Virtual Mixup Training for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation
Paper and Code
May 24, 2019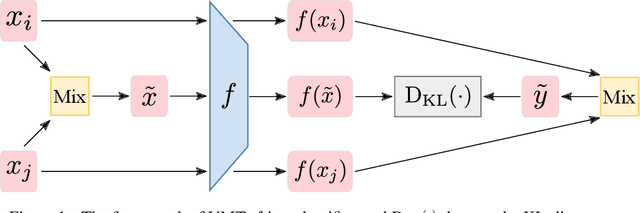
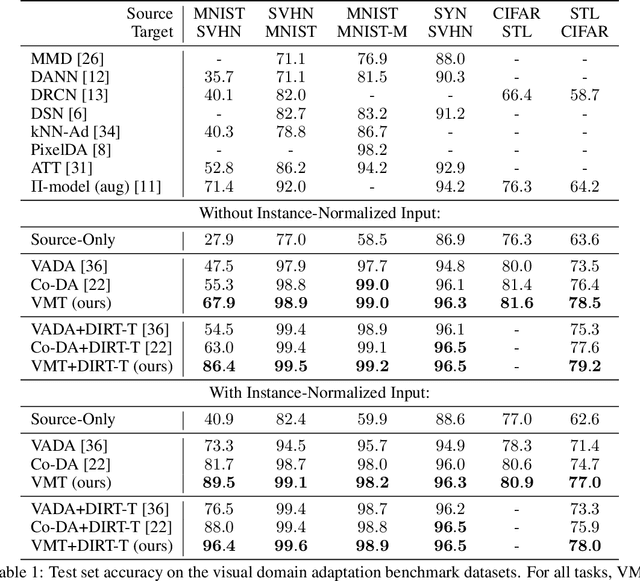
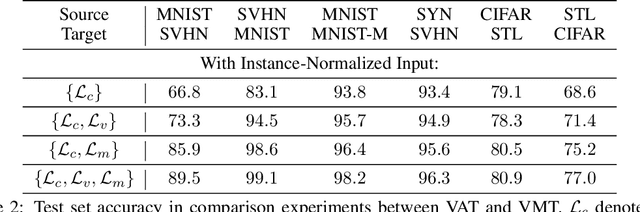
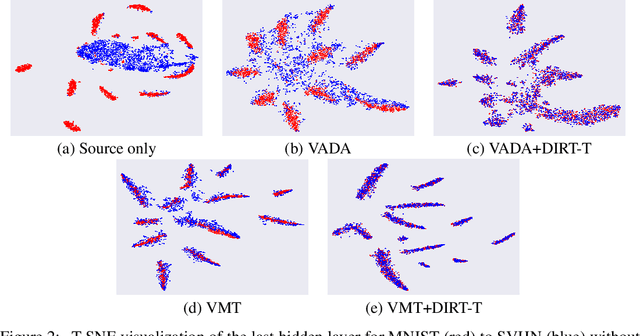
We study the problem of unsupervised domain adaptation which aims to adapt models trained on a labeled source domain to a completely unlabeled target domain. Domain adversarial training is a promising approach and has been a basis for many state-of-the-art models in unsupervised domain adaptation. The idea of domain adversarial training is to align the feature space between the source and target domains by adversarially training a domain classifier and a feature encoder. Recently, cluster assumption has been applied to unsupervised domain adaptation and achieved strong performance. In this paper, we propose a new regularization method called Virtual Mixup Training (VMT), which is able to further constrain the hypothesis of cluster assumption. The idea of VMT is to impose a locally-Lipschitz constraint on the model by smoothing the output distribution along the lines between pairs of training samples. Unlike the traditional mixup model, our method constructs the combination samples without using the label information, allowing it to be applicable to unsupervised domain adaptation. The proposed method is generic and can be combined with existing methods using domain adversarial training. We combine VMT with a recent state-of-the-art model called VADA, and extensive experiments demonstrate that VMT significantly improves the performance of VADA on several domain adaptation benchmark datasets. For the challenging task of adapting MNIST to SVHN, when not using instance normalization, VMT improves the accuracy of VADA by over 30%. When using instance normalization, our model achieves an accuracy of 96.4%, which is very close to the accuracy (96.5%) of the train-on-target model. Code will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge