(q,p)-Wasserstein GANs: Comparing Ground Metrics for Wasserstein GANs
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2019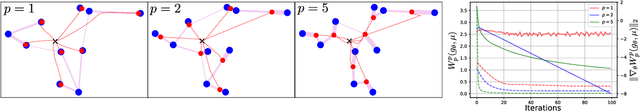
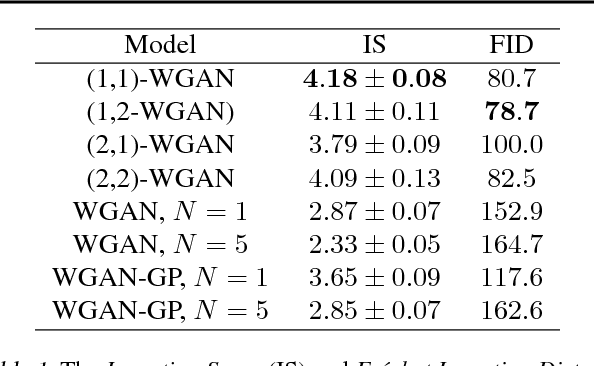
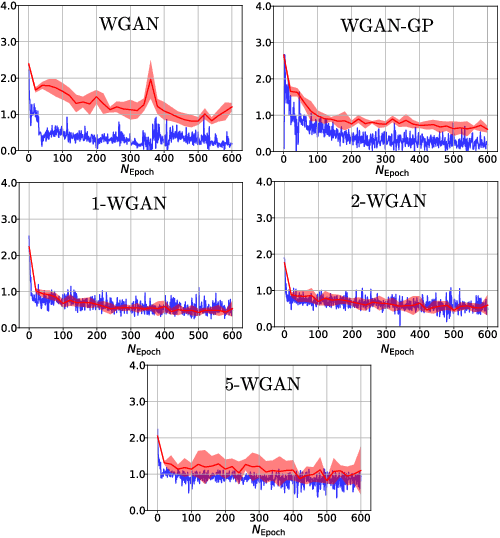
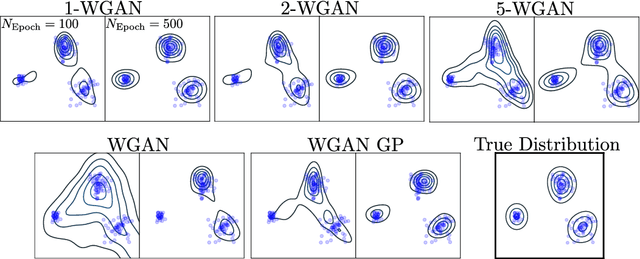
Generative Adversial Networks (GANs) have made a major impact in computer vision and machine learning as generative models. Wasserstein GANs (WGANs) brought Optimal Transport (OT) theory into GANs, by minimizing the $1$-Wasserstein distance between model and data distributions as their objective function. Since then, WGANs have gained considerable interest due to their stability and theoretical framework. We contribute to the WGAN literature by introducing the family of $(q,p)$-Wasserstein GANs, which allow the use of more general $p$-Wasserstein metrics for $p\geq 1$ in the GAN learning procedure. While the method is able to incorporate any cost function as the ground metric, we focus on studying the $l^q$ metrics for $q\geq 1$. This is a notable generalization as in the WGAN literature the OT distances are commonly based on the $l^2$ ground metric. We demonstrate the effect of different $p$-Wasserstein distances in two toy examples. Furthermore, we show that the ground metric does make a difference, by comparing different $(q,p)$ pairs on the MNIST and CIFAR-10 datasets. Our experiments demonstrate that changing the ground metric and $p$ can notably improve on the common $(q,p) = (2,1)$ case.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge