Utterance-by-utterance overlap-aware neural diarization with Graph-PIT
Paper and Code
Jul 28, 2022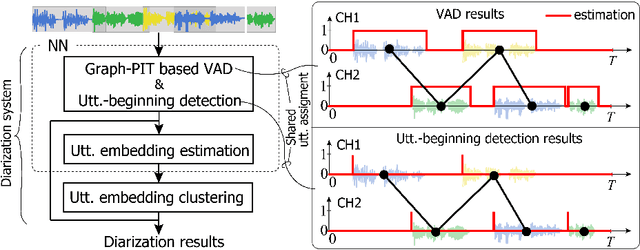
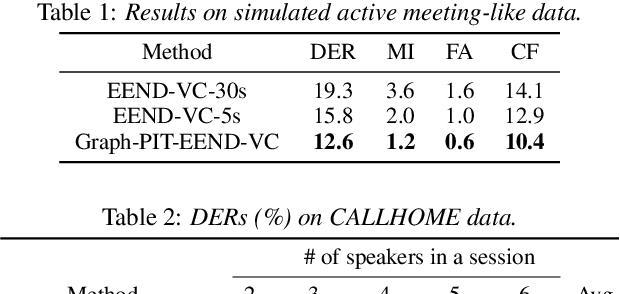
Recent speaker diarization studies showed that integration of end-to-end neural diarization (EEND) and clustering-based diarization is a promising approach for achieving state-of-the-art performance on various tasks. Such an approach first divides an observed signal into fixed-length segments, then performs {\it segment-level} local diarization based on an EEND module, and merges the segment-level results via clustering to form a final global diarization result. The segmentation is done to limit the number of speakers in each segment since the current EEND cannot handle a large number of speakers. In this paper, we argue that such an approach involving the segmentation has several issues; for example, it inevitably faces a dilemma that larger segment sizes increase both the context available for enhancing the performance and the number of speakers for the local EEND module to handle. To resolve such a problem, this paper proposes a novel framework that performs diarization without segmentation. However, it can still handle challenging data containing many speakers and a significant amount of overlapping speech. The proposed method can take an entire meeting for inference and perform {\it utterance-by-utterance} diarization that clusters utterance activities in terms of speakers. To this end, we leverage a neural network training scheme called Graph-PIT proposed recently for neural source separation. Experiments with simulated active-meeting-like data and CALLHOME data show the superiority of the proposed approach over the conventional methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge