Vulnerable Road User Detection Using Smartphone Sensors and Recurrence Quantification Analysis
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2020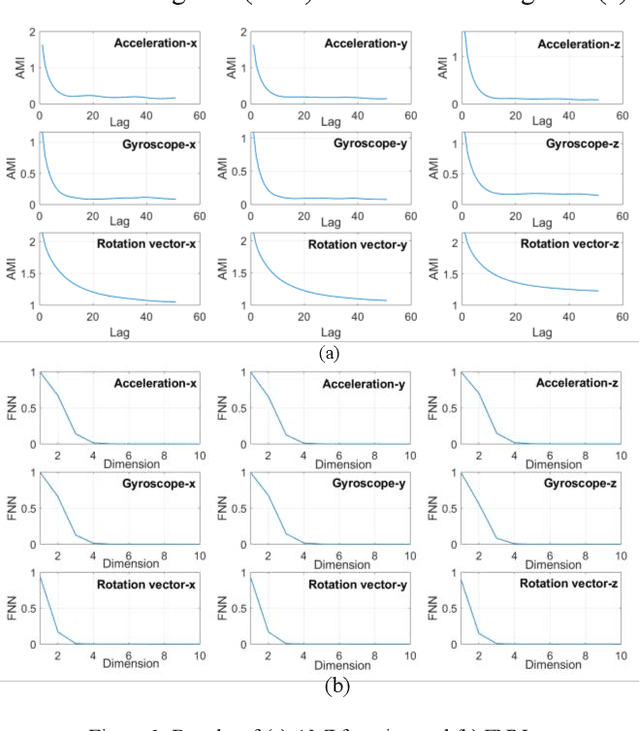
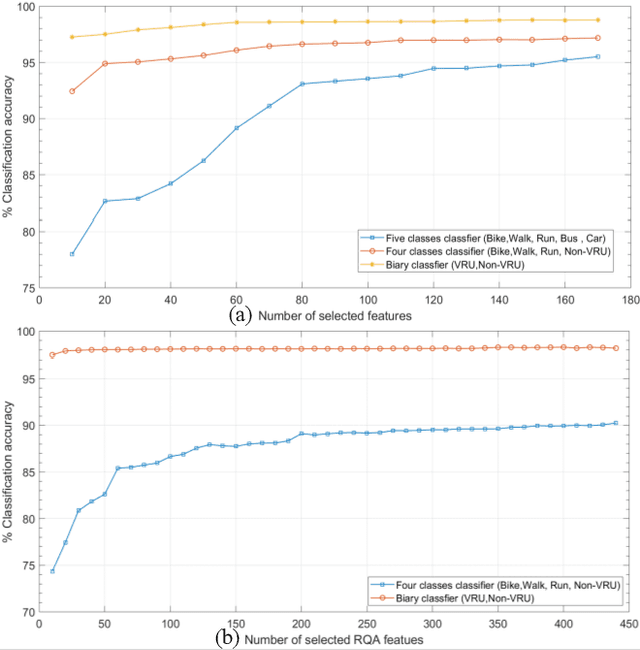
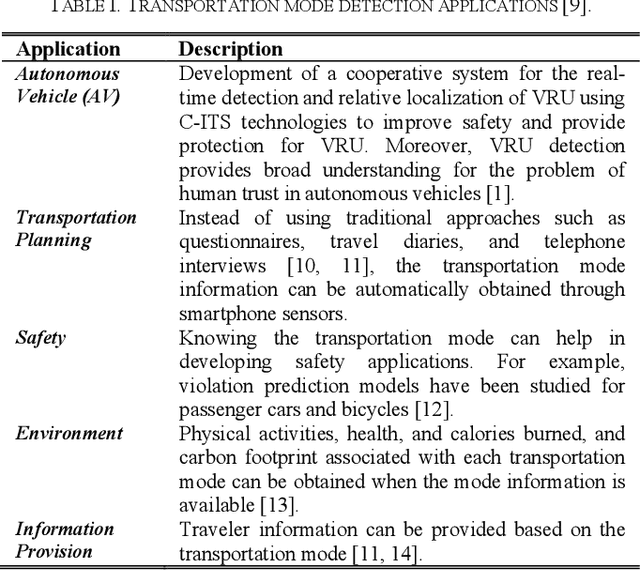
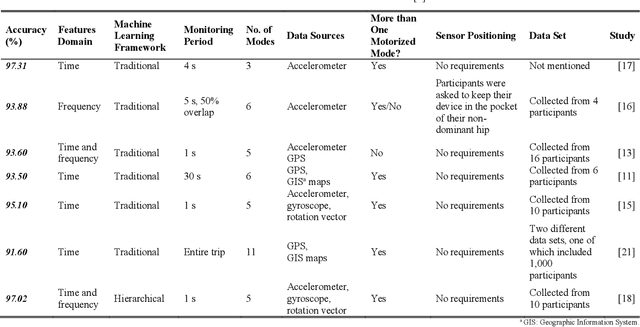
With the fast advancements of the Autonomous Vehicle (AV) industry, detection of Vulnerable Road Users (VRUs) using smartphones is critical for safety applications of Cooperative Intelligent Transportation Systems (C-ITSs). This study explores the use of low-power smartphone sensors and the Recurrence Quantification Analysis (RQA) features for this task. These features are computed over a thresholded similarity matrix extracted from nine channels: accelerometer, gyroscope, and rotation vector in each direction (x, y, and z). Given the high-power consumption of GPS, GPS data is excluded. RQA features are added to traditional time domain features to investigate the classification accuracy when using binary, four-class, and five-class Random Forest classifiers. Experimental results show a promising performance when only using RQA features with a resulted accuracy of 98. 34% and a 98. 79% by adding time domain features. Results outperform previous reported accuracy, demonstrating that RQA features have high classifying capability with respect to VRU detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge