Voice Pathology Detection Using Deep Learning: a Preliminary Study
Paper and Code
Jul 12, 2019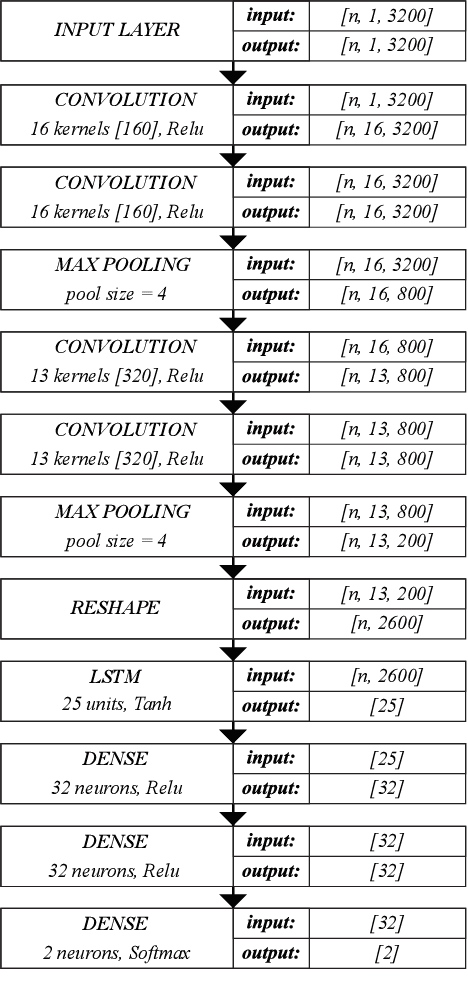
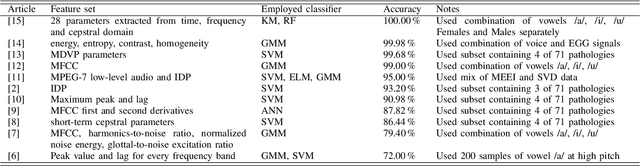


This paper describes a preliminary investigation of Voice Pathology Detection using Deep Neural Networks (DNN). We used voice recordings of sustained vowel /a/ produced at normal pitch from German corpus Saarbruecken Voice Database (SVD). This corpus contains voice recordings and electroglottograph signals of more than 2 000 speakers. The idea behind this experiment is the use of convolutional layers in combination with recurrent Long-Short-Term-Memory (LSTM) layers on raw audio signal. Each recording was split into 64 ms Hamming windowed segments with 30 ms overlap. Our trained model achieved 71.36% accuracy with 65.04% sensitivity and 77.67% specificity on 206 validation files and 68.08% accuracy with 66.75% sensitivity and 77.89% specificity on 874 testing files. This is a promising result in favor of this approach because it is comparable to similar previously published experiment that used different methodology. Further investigation is needed to achieve the state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge