Universal Link Predictor By In-Context Learning on Graphs
Paper and Code
Feb 15, 2024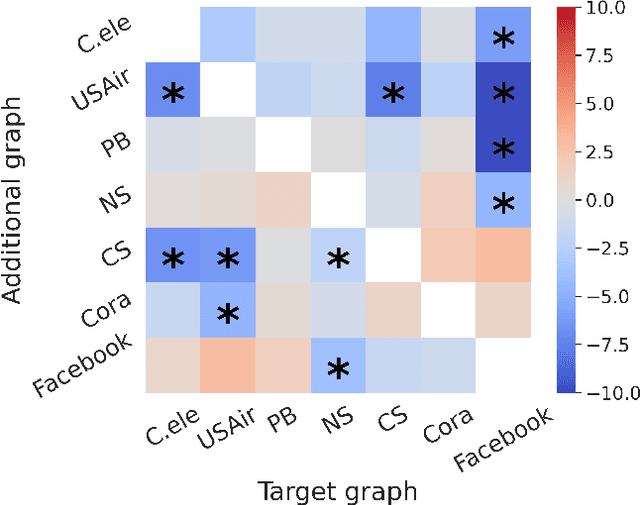
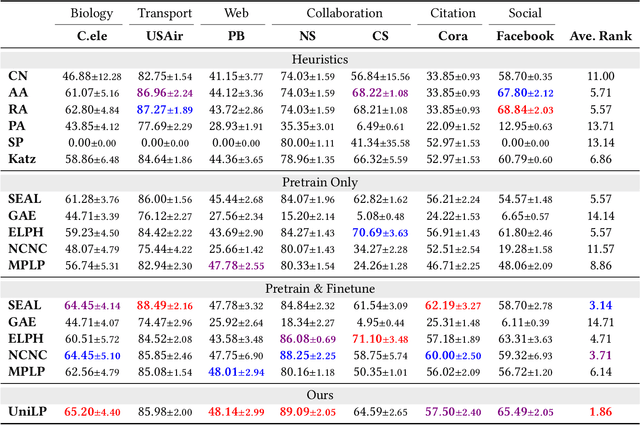
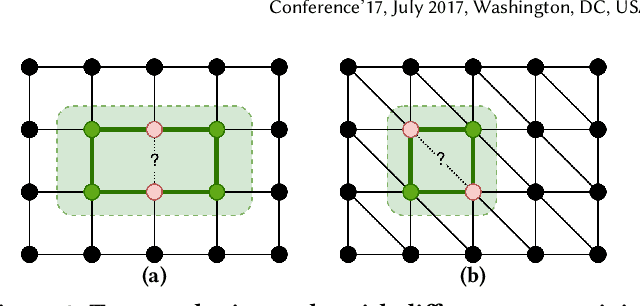
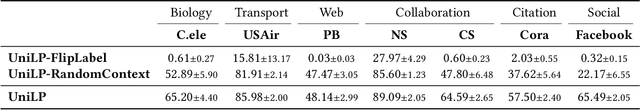
Link prediction is a crucial task in graph machine learning, where the goal is to infer missing or future links within a graph. Traditional approaches leverage heuristic methods based on widely observed connectivity patterns, offering broad applicability and generalizability without the need for model training. Despite their utility, these methods are limited by their reliance on human-derived heuristics and lack the adaptability of data-driven approaches. Conversely, parametric link predictors excel in automatically learning the connectivity patterns from data and achieving state-of-the-art but fail short to directly transfer across different graphs. Instead, it requires the cost of extensive training and hyperparameter optimization to adapt to the target graph. In this work, we introduce the Universal Link Predictor (UniLP), a novel model that combines the generalizability of heuristic approaches with the pattern learning capabilities of parametric models. UniLP is designed to autonomously identify connectivity patterns across diverse graphs, ready for immediate application to any unseen graph dataset without targeted training. We address the challenge of conflicting connectivity patterns-arising from the unique distributions of different graphs-through the implementation of In-context Learning (ICL). This approach allows UniLP to dynamically adjust to various target graphs based on contextual demonstrations, thereby avoiding negative transfer. Through rigorous experimentation, we demonstrate UniLP's effectiveness in adapting to new, unseen graphs at test time, showcasing its ability to perform comparably or even outperform parametric models that have been finetuned for specific datasets. Our findings highlight UniLP's potential to set a new standard in link prediction, combining the strengths of heuristic and parametric methods in a single, versatile framework.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge