Unlocking High-Accuracy Differentially Private Image Classification through Scale
Paper and Code
Apr 28, 2022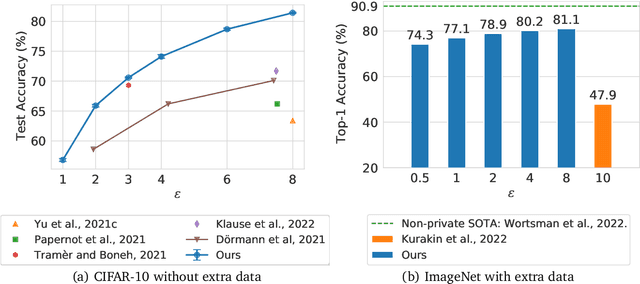
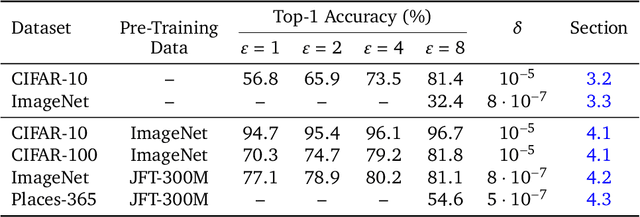
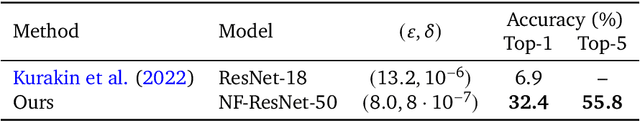
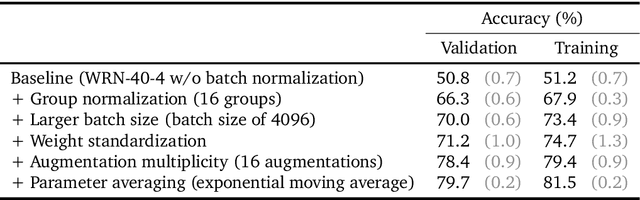
Differential Privacy (DP) provides a formal privacy guarantee preventing adversaries with access to a machine learning model from extracting information about individual training points. Differentially Private Stochastic Gradient Descent (DP-SGD), the most popular DP training method, realizes this protection by injecting noise during training. However previous works have found that DP-SGD often leads to a significant degradation in performance on standard image classification benchmarks. Furthermore, some authors have postulated that DP-SGD inherently performs poorly on large models, since the norm of the noise required to preserve privacy is proportional to the model dimension. In contrast, we demonstrate that DP-SGD on over-parameterized models can perform significantly better than previously thought. Combining careful hyper-parameter tuning with simple techniques to ensure signal propagation and improve the convergence rate, we obtain a new SOTA on CIFAR-10 of 81.4% under (8, 10^{-5})-DP using a 40-layer Wide-ResNet, improving over the previous SOTA of 71.7%. When fine-tuning a pre-trained 200-layer Normalizer-Free ResNet, we achieve a remarkable 77.1% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet under (1, 8*10^{-7})-DP, and achieve 81.1% under (8, 8*10^{-7})-DP. This markedly exceeds the previous SOTA of 47.9% under a larger privacy budget of (10, 10^{-6})-DP. We believe our results are a significant step towards closing the accuracy gap between private and non-private image classification.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge