Unsupervised augmentation optimization for few-shot medical image segmentation
Paper and Code
Jun 08, 2023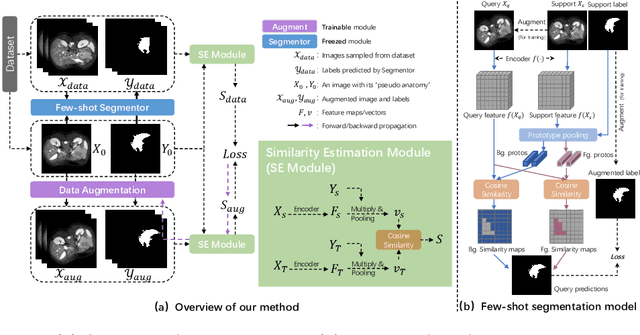
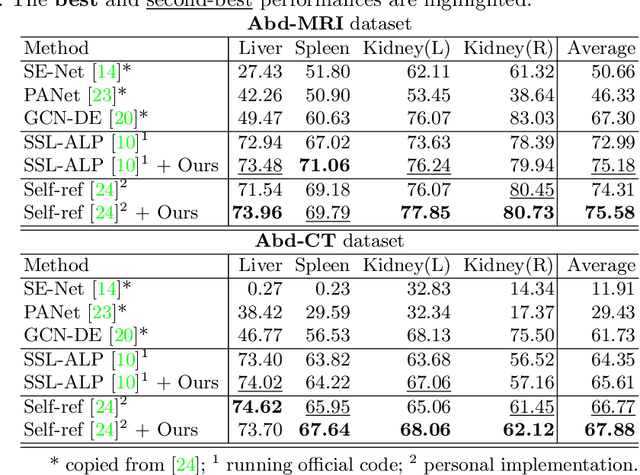
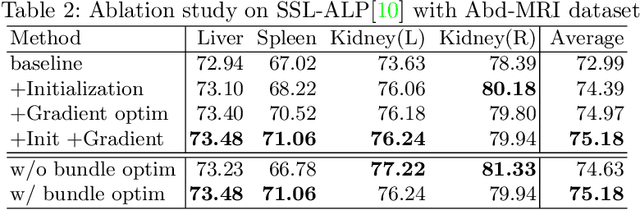
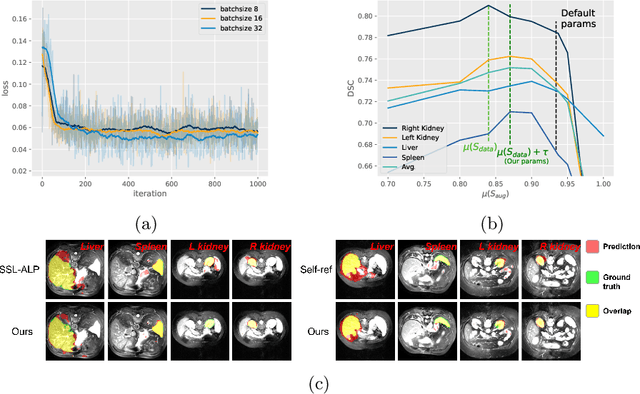
The augmentation parameters matter to few-shot semantic segmentation since they directly affect the training outcome by feeding the networks with varying perturbated samples. However, searching optimal augmentation parameters for few-shot segmentation models without annotations is a challenge that current methods fail to address. In this paper, we first propose a framework to determine the ``optimal'' parameters without human annotations by solving a distribution-matching problem between the intra-instance and intra-class similarity distribution, with the intra-instance similarity describing the similarity between the original sample of a particular anatomy and its augmented ones and the intra-class similarity representing the similarity between the selected sample and the others in the same class. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our optimized augmentation in boosting few-shot segmentation models. We greatly improve the top competing method by 1.27\% and 1.11\% on Abd-MRI and Abd-CT datasets, respectively, and even achieve a significant improvement for SSL-ALP on the left kidney by 3.39\% on the Abd-CT dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge