xView3-SAR: Detecting Dark Fishing Activity Using Synthetic Aperture Imagery
Paper and Code
Jun 02, 2022
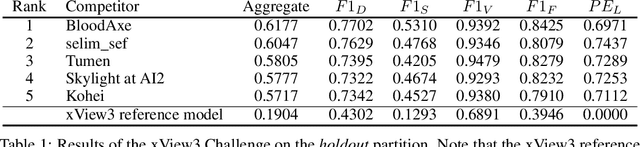

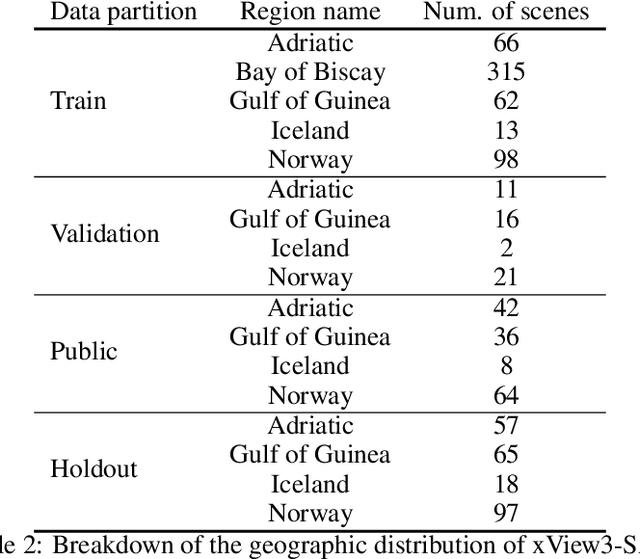
Unsustainable fishing practices worldwide pose a major threat to marine resources and ecosystems. Identifying vessels that evade monitoring systems -- known as "dark vessels" -- is key to managing and securing the health of marine environments. With the rise of satellite-based synthetic aperture radar (SAR) imaging and modern machine learning (ML), it is now possible to automate detection of dark vessels day or night, under all-weather conditions. SAR images, however, require domain-specific treatment and is not widely accessible to the ML community. Moreover, the objects (vessels) are small and sparse, challenging traditional computer vision approaches. We present the largest labeled dataset for training ML models to detect and characterize vessels from SAR. xView3-SAR consists of nearly 1,000 analysis-ready SAR images from the Sentinel-1 mission that are, on average, 29,400-by-24,400 pixels each. The images are annotated using a combination of automated and manual analysis. Co-located bathymetry and wind state rasters accompany every SAR image. We provide an overview of the results from the xView3 Computer Vision Challenge, an international competition using xView3-SAR for ship detection and characterization at large scale. We release the data (https://iuu.xview.us/) and code (https://github.com/DIUx-xView) to support ongoing development and evaluation of ML approaches for this important application.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge