Unsupervised Learning of Depth, Optical Flow and Pose with Occlusion from 3D Geometry
Paper and Code
Mar 02, 2020

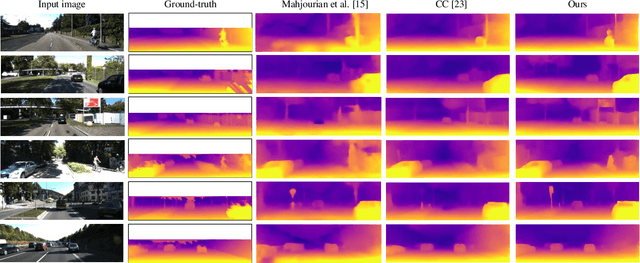
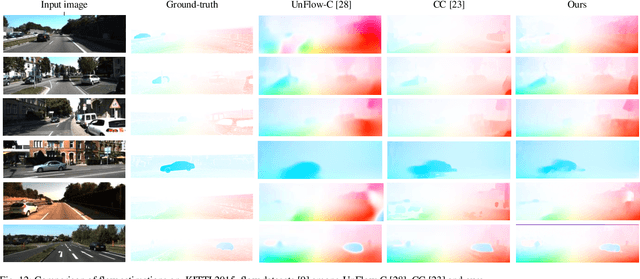
In autonomous driving, monocular sequences contain lots of information. Monocular depth estimation, camera ego-motion estimation and optical flow estimation in consecutive frames are high-profile concerns recently. By analyzing tasks above, pixels in the first frame are modeled into three parts: the rigid region, the non-rigid region, and the occluded region. In joint unsupervised training of depth and pose, we can segment the occluded region explicitly. The occlusion information is used in unsupervised learning of depth, pose and optical flow, as the image reconstructed by depth, pose and flow will be invalid in occluded regions. A less-than-mean mask is designed to further exclude the mismatched pixels which are interfered with motion or illumination change in the training of depth and pose networks. This method is also used to exclude some trivial mismatched pixels in the training of the flow net. Maximum normalization is proposed for smoothness term of depth-pose networks to restrain degradation in textureless regions. In the occluded region, as depth and camera motion can provide more reliable motion estimation, they can be used to instruct unsupervised learning of flow. Our experiments in KITTI dataset demonstrate that the model based on three regions, full and explicit segmentation of occlusion, rigid region and non-rigid region with corresponding unsupervised losses can improve performance on three tasks significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge