Understanding and Measuring Robustness of Multimodal Learning
Paper and Code
Dec 28, 2021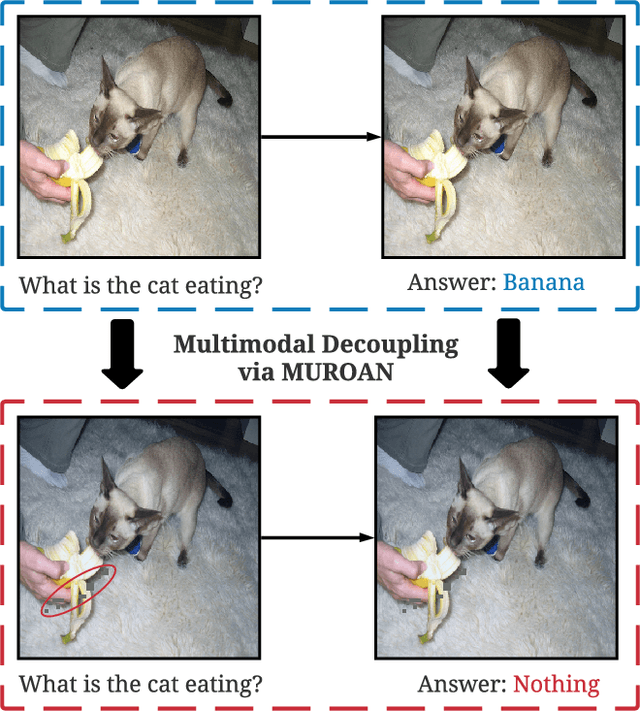
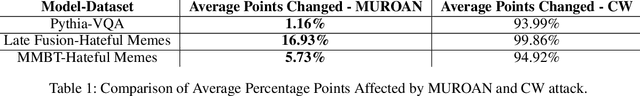
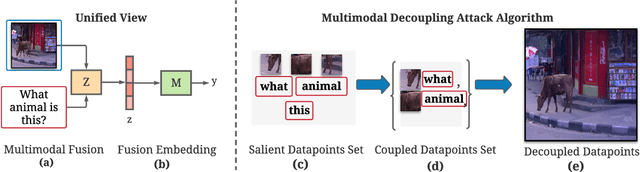
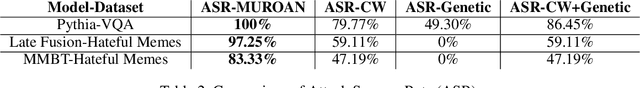
The modern digital world is increasingly becoming multimodal. Although multimodal learning has recently revolutionized the state-of-the-art performance in multimodal tasks, relatively little is known about the robustness of multimodal learning in an adversarial setting. In this paper, we introduce a comprehensive measurement of the adversarial robustness of multimodal learning by focusing on the fusion of input modalities in multimodal models, via a framework called MUROAN (MUltimodal RObustness ANalyzer). We first present a unified view of multimodal models in MUROAN and identify the fusion mechanism of multimodal models as a key vulnerability. We then introduce a new type of multimodal adversarial attacks called decoupling attack in MUROAN that aims to compromise multimodal models by decoupling their fused modalities. We leverage the decoupling attack of MUROAN to measure several state-of-the-art multimodal models and find that the multimodal fusion mechanism in all these models is vulnerable to decoupling attacks. We especially demonstrate that, in the worst case, the decoupling attack of MUROAN achieves an attack success rate of 100% by decoupling just 1.16% of the input space. Finally, we show that traditional adversarial training is insufficient to improve the robustness of multimodal models with respect to decoupling attacks. We hope our findings encourage researchers to pursue improving the robustness of multimodal learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge