What Goes Into a LM Acceptability Judgment? Rethinking the Impact of Frequency and Length
Paper and Code
Nov 04, 2024


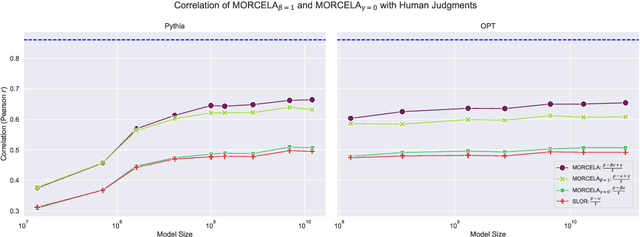
When comparing the linguistic capabilities of language models (LMs) with humans using LM probabilities, factors such as the length of the sequence and the unigram frequency of lexical items have a significant effect on LM probabilities in ways that humans are largely robust to. Prior works in comparing LM and human acceptability judgments treat these effects uniformly across models, making a strong assumption that models require the same degree of adjustment to control for length and unigram frequency effects. We propose MORCELA, a new linking theory between LM scores and acceptability judgments where the optimal level of adjustment for these effects is estimated from data via learned parameters for length and unigram frequency. We first show that MORCELA outperforms a commonly used linking theory for acceptability--SLOR (Pauls and Klein, 2012; Lau et al. 2017)--across two families of transformer LMs (Pythia and OPT). Furthermore, we demonstrate that the assumed degrees of adjustment in SLOR for length and unigram frequency overcorrect for these confounds, and that larger models require a lower relative degree of adjustment for unigram frequency, though a significant amount of adjustment is still necessary for all models. Finally, our subsequent analysis shows that larger LMs' lower susceptibility to frequency effects can be explained by an ability to better predict rarer words in context.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge