Understanding Pooling in Graph Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Oct 11, 2021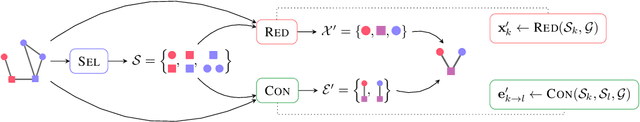
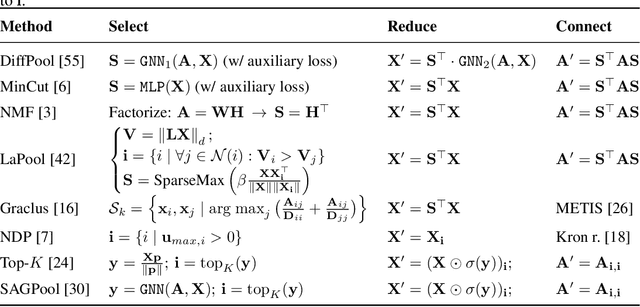
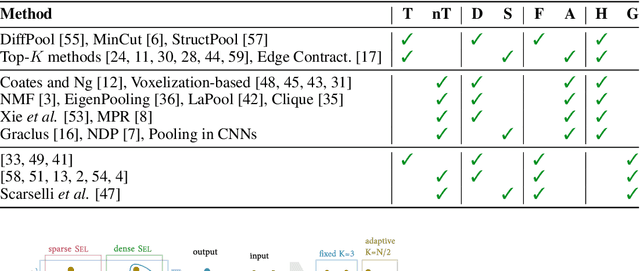
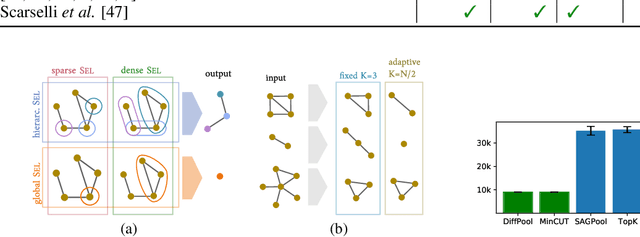
Inspired by the conventional pooling layers in convolutional neural networks, many recent works in the field of graph machine learning have introduced pooling operators to reduce the size of graphs. The great variety in the literature stems from the many possible strategies for coarsening a graph, which may depend on different assumptions on the graph structure or the specific downstream task. In this paper we propose a formal characterization of graph pooling based on three main operations, called selection, reduction, and connection, with the goal of unifying the literature under a common framework. Following this formalization, we introduce a taxonomy of pooling operators and categorize more than thirty pooling methods proposed in recent literature. We propose criteria to evaluate the performance of a pooling operator and use them to investigate and contrast the behavior of different classes of the taxonomy on a variety of tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge