Using Convolutional Variational Autoencoders to Predict Post-Trauma Health Outcomes from Actigraphy Data
Paper and Code
Nov 20, 2020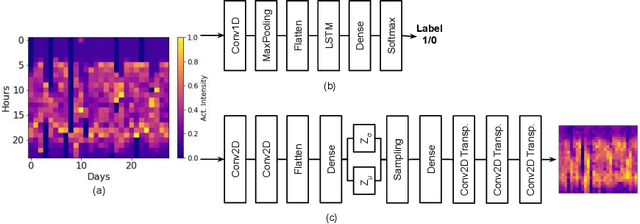
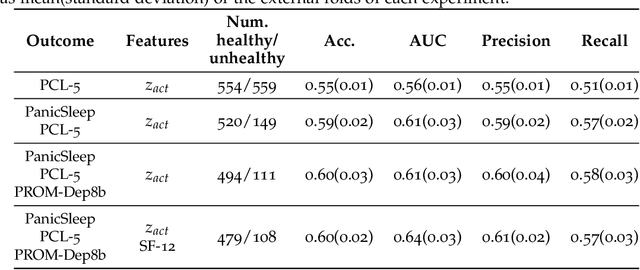
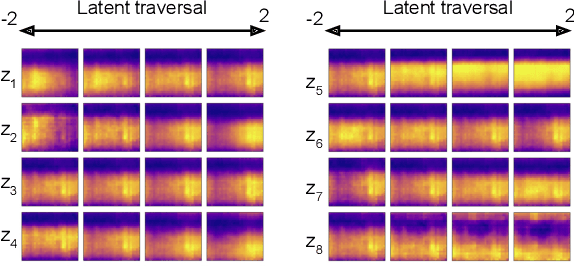
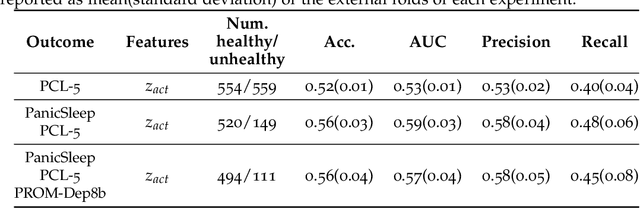
Depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are psychiatric conditions commonly associated with experiencing a traumatic event. Estimating mental health status through non-invasive techniques such as activity-based algorithms can help to identify successful early interventions. In this work, we used locomotor activity captured from 1113 individuals who wore a research grade smartwatch post-trauma. A convolutional variational autoencoder (VAE) architecture was used for unsupervised feature extraction from four weeks of actigraphy data. By using VAE latent variables and the participant's pre-trauma physical health status as features, a logistic regression classifier achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.64 to estimate mental health outcomes. The results indicate that the VAE model is a promising approach for actigraphy data analysis for mental health outcomes in long-term studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge