Two-Stream Compare and Contrast Network for Vertebral Compression Fracture Diagnosis
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2020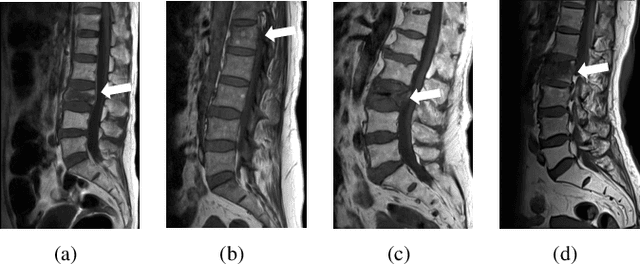
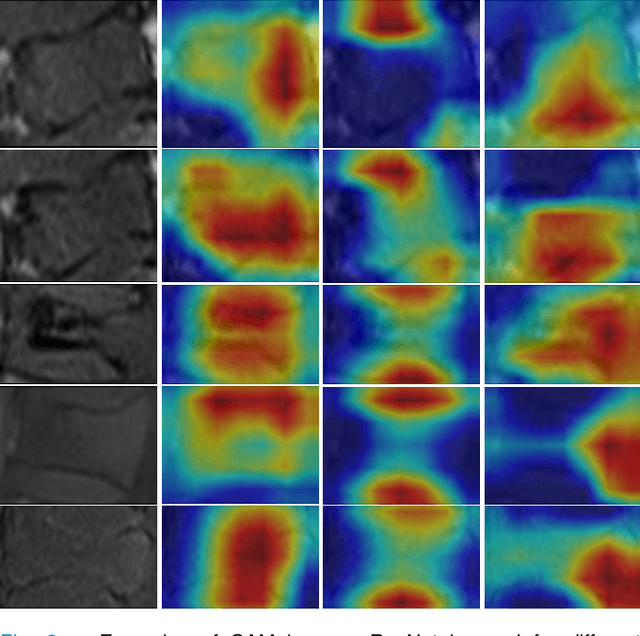
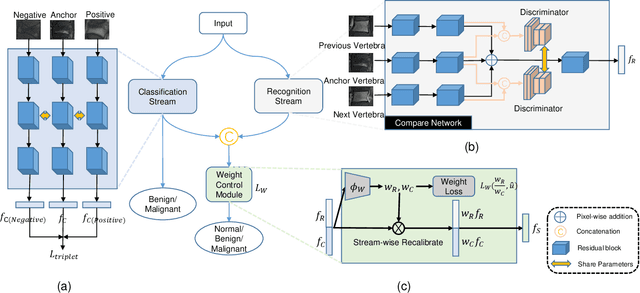
Differentiating Vertebral Compression Fractures (VCFs) associated with trauma and osteoporosis (benign VCFs) or those caused by metastatic cancer (malignant VCFs) are critically important for treatment decisions. So far, automatic VCFs diagnosis is solved in a two-step manner, i.e. first identify VCFs and then classify it into benign or malignant. In this paper, we explore to model VCFs diagnosis as a three-class classification problem, i.e. normal vertebrae, benign VCFs, and malignant VCFs. However, VCFs recognition and classification require very different features, and both tasks are characterized by high intra-class variation and high inter-class similarity. Moreover, the dataset is extremely class-imbalanced. To address the above challenges, we propose a novel Two-Stream Compare and Contrast Network (TSCCN) for VCFs diagnosis. This network consists of two streams, a recognition stream which learns to identify VCFs through comparing and contrasting between adjacent vertebra, and a classification stream which compares and contrasts between intra-class and inter-class to learn features for fine-grained classification. The two streams are integrated via a learnable weight control module which adaptively sets their contribution. The TSCCN is evaluated on a dataset consisting of 239 VCFs patients and achieves the average sensitivity and specificity of 92.56\% and 96.29\%, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge