Voice Mimicry Attacks Assisted by Automatic Speaker Verification
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2019

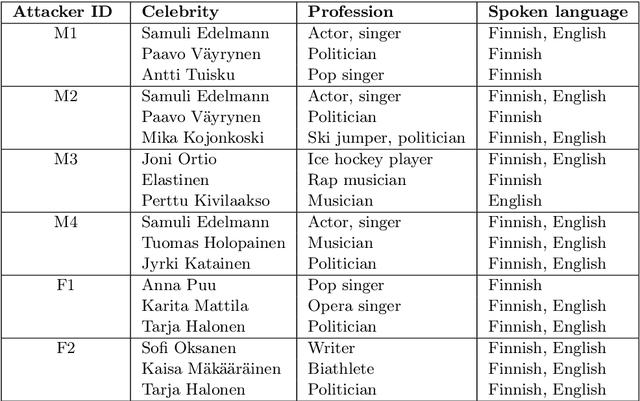

In this work, we simulate a scenario, where a publicly available ASV system is used to enhance mimicry attacks against another closed source ASV system. In specific, ASV technology is used to perform a similarity search between the voices of recruited attackers (6) and potential target speakers (7,365) from VoxCeleb corpora to find the closest targets for each of the attackers. In addition, we consider 'median', 'furthest', and 'common' targets to serve as a reference points. Our goal is to gain insights how well similarity rankings transfer from the attacker's ASV system to the attacked ASV system, whether the attackers are able to improve their attacks by mimicking, and how the properties of the voices of attackers change due to mimicking. We address these questions through ASV experiments, listening tests, and prosodic and formant analyses. For the ASV experiments, we use i-vector technology in the attacker side, and x-vectors in the attacked side. For the listening tests, we recruit listeners through crowdsourcing. The results of the ASV experiments indicate that the speaker similarity scores transfer well from one ASV system to another. Both the ASV experiments and the listening tests reveal that the mimicry attempts do not, in general, help in bringing attacker's scores closer to the target's. A detailed analysis shows that mimicking does not improve attacks, when the natural voices of attackers and targets are similar to each other. The analysis of prosody and formants suggests that the attackers were able to considerably change their speaking rates when mimicking, but the changes in F0 and formants were modest. Overall, the results suggest that untrained impersonators do not pose a high threat towards ASV systems, but the use of ASV systems to attack other ASV systems is a potential threat.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge