterogeneous and can be impacted differently by domain shift. In xMUDA, modalities learn from each other through mutual mimicking, disentangled from the segmentation objective, to prevent the stronger modality from adopting false predictions from the weaker one. We evaluate on new UDA scenarios including day-to-night, country-to-country and dataset-to-dataset, leveraging recent autonomous driving datasets. xMUDA brings large improvements over uni-modal UDA on all tested scenarios, and is complementary to state-of-the-art UDA techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge